NEED OF QUALITY EDUCATION IN BOTH MOROCCO* AND EMIRATES* :) INDUSTRY BRANDING, AVIATION BRANDING AND BENCHMARK OF MOROCCO* AND EMIRATES* : BRANDING, IMPORTANCE OF CONFERENCES AND HIGH ETHICS VALUES IN MOROCCO AND EMIRATES :) GREAT MOSQUES AND GREEN PROJECTS IN TOURISM IN MOROCCO AND EMIRATES AND HIGH PILGRIMAGE IN MOROCCO :) RICHNESS OF DIVERSITY IN MOROCCO AND EMIRATES :) LE LAIT ET LE MIEL SONT LA RICHESSE DU MAROC* ET DES EMIRATES* :) Advanced Technology in Morocco* and in Emirates* :) Green Tourism and Craft need Sustainability and Quality of Service in both Morocco and Emirates and we have a new vision 2030 of excellence :We need triple certification in Quality, Safety and Environment thus ISO 14001 and ISO 9001. UN SECTEUR CLE DE L’ECONOMIE MAROCAINE :LA RICHESSE DE L ECONOMIE BLEU ET L’EXPORT DU POISSONS MAROCAINS contribuant à la création d’emplois et à la génération de revenus, tout en renforçant la position du pays sur les marchés mondiaux des produits de la mer :) LA RECHERCHE SPACIALE ET LES MEILLEURS UNIVERSITES DE RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE AU MAROC* ET AUX EMIRATS* :) INDUSTRIE DES AUTOMOBILES TRES AVANCEE AU MAROC* ET AUX EMIRATS* : LES INVESTISSEURS AIMENT LA STABILITE AU MAROC* ET AUX EMIRATS* ET LA STABILITE ATTIRE EGALEMENT LES TOURISTES : EXCELLENT EDUCATION AND GREAT INNOVATION IN MOROCCO* AND IN EMIRATES* :INTERCULTURAL TOURISM AND EXCHANGE OF CULTURE AND IDEAS AND HIGH TOLERANCE AND DIVERSITY IN MOROCCO* AND EMIRATES* :) AND GOLD HOSPITALITY OF MOROCCO* AND EMIRATES* :) EXCELLENCE AND IDENTITY AND HIGH NOBLE VALUES OF MOROCCO AND EMIRATES : MOROCCO* RICHNESS AND ALLIANCE WITH EMIRATES* IN MANY FIELDS : AND THE WINNER AS ALWAYS IS MY SWEETHEART HUSBAND HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* BY GOD JUSTICE :) MY DAD BIDEN* AND DAD OBAMA* GLORY IN THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA* :) IT IS ALL ABOUT ETHICS :) LA COURONNE EST SIMPLEMENT L’ETHIQUE*ET PRIER SANS CESSE ET ATTEINDRE L’EXCELLENCE* :) GOD EXAM IS SIMPLY ETHICS* AND LOYALTY* TO GOD OUR CREATOR :) EXCELLENCE IN BLUE ECONOMY AND GREEN TOURISM IN MOROCCO* AND EMIRATES* :) شجرة وصلت السماء بالعمل الصالح الصدقة وهي الشمعة وسط 12 شمعة للقدس التي وصلت السماء بباب الصبر متل سيدنا أيوب وسيدنا يعقوب :شجرة طيبة أصلها تابت وفرعها في السماء : SEAL OF HONOR OF CHAMPIONS AMERICANS* and STRAIGHT GLORY OF GOD : GOD BLESS MY LOVELY AMERICA* OF HEAVEN : ALMANARA AND TREE OF LIFE :) LE JASMIN* AMAL* ELBATJI* : Arbre de vie donne des fruits de sagesse et d’intelligence comme 12 dates chaque mois : It is about having Excellent Credentials : البلد الذي يصنع غدائه يتمتع بإكتفاء ذاتي : LA CONFORMITE EST ETRE CONFORME à LA PAROLE DE DIEU VIVANT : L’IMPORTANCE DE METTRE TOUJOURS UNE VIRGULE ET ATTEINDRE L’EXCELLENCE :2030 EXCELLENCE AND RICHNESS IN BLUE OCEAN ECONOMY AND GREEN TOURISM IDEAS PLAN FOR MOROCCO* AND EMIRATES*un secteur clé de l’économie marocaine, contribuant à la création d’emplois et à la génération de revenus, tout en renforçant la position du pays sur les marchés mondiaux des produits de la mer.LA RICHESSE DE L ECONOMIE BLEU ET L’EXPORT DU POISSONS MAROCAINS LA RECHERCHE SPACIALE ET LES MEILLEURS UNIVERSITES DE RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE AU MAROC* ET AUX EMIRATS* :) INDUSTRIE DES AUTOMOBILES TRES AVANCEE AU MAROC* ET AUX EMIRATS* : LES INVESTISSEURS AIMENT LA STABILITE AU MAROC* ET AUX EMIRATS* ET LA STABILITE ATTIRE EGALEMENT LES TOURISTES : EXCELLENT EDUCATION AND GREAT INNOVATION IN MOROCCO* AND IN EMIRATES* :INTERCULTURAL TOURISM AND EXCHANGE OF CULTURE AND IDEAS AND HIGH TOLERANCE AND DIVERSITY IN MOROCCO* AND EMIRATES* :) AND GOLD HOSPITALITY OF MOROCCO* AND EMIRATES* :) EXCELLENCE AND IDENTITY AND HIGH NOBLE VALUES OF MOROCCO AND EMIRATES : MOROCCO* RICHNESS AND ALLIANCE WITH EMIRATES* IN MANY FIELDS : AND THE WINNER AS ALWAYS IS MY SWEETHEART HUSBAND HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* BY GOD JUSTICE :) MY DAD BIDEN* AND DAD OBAMA* GLORY IN THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA* :) IT IS ALL ABOUT ETHICS :) LA COURONNE EST SIMPLEMENT L’ETHIQUE*ET PRIER SANS CESSE ET ATTEINDRE L’EXCELLENCE* :) GOD EXAM IS SIMPLY ETHICS* AND LOYALTY* TO GOD OUR CREATOR :) EXCELLENCE IN BLUE ECONOMY AND GREEN TOURISM IN MOROCCO* AND EMIRATES* :) شجرة وصلت السماء بالعمل الصالح الصدقة وهي الشمعة وسط 12 شمعة للقدس التي وصلت السماء بباب الصبر متل سيدنا أيوب وسيدنا يعقوب :شجرة طيبة أصلها تابت وفرعها في السماء : SEAL OF HONOR OF CHAMPIONS AMERICANS* and STRAIGHT GLORY OF GOD : GOD BLESS MY LOVELY AMERICA* OF HEAVEN : ALMANARA AND TREE OF LIFE :) LE JASMIN* AMAL* ELBATJI* : Arbre de vie donne des fruits de sagesse et d’intelligence comme 12 dates chaque mois : It is about having Excellent Credentials : البلد الذي يصنع غدائه يتمتع بإكتفاء ذاتي : LA CONFORMITE EST ETRE CONFORME à LA PAROLE DE DIEU VIVANT : L’IMPORTANCE DE METTRE TOUJOURS UNE VIRGULE ET ATTEINDRE L’EXCELLENCE :2030 EXCELLENCE AND RICHNESS IN BLUE OCEAN ECONOMY AND GREEN TOURISM IDEAS PLAN FOR MOROCCO* AND EMIRATES*
AND THE WINNER AS ALWAYS IS MY SWEETHEART HUSBAND HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* 🙂
BY GOD JUSTICE 🙂











EXCELLENCE AND IDENTITY





















AUX HAUTS CIEUX : HASSAN2* AU PARADIS DU DIEU VIVANT DE GLOIRE 🙂






AMAL* CLAIRE* : TREE OF LIFE AND ALMANARA*
القدس العروس شفافة كالماء الطول والعرض متساويان ونورعلى نور 🙂
أصلها تابت 🙂
وفرعها في السماء كشجرة الحياة 🙂


LA TERRE PROMISE : LE LAIT ET LE MIEL 🙂

LA CONFORMITE à LA PAROLE VIVANTE DE DIEU 🙂
LE PROJET DE DIEU VIVANT 🙂





































The Quality of Education in Morocco
The quality of education in Morocco has been a topic of concern and focus for improvement over the years. While there have been efforts to enhance various aspects of the education system, challenges persist that impact the overall quality of education. Some of the key factors affecting the quality of education in Morocco include:
Infrastructure and Resources: Disparities in infrastructure and resources exist between urban and rural areas, with urban schools generally having better facilities, materials, and resources. Improving infrastructure and ensuring equitable distribution of resources are essential for enhancing the learning environment.
Teacher Quality and Training: The quality of teaching is a crucial determinant of education quality. However, there are concerns about teacher qualifications, training, and professional development opportunities. Investing in teacher training programs and providing ongoing support can improve teaching standards and student outcomes.
Curriculum Relevance: The relevance and adequacy of the curriculum have been questioned, with calls for updates to better meet the needs of students and align with modern trends and skills required in the job market. Curriculum reform efforts are underway to address these concerns and make education more relevant and responsive to societal needs.
Assessment and Evaluation: There have been criticisms of the assessment and evaluation methods used in Moroccan schools, with concerns about overemphasis on rote memorization and standardized testing. Moving towards more holistic assessment methods that measure critical thinking, problem-solving, and practical skills can provide a more accurate reflection of student learning.
Access to Education: While access to education has improved significantly in recent years, there are still challenges related to school enrollment, particularly among marginalized groups such as girls, children from rural areas, and those from low-income families. Efforts to improve access to education, reduce dropout rates, and address barriers to enrollment are critical for enhancing educational quality.
Language of Instruction: The language of instruction, particularly the transition from Arabic to French and other languages in higher education, has been a subject of debate. Ensuring effective language policies and support mechanisms can facilitate better learning outcomes for students.
ICT Integration: The integration of information and communication technologies (ICT) in education has the potential to enhance teaching and learning outcomes. However, there are challenges related to access to technology, teacher training in ICT skills, and the integration of digital resources into the curriculum.
Inclusive Education: Providing equitable access to education for students with disabilities and special needs remains a challenge. Improving infrastructure, teacher training, and support services can help create a more inclusive learning environment.
Addressing these challenges requires coordinated efforts from government authorities, educational institutions, teachers, parents, and other stakeholders. By addressing these key areas, Morocco can work towards improving the quality of education and ensuring that all students have access to high-quality learning opportunities.
The Quality of Education in Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has made significant strides in improving the quality of education over the past few decades. Here are some factors contributing to the quality of education in the Emirates:
Investment in Infrastructure: The UAE has invested heavily in modern educational infrastructure, including state-of-the-art schools, universities, and educational facilities. These facilities are equipped with advanced technology and resources to support effective teaching and learning.
Qualified Teachers: The UAE attracts skilled and experienced teachers from around the world through competitive salary packages and benefits. Many teachers in the UAE are native English speakers or possess strong English language proficiency, which contributes to the quality of language instruction.
Curriculum Development: The UAE has developed modern, comprehensive curricula that are aligned with international standards and best practices. Emphasis is placed on core subjects such as mathematics, science, and languages, as well as on developing critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills.
International Partnerships: The UAE has established partnerships with leading international educational institutions and organizations to enhance the quality of education. These partnerships facilitate knowledge exchange, curriculum development, teacher training, and research collaboration.
Focus on STEM Education: The UAE places a strong emphasis on Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) education to prepare students for careers in key sectors such as engineering, information technology, and healthcare. Specialized STEM programs and initiatives are implemented to foster interest and proficiency in these fields.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship: The UAE encourages innovation and entrepreneurship in education, with initiatives aimed at fostering creativity, problem-solving, and leadership skills among students. Entrepreneurship education is integrated into the curriculum, and opportunities for experiential learning and startup incubation are provided.
Inclusive Education: The UAE is committed to providing inclusive education for students with disabilities and special needs. Schools and educational institutions are equipped with facilities and resources to support students with diverse learning requirements, and specialized support services are available.
Quality Assurance: The UAE has established rigorous quality assurance mechanisms to monitor and evaluate the performance of educational institutions and ensure compliance with standards. Accreditation and licensing processes are in place to maintain high standards of education.
Digital Learning: The UAE is at the forefront of digital learning initiatives, with widespread integration of technology in education. Digital resources, online learning platforms, and interactive multimedia tools are used to enhance teaching and learning experiences.
Professional Development: Continuous professional development opportunities are provided for teachers and educational leaders to enhance their knowledge, skills, and pedagogical practices. Training programs, workshops, and conferences are conducted to keep educators updated with the latest trends and best practices in education.
Overall, the UAE's commitment to excellence in education, coupled with strategic investments and partnerships, has contributed to the high quality of education in the country.
Need for Education in Morocco
In Morocco, like in many countries, there are various needs in education that are essential for the development of the nation and its people. Some of the key areas of focus include:
Access to Education: Ensuring that all children, regardless of their socio-economic background, gender, or geographic location, have access to quality education. This includes addressing barriers such as poverty, lack of infrastructure, and cultural norms that may hinder children from attending school.
Quality of Education: Improving the quality of education provided in schools by investing in teacher training, curriculum development, and educational resources. Emphasis should be placed on promoting critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and digital literacy to prepare students for the challenges of the 21st century.
Equity in Education: Addressing disparities in educational outcomes among different regions and social groups. This involves targeted interventions to support marginalized communities, including rural populations, girls, and children with disabilities.
Technical and Vocational Education: Strengthening technical and vocational education and training (TVET) programs to equip young people with the skills needed for employment in various sectors of the economy. This includes collaboration with industry partners to ensure that TVET programs are aligned with labor market needs.
Higher Education: Enhancing the quality and relevance of higher education institutions to foster innovation, research, and entrepreneurship. This may involve expanding access to higher education, promoting international collaboration, and improving the employability of graduates.
Digital Literacy: Integrating technology into education to enhance learning outcomes and prepare students for a digital future. This includes providing access to computers, internet connectivity, and digital learning resources, as well as training teachers to effectively use technology in the classroom.
Language Skills: Strengthening language skills, particularly proficiency in Arabic, French, and English, to facilitate communication and participation in the global economy.
Curriculum Reform: Updating the curriculum to reflect current societal needs, promote cultural diversity, and instill values of tolerance, citizenship, and environmental sustainability.
Teacher Recruitment and Retention: Improving teacher recruitment, training, and support systems to attract and retain qualified educators, particularly in remote and underserved areas.
Parental and Community Involvement: Encouraging parental and community involvement in education through initiatives such as parent-teacher associations, community schools, and adult education programs.
Addressing these education needs requires a comprehensive and multi-stakeholder approach involving government, civil society, the private sector, and international partners. By investing in education, Morocco can empower its citizens, promote social inclusion, and drive sustainable development.
Need for Education in Emirates
In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), education is a top priority for the government as it plays a crucial role in the country's development and prosperity. Despite significant progress in recent years, there are still several areas where attention is needed to further enhance the education system:
Quality Education for All: Ensuring access to quality education for all residents, including nationals and expatriates, regardless of socio-economic status, ethnicity, or gender. This involves addressing barriers to education such as affordability, transportation, and cultural factors.
21st Century Skills: Aligning the education system with the demands of the 21st century by focusing on the development of critical thinking, creativity, communication, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. Emphasizing these skills will better prepare students for the rapidly changing global economy.
STEM Education: Increasing emphasis on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education to meet the growing demand for skilled professionals in these fields. This includes enhancing STEM curriculum, providing specialized training for teachers, and promoting STEM-related extracurricular activities.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Encouraging innovation and entrepreneurship by integrating entrepreneurship education into the curriculum, supporting student-led startups, and fostering partnerships between educational institutions and the private sector.
Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET): Strengthening TVET programs to provide alternative pathways for students who are interested in pursuing technical and vocational careers. This includes expanding access to TVET programs, modernizing vocational training facilities, and enhancing industry partnerships for work-integrated learning opportunities.
Inclusive Education: Promoting inclusive education for students with disabilities by providing appropriate accommodations, specialized support services, and training for teachers and staff. Inclusive education ensures that all students have equal opportunities to learn and succeed.
Teacher Professional Development: Investing in continuous professional development for teachers to enhance their subject knowledge, pedagogical skills, and ability to integrate technology into teaching and learning. Well-trained and motivated teachers are essential for delivering quality education.
Language Proficiency: Improving language proficiency, particularly in English, to enhance communication skills and facilitate access to higher education and employment opportunities in the global marketplace.
Curriculum Reform: Continuously updating the curriculum to reflect global best practices, promote cultural diversity, and address emerging challenges such as climate change, sustainability, and digital citizenship.
Parent and Community Engagement: Encouraging active involvement of parents and the community in the education process through initiatives such as parent-teacher associations, community outreach programs, and volunteering opportunities.
By addressing these education needs, the UAE can further enhance its human capital development, drive economic growth, and foster social cohesion and innovation in the country.
Industry Branding in Morocco
In Morocco, industry branding plays a crucial role in enhancing the country's competitiveness, attracting investment, promoting exports, and positioning its industries in the global market. Here are some aspects of industry branding in Morocco:
Tourism: Morocco is known for its rich history, diverse culture, and stunning landscapes. The tourism industry in Morocco focuses on branding the country as a unique destination offering a blend of traditional and modern experiences. This includes highlighting its historical sites, such as the ancient medinas and UNESCO World Heritage sites, as well as promoting adventure tourism, luxury resorts, and eco-tourism initiatives.
Agriculture: Morocco has a strong agricultural sector, producing a variety of products including citrus fruits, olives, cereals, and vegetables. Industry branding efforts aim to position Moroccan agricultural products as high-quality, sustainable, and globally competitive. This involves promoting initiatives such as organic farming practices, fair trade partnerships, and geographical indications (e.g., Argan oil from Morocco).
Textiles and Apparel: The textile and apparel industry is one of Morocco's key economic sectors, with a focus on manufacturing and exporting garments and textiles. Industry branding initiatives aim to showcase Moroccan textiles as a blend of traditional craftsmanship and modern design, emphasizing quality, innovation, and compliance with international standards.
Automotive: Morocco has emerged as a significant hub for automotive manufacturing, attracting investment from major international companies. Industry branding efforts focus on positioning Morocco as a competitive location for automotive production, leveraging factors such as skilled labor, strategic geographic location, infrastructure development, and government incentives.
Renewable Energy: With abundant solar and wind resources, Morocco has prioritized the development of renewable energy projects. Industry branding in this sector emphasizes Morocco's commitment to sustainability, innovation in renewable technologies, and its role as a regional leader in addressing climate change.
Technology and Innovation: Morocco aims to position itself as a hub for technology and innovation in the region. Industry branding initiatives focus on promoting technology parks, startup incubators, and initiatives to support entrepreneurship and digital transformation.
Pharmaceuticals: The pharmaceutical industry in Morocco has experienced significant growth, with a focus on manufacturing generic drugs and expanding exports to regional and international markets. Industry branding efforts aim to highlight Morocco's capabilities in pharmaceutical production, research, and regulatory compliance.
Overall, industry branding in Morocco involves showcasing the country's unique strengths, fostering innovation and competitiveness, and attracting investment and partnerships to support economic growth and development.
Industry Branding in Emirates
In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), industry branding plays a crucial role in positioning the country as a global hub for various sectors. Here are some key areas of industry branding in the Emirates:
Tourism and Hospitality: The UAE, particularly Dubai and Abu Dhabi, is renowned for its luxury tourism and hospitality offerings. Industry branding efforts focus on promoting iconic landmarks such as the Burj Khalifa, Palm Jumeirah, and Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque, as well as world-class hotels, shopping malls, and entertainment attractions. The country positions itself as a destination for luxury travel, business tourism, and cultural experiences.
Aviation and Aerospace: The UAE is home to Emirates Airlines and Etihad Airways, two of the world's leading airlines, as well as Dubai International Airport, one of the busiest airports globally. Industry branding initiatives highlight the Emirates' role as a global aviation hub, with state-of-the-art facilities, extensive flight networks, and premium services. Additionally, the UAE is investing in aerospace and space exploration initiatives, further enhancing its reputation in this sector.
Finance and Business Services: Dubai and Abu Dhabi are major financial centers in the region, offering a range of financial services such as banking, insurance, and investment management. Industry branding efforts focus on promoting the Emirates as a business-friendly environment with modern infrastructure, favorable regulatory frameworks, and strategic geographic location for trade and investment. Free zones like Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) and Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM) play a significant role in attracting international businesses.
Real Estate and Construction: The UAE is known for its ambitious real estate projects and innovative architectural designs, including the Burj Khalifa, Burj Al Arab, and The Palm Jumeirah. Industry branding emphasizes the Emirates as a center for real estate investment, property development, and urban planning, showcasing luxury residences, commercial spaces, and mixed-use developments.
Energy and Sustainability: The UAE is a major producer of oil and gas, but it is also investing in renewable energy and sustainability initiatives. Industry branding focuses on promoting the Emirates' commitment to clean energy, green technologies, and sustainable development projects such as Masdar City and the Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park.
Technology and Innovation: The UAE aims to become a leader in technology and innovation in the Middle East. Industry branding initiatives highlight initiatives such as Dubai Internet City, Dubai Silicon Oasis, and Abu Dhabi's Hub71, showcasing the Emirates as a hub for tech startups, digital innovation, and research and development.
Healthcare and Wellness: The UAE is investing in healthcare infrastructure and services to become a destination for medical tourism and wellness retreats. Industry branding efforts focus on promoting world-class hospitals, medical facilities, and wellness resorts, attracting international patients seeking high-quality healthcare services.
Overall, industry branding in the Emirates involves showcasing the country's strengths, fostering innovation and investment, and positioning it as a global leader in various sectors.
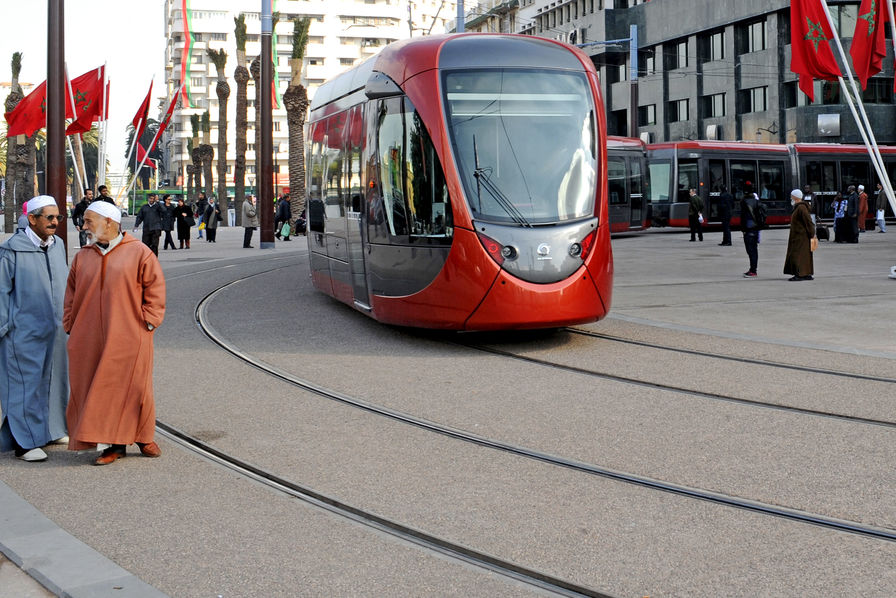
AVIATION BRANDING IN MOROCCO
When it comes to branding in the aviation sector in Morocco, here are some aspects to consider:
National Carrier Branding: Royal Air Maroc (RAM) is the national carrier of Morocco and is a key player in the country's aviation sector. Its branding reflects Moroccan culture, often incorporating elements such as traditional patterns, colors, and imagery. RAM's branding aims to convey a sense of national pride and hospitality while also positioning itself as a modern and reliable airline.
Regional and Low-Cost Carriers: In addition to RAM, there are regional airlines and low-cost carriers operating in Morocco, such as Air Arabia Maroc and Royal Air Maroc Express. Each of these carriers has its own branding strategy tailored to its target market, whether it's budget-conscious travelers or those seeking regional connectivity.
Airport Branding: Morocco has several international airports, including Mohammed V International Airport in Casablanca and Marrakech Menara Airport. These airports often have their own branding efforts to create a positive passenger experience and promote tourism. This includes signage, digital displays, and other elements designed to reflect the country's culture and hospitality.
Tourism Promotion: Aviation branding in Morocco is closely linked to the country's broader tourism promotion efforts. Airlines, airports, and tourism authorities often collaborate on marketing campaigns to attract visitors to Morocco, highlighting its diverse attractions, cultural heritage, and hospitality.
Partnerships and Alliances: Moroccan airlines may form partnerships and alliances with international carriers to expand their reach and enhance their branding. For example, RAM is a member of the Oneworld alliance, which allows it to offer passengers access to a wider network of destinations and benefits.
Digital Presence: Like elsewhere in the world, Moroccan airlines and airports invest in their digital presence to engage with passengers and promote their services. This includes active social media presence, user-friendly websites, and mobile apps to enhance the passenger experience.
Safety and Reliability: In addition to promoting the cultural aspects of Morocco, aviation branding in the country also emphasizes safety and reliability. This is particularly important for attracting international travelers and ensuring repeat business from domestic passengers.
When considering aviation branding in Morocco, it's essential to understand the cultural nuances, target demographics, and competitive landscape to develop effective strategies that resonate with travelers and promote the country's aviation sector.
Aviation branding in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), particularly in Emirates, the flagship carrier, is characterized by luxury, innovation, and world-class service. Here are some key aspects of aviation branding in the Emirates:
AVIATION BRANDING IN EMIRATES
Emirates Airlines: Emirates is one of the world's leading airlines known for its exceptional service, modern fleet, and extensive route network. The airline's branding emphasizes luxury, comfort, and sophistication. The iconic Emirates logo featuring a stylized falcon in flight is instantly recognizable, symbolizing strength, grace, and the airline's Emirati heritage.
Luxury and Comfort: Emirates is renowned for its luxurious onboard experience, including spacious seating, gourmet cuisine, state-of-the-art entertainment systems, and attentive service. The airline's branding reflects these qualities, positioning Emirates as a premium carrier that prioritizes passenger comfort and satisfaction.
Innovation and Technology: Emirates has a reputation for innovation and technological advancement in the aviation industry. From introducing the world's first private suites in First Class to pioneering in-flight entertainment systems, Emirates' branding highlights its commitment to pushing the boundaries of air travel and delivering cutting-edge experiences to passengers.
Global Connectivity: Emirates' branding emphasizes its extensive global network, connecting passengers to destinations across six continents. The airline's partnerships with other carriers and membership in the Star Alliance help reinforce its position as a leading global player in the aviation industry.
Cultural Heritage: While Emirates is a global airline, its branding also celebrates its Emirati heritage and identity. This is evident in its use of traditional Arabic motifs, cultural symbols, and hospitality values to create a distinct brand identity that resonates with both local and international passengers.
Sponsorships and Marketing: Emirates is known for its high-profile sponsorships and marketing campaigns, which help raise brand awareness and enhance its global visibility. From sports sponsorships, such as the Emirates Stadium in London and partnerships with major football clubs, to celebrity endorsements and iconic advertising campaigns, Emirates leverages various marketing channels to promote its brand and services.
Customer Loyalty: Emirates places a strong emphasis on customer loyalty and rewards programs, such as Emirates Skywards, which offers members exclusive benefits, privileges, and rewards for their continued patronage. These programs contribute to building brand loyalty and fostering long-term relationships with passengers.
Overall, aviation branding in the Emirates, particularly through Emirates Airlines, is characterized by a combination of luxury, innovation, cultural heritage, and global connectivity, positioning the airline as a leading player in the global aviation industry.
Benchmarking in Morocco
Benchmarking in Morocco refers to the process of evaluating and comparing the performance of businesses, industries, or sectors within the Moroccan economy against local or international standards or against competitors. This practice helps companies and policymakers identify areas for improvement, set goals, and develop strategies to enhance their competitiveness and efficiency.
In Morocco, benchmarking can cover various aspects such as:
Financial Performance: Comparing financial metrics such as revenue, profitability, and return on investment with industry peers or global benchmarks.
Operational Efficiency: Assessing productivity, process efficiency, and resource utilization to identify best practices and areas for optimization.
Quality Standards: Evaluating product or service quality against industry standards or leading competitors to maintain or improve quality levels.
Customer Satisfaction: Measuring customer satisfaction levels and comparing them with industry benchmarks to identify areas for improvement in customer service and experience.
Innovation and Technology: Benchmarking technology adoption, innovation practices, and research and development investments to stay competitive in the digital economy.
Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Comparing environmental and social performance against industry peers or global sustainability standards to drive responsible business practices.
Market Share and Competitive Positioning: Analyzing market share, brand perception, and competitive positioning relative to industry rivals to identify opportunities for growth and market expansion.
Benchmarking initiatives in Morocco may be conducted by individual companies, industry associations, government agencies, or international organizations to support economic development and competitiveness in the country. These efforts often involve collaboration, data sharing, and the adoption of best practices to drive continuous improvement and innovation across various sectors of the Moroccan economy.
Benchmarking in Emirates
Benchmarking in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), commonly referred to as "the Emirates," involves evaluating and comparing the performance of businesses, industries, or sectors within the UAE economy against local or international standards, as well as against competitors. This practice helps organizations identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, ultimately enhancing their competitiveness and efficiency.
In the UAE, benchmarking can cover various dimensions such as:
Financial Performance: Comparing financial metrics like revenue, profitability, and return on investment with industry peers or global benchmarks to gauge financial health and effectiveness.
Operational Excellence: Assessing productivity, process efficiency, and resource utilization to identify best practices and opportunities for optimization in operations.
Service Quality: Evaluating service quality standards against industry benchmarks or leading competitors to ensure excellence in customer service and experience.
Innovation and Technology Adoption: Benchmarking technology adoption, innovation practices, and research and development investments to stay abreast of global technological advancements and foster innovation within the UAE's economy.
Sustainability and Environmental Standards: Comparing environmental performance and sustainability practices against international standards to promote responsible business practices and environmental stewardship.
Market Positioning and Competitiveness: Analyzing market share, brand perception, and competitive positioning relative to industry rivals to identify opportunities for growth and enhance competitiveness in local and international markets.
Regulatory Compliance and Governance: Benchmarking regulatory compliance practices and corporate governance standards against global benchmarks to ensure adherence to international best practices and regulatory requirements.
Benchmarking initiatives in the UAE may be driven by individual companies, industry associations, government agencies, or international organizations to support economic development, promote innovation, and enhance competitiveness across various sectors of the UAE's dynamic economy. Collaboration, data sharing, and the adoption of best practices are often key elements of successful benchmarking efforts in the Emirates.
Branding in Morocco
Branding in Morocco reflects a blend of traditional elements and modern influences, influenced by the country's rich history, diverse culture, and evolving market trends. Here are some key aspects of branding in Morocco:
1. Cultural Sensitivity: Moroccan branding often emphasizes cultural values, traditions, and heritage. Brands may incorporate elements such as traditional Moroccan patterns, colors, and motifs in their logos, packaging, and marketing materials to resonate with local consumers.
2. Language: Arabic and French are the two main languages used in branding and advertising in Morocco. Brands often use a mix of both languages in their campaigns to reach a wider audience.
3. Hospitality and Warmth: Moroccan culture is known for its hospitality and warmth, which often translates into branding strategies. Companies may emphasize friendly customer service, personalized experiences, and a welcoming atmosphere to create a positive brand image.
4. Quality and Authenticity: Moroccan consumers value quality and authenticity in products and services. Brands that emphasize craftsmanship, natural ingredients, and traditional production methods often resonate well with local consumers.
5. Islamic Values: As a predominantly Muslim country, Islamic values and principles may influence branding and marketing strategies. Brands may avoid using imagery or content that contradicts Islamic beliefs and may instead incorporate themes of modesty, respect, and social responsibility.
6. Digital Marketing: With the increasing use of technology and social media in Morocco, digital marketing plays a significant role in branding efforts. Brands utilize platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube to engage with consumers, showcase their products, and drive sales.
7. Global Influences: While traditional Moroccan elements are prominent in branding, global influences also play a role, particularly in urban areas. International brands entering the Moroccan market often adapt their branding strategies to align with local preferences while maintaining their global identity.
8. Tourism Branding: Morocco's tourism industry relies heavily on branding to attract visitors. The country's branding efforts often highlight its diverse landscapes, rich history, cultural attractions, and hospitality to position itself as a desirable travel destination.
Overall, branding in Morocco involves a delicate balance between honoring traditional values and embracing modernity to connect with consumers in an evolving market landscape.
Branding in Emirates
Branding in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), particularly in cities like Dubai and Abu Dhabi, is characterized by innovation, luxury, and global appeal. Here are some key aspects of branding in the Emirates:
1. Luxury and Opulence: Many brands in the UAE, especially in sectors like hospitality, fashion, and automotive, emphasize luxury and opulence in their branding. This reflects the country's affluent consumer base and its status as a global hub for luxury shopping and lifestyle experiences.
2. Global Outlook: The UAE is known for its cosmopolitan nature and diverse expatriate population. Brands often adopt a global outlook in their branding strategies, aiming to appeal to both local Emirati nationals and the international community.
3. Innovation and Modernity: Dubai, in particular, is recognized for its futuristic skyline and commitment to innovation. Brands often incorporate themes of technology, progress, and modernity in their branding to align with the city's image as a dynamic business and tourism destination.
4. Hospitality and Service Excellence: Given the importance of tourism and hospitality to the UAE's economy, brands in these sectors prioritize exceptional service and guest experiences. Hospitality brands often emphasize luxury amenities, personalized service, and world-class facilities in their branding efforts.
5. Islamic Values: While the UAE is a modern and cosmopolitan society, Islamic values and traditions are still important considerations in branding. Brands may incorporate elements of Islamic art, architecture, and culture in a respectful manner, particularly during religious holidays and events.
6. Sustainability: With growing global awareness of environmental issues, sustainability has become an increasingly important aspect of branding in the UAE. Many brands highlight their commitment to sustainability initiatives, such as green building practices, renewable energy, and eco-friendly products.
7. Digital Marketing: The UAE has one of the highest rates of internet penetration and social media usage in the world. Brands leverage digital marketing channels such as social media, influencer partnerships, and online advertising to reach their target audience effectively.
8. Events and Sponsorships: Events like the Dubai Shopping Festival, Dubai World Expo, and Abu Dhabi Grand Prix provide opportunities for brands to enhance their visibility through sponsorships, activations, and experiential marketing campaigns.
9. National Pride: Brands in the UAE may also tap into a sense of national pride and patriotism, particularly during national holidays and celebrations. Emirati symbols, colors, and motifs may be incorporated into branding to connect with local consumers emotionally.
Overall, branding in the Emirates reflects a dynamic blend of luxury, innovation, global connectivity, and cultural sensitivity, tailored to the unique market landscape of this rapidly developing region.
Importance of conferences in Morocco
Conferences play a significant role in Morocco, contributing to various aspects of the country's development and growth.
Here are several reasons highlighting their importance:
1. Economic Impact: Conferences attract domestic and international participants, leading to increased economic activity. Attendees spend money on accommodation, transportation, dining, and shopping, benefiting local businesses and boosting the hospitality sector.
2. Knowledge Sharing and Networking: Conferences provide platforms for professionals, researchers, policymakers, and academics to exchange ideas, share research findings, and discuss current trends and challenges in their respective fields. These interactions facilitate networking opportunities, collaborations, and partnerships, fostering innovation and advancement.
3. Skills Enhancement and Capacity Building: Through workshops, seminars, and presentations, conferences offer opportunities for skill development and capacity building. Participants can learn about new technologies, methodologies, best practices, and industry standards, enhancing their competencies and staying updated in their fields.
4. Promotion of Research and Innovation: Academic and research conferences in Morocco showcase the latest research findings, innovations, and discoveries across various disciplines. They provide a platform for researchers to present their work, receive feedback, and gain recognition, thereby promoting academic excellence and driving innovation.
5. Cultural Exchange and Tourism: Hosting conferences in Morocco allows participants to experience the country's rich cultural heritage, traditions, and attractions. This cultural exchange fosters mutual understanding and appreciation among attendees while promoting tourism and showcasing Morocco as a premier destination for business and leisure travelers.
6. Stimulating Investment and Business Opportunities: Conferences serve as forums for showcasing investment opportunities, promoting economic sectors, and attracting foreign direct investment. They facilitate business networking, market exploration, and partnerships, leading to potential investments, trade agreements, and economic growth.
7. Policy Formulation and Advocacy: Conferences provide platforms for policymakers, government officials, and stakeholders to discuss pressing issues, formulate policies, and advocate for change. They offer opportunities to address socio-economic challenges, explore sustainable development strategies, and promote inclusive growth agendas.
8. Global Visibility and Reputation: Hosting or participating in international conferences enhances Morocco's global visibility, positioning it as a hub for knowledge exchange, innovation, and collaboration. It elevates the country's reputation in various fields and strengthens its diplomatic relations with other nations.
Overall, conferences play a vital role in fostering socio-economic development, promoting innovation, and enhancing Morocco's global competitiveness and reputation on the world stage.
Importance of conferences in Emirates
Conferences hold significant importance in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), contributing to various aspects of the country's development and global engagement. Here are several reasons highlighting their importance:
1. Economic Impact: Conferences attract a diverse range of participants, including business professionals, academics, and industry experts, leading to increased economic activity. Attendees spend on accommodation, transportation, dining, shopping, and entertainment, thereby boosting the hospitality, retail, and service sectors.
2. Knowledge Exchange and Innovation: Conferences provide platforms for sharing knowledge, best practices, and research findings across various sectors and disciplines. They facilitate discussions on emerging trends, technologies, and innovations, fostering collaboration, learning, and intellectual growth among participants.
3. Business Networking and Investment Opportunities: Conferences serve as networking hubs where entrepreneurs, investors, and business leaders gather to forge partnerships, explore investment opportunities, and expand their professional networks. These interactions can lead to business deals, joint ventures, and strategic alliances, driving economic growth and innovation.
4. Promotion of Tourism and Hospitality: Hosting conferences in the UAE promotes tourism by showcasing the country's world-class infrastructure, hospitality services, and tourist attractions. Attendees often extend their stays to explore the country, contributing to the tourism industry's growth and revenue generation.
5. Destination Branding and Global Visibility: Hosting international conferences enhances the UAE's reputation as a leading destination for business, innovation, and knowledge exchange. It reinforces the country's image as a global hub for commerce, culture, and diplomacy, attracting attention and investment from around the world.
6. Skills Development and Capacity Building: Conferences offer workshops, seminars, and training sessions that enable participants to enhance their skills, knowledge, and competencies. These capacity-building activities empower individuals and organizations to stay abreast of industry trends, regulations, and best practices, driving professional development and excellence.
7. Diplomatic and Cultural Exchange: Conferences bring together delegates from diverse backgrounds, cultures, and nations, fostering diplomatic relations and cultural exchange. They provide opportunities for dialogue, collaboration, and mutual understanding, promoting peace, stability, and cooperation on regional and global issues.
8. Policy Dialogue and Advocacy: Conferences serve as platforms for policymakers, government officials, and stakeholders to discuss pressing issues, formulate policies, and advocate for change. They address socio-economic challenges, explore innovative solutions, and shape agendas for sustainable development and inclusive growth.
Overall, conferences play a crucial role in driving economic growth, fostering innovation, promoting tourism, and enhancing the UAE's global standing as a dynamic and forward-thinking nation.
HIGH ETHICS VALUES IN MOROCCO
Morocco, like any other nation, has a set of ethical values that are influenced by its cultural, historical, religious, and social contexts. Some key ethical values commonly found in Moroccan society include:
Islamic Principles: Morocco is a predominantly Muslim country, and Islamic principles heavily influence its ethical values. Concepts such as honesty, integrity, justice, compassion, and generosity are highly valued.
Respect for Family: Family is central to Moroccan society, and respecting elders, caring for family members, and maintaining familial harmony are considered important ethical values.
Hospitality: Moroccans are known for their hospitality towards guests. Welcoming strangers, offering food and shelter, and treating guests with kindness and respect are deeply ingrained ethical norms.
Respect for Authority: Traditional Moroccan society places a high value on respect for authority figures, including parents, teachers, religious leaders, and government officials.
Community Solidarity: Moroccans often prioritize the well-being of the community over individual interests. Concepts such as solidarity, cooperation, and collective responsibility are important ethical values.
Honor and Reputation: Personal honor and reputation are highly regarded in Moroccan culture. Behaving with dignity, avoiding shame, and upholding one's reputation are considered ethical imperatives.
Modesty and Decency: Modesty in dress and behavior is valued in Moroccan society, particularly for women. Respectful interactions and adherence to cultural norms regarding modesty are considered ethical behaviors.
Environmental Stewardship: With its diverse natural landscapes and ecosystems, environmental conservation is increasingly becoming an important ethical value in Morocco. Preserving the environment for future generations is gaining recognition as an ethical imperative.
Work Ethic: Hard work, dedication, and perseverance are esteemed ethical values in Moroccan society. Individuals are often judged based on their commitment to their work and their contribution to the community.
Education: Valuing education and intellectual pursuits is seen as an ethical obligation in Moroccan culture. Parents often prioritize the education of their children, and respect for teachers and scholars is deeply ingrained.
It's important to note that while these values are prevalent in Moroccan society, there may be variations in how individuals prioritize and interpret them based on factors such as education, socioeconomic status, and exposure to diverse influences. Additionally, Morocco's ethical landscape is evolving, influenced by globalization, urbanization, and other contemporary factors.
HIGH ETHICS VALUES IN EMIRATES
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a country with a diverse population and a unique cultural landscape, influenced by its Islamic heritage, Bedouin traditions, and modernization efforts. As such, ethical values in the UAE reflect a blend of religious, cultural, and societal norms. Here are some key ethics values commonly found in the Emirates:
Islamic Principles: Islam plays a central role in the ethical framework of the UAE. Values such as honesty, integrity, compassion, justice, and generosity are deeply rooted in Islamic teachings and are highly valued in Emirati society.
Hospitality: Similar to Morocco, hospitality is a cherished value in the UAE. Emiratis take pride in welcoming guests warmly, offering hospitality, and demonstrating generosity towards visitors and strangers alike.
Respect for Authority and Hierarchy: Respect for authority figures, elders, and hierarchical structures is ingrained in Emirati culture. This includes deference to government officials, employers, and family elders.
Family Values: Family is highly valued in Emirati society, and maintaining close-knit familial ties is considered essential. Respect for parents, care for elders, and support for family members are significant ethical values.
Modesty and Decorum: Modesty in dress, behavior, and speech is important in Emirati culture, particularly in public settings. Adhering to cultural norms regarding modesty and showing respect through one's conduct are considered ethical behaviors.
Community Cohesion: Emiratis place a strong emphasis on community cohesion and solidarity. Supporting fellow community members, participating in communal activities, and contributing to the well-being of the community are valued ethical principles.
Work Ethic: Emiratis generally value hard work, dedication, and professionalism. Demonstrating commitment to one's work, striving for excellence, and contributing positively to the workplace are seen as ethical obligations.
Charity and Philanthropy: Giving to those in need is an important ethical value in the UAE, reflecting the Islamic concept of Zakat (charitable giving). Emiratis often engage in charitable activities, including donating to mosques, supporting humanitarian causes, and participating in community development projects.
Respect for Cultural Diversity: The UAE is a multicultural society, with expatriates from various backgrounds living alongside Emirati nationals. Respect for cultural diversity, tolerance, and understanding are emphasized as ethical values, promoting harmony and coexistence among different communities.
Environmental Sustainability: With growing concerns about environmental conservation and sustainability, there is increasing emphasis on ethical stewardship of the environment in the UAE. Efforts to protect natural resources, reduce carbon footprint, and promote eco-friendly practices are gaining prominence.
These ethical values provide a framework for understanding the principles that guide behavior and interactions within Emirati society. However, it's important to recognize that individual interpretations and expressions of these values may vary based on factors such as personal beliefs, upbringing, and exposure to different cultural influences.
*******************************************************
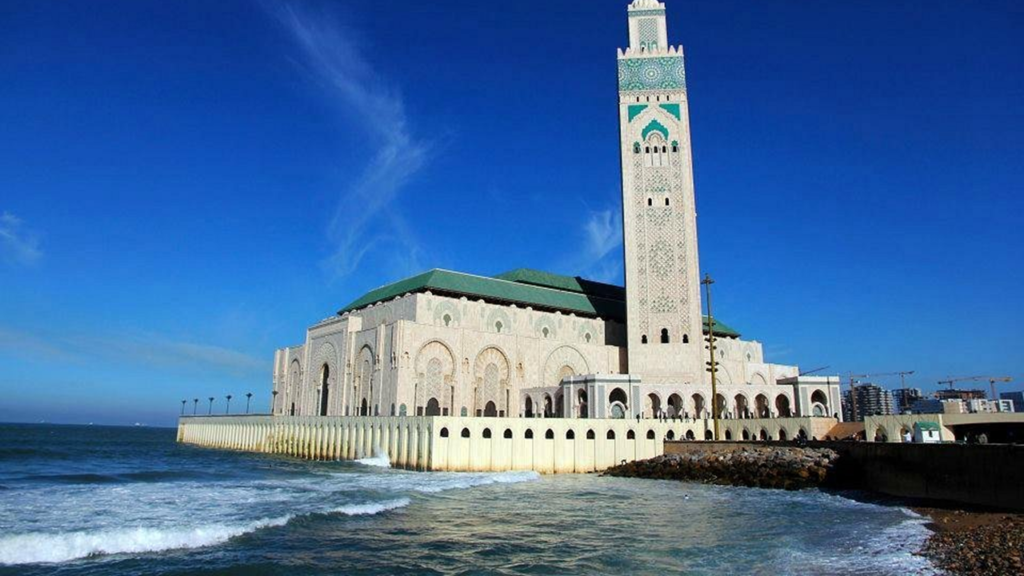
GREAT MOSQUES IN MOROCCO
Morocco is home to numerous mosques that play a central role in the spiritual and cultural life of the country.
Here are some of the most famous mosques in Morocco:
-The Hassan II Mosque in Casablanca: This impressive mosque is one of the largest in the world and is famous for its 210 meter high minaret, the tallest minaret in the world. It can accommodate up to 25,000 worshipers inside and 80,000 on its outdoor esplanade.
-The Karaouiyine Mosque in Fez: Founded in the 9th century, this mosque is one of the oldest and most important in the world. It is also home to Al-Qaraouiyine University, considered the oldest continuously operating university in the world.
-The Moulay Ismail Mosque in Meknes: This impressive mosque was built in the 17th century by Sultan Moulay Ismail. It is known for its magnificent architecture and its immense interior courtyard.
-The Koutoubia Mosque in Marrakech: This emblematic mosque is famous for its Hispano-Moorish style minaret. It is considered one of the most important symbols of the city of Marrakech.
-The Al-Qarawiyyin Mosque in Fez: In addition to its spiritual role, this mosque is also associated with Al-Qaraouiyine University, one of the oldest educational institutions in the world.
-The Tin Mal Mosque in the Atlas Mountains: This historic mosque was built in the 12th century by the Almohads. It is located in a picturesque setting and is a remarkable example of Berber architecture.
These mosques illustrate the rich history and culture of Morocco, as well as the importance of Islam in the daily lives of its inhabitants. Each of them also offers unique architecture and artistic details that demonstrate traditional Moroccan artisanal know-how.
GREAT MOSQUES IN EMIRATES
The UAE is also home to several notable mosques that are important centers of worship and architectural symbols.
Here are some of the most iconic mosques in the UAE:
-The Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque in Abu Dhabi: This mosque is one of the largest in the world and is named after the late Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan, founder of the United Arab Emirates. It is famous for its magnificent architecture, its vast spaces and its impressive Swarovski crystal chandelier.
-Al Noor Mosque in Sharjah: Located on the banks of the Khalid Lagoon, this mosque is a remarkable example of modern Islamic architecture. Its elegant design and beautiful location make it an important place of worship and a popular tourist attraction.
-The Jumeirah Mosque in Dubai: This mosque is an icon of the city of Dubai. It offers guided tours open to the public to promote understanding of Islamic culture and religion among non-Muslims.
-Al Badiyah Mosque in Fujairah: Considered the oldest mosque in the United Arab Emirates, this small adobe mosque offers a fascinating insight into the region's traditional Islamic architecture.
-Sheikh Khalifa Bin Zayed Al Nahyan Mosque in Al Ain: This imposing and beautifully designed mosque is an important place of worship in Al Ain, one of the oldest cities in the United Arab Emirates.
These mosques illustrate the UAE's commitment to Islam and its desire to promote religious tolerance and intercultural dialogue by opening their doors to visitors of all faiths. In addition to their religious function, these mosques represent impressive architectural works that reflect the beauty and grandeur of Islamic art.
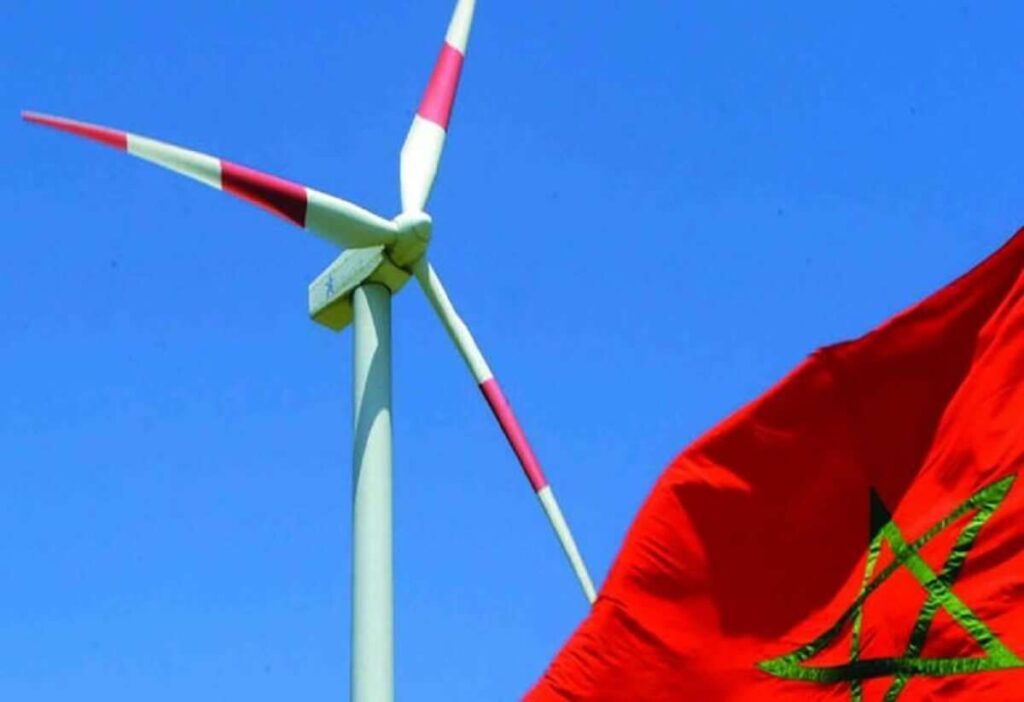
Green projects in Tourism in Morocco
Green projects in tourism in Morocco focus on promoting sustainable practices, conserving natural resources, and minimizing the environmental impact of tourism activities. Here are some specific examples:
Renewable Energy Integration: Morocco has made significant investments in renewable energy, particularly solar and wind power. Many tourism facilities, such as hotels and resorts, are incorporating renewable energy technologies to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and decrease their carbon footprint.
Eco-Lodges and Sustainable Accommodations: There's a growing trend in Morocco towards eco-friendly accommodations, including eco-lodges, sustainable guesthouses, and desert camps that prioritize environmentally responsible practices. These establishments often use locally sourced materials, employ energy-efficient designs, and implement waste reduction and recycling programs.
Community-Based Tourism Initiatives: Community-based tourism projects empower local communities by involving them in tourism activities and revenue-sharing mechanisms. These initiatives provide opportunities for cultural exchange, homestays, and guided tours led by community members, thereby supporting rural economies and promoting sustainable development.
Protected Area Management: Morocco has designated numerous protected areas, including national parks, nature reserves, and biosphere reserves, where sustainable tourism practices are encouraged. These areas offer opportunities for wildlife observation, hiking, and nature-based activities while preserving biodiversity and ecosystems.
Waste Management Programs: Efforts to address waste management issues in tourism include initiatives focused on waste reduction, segregation, recycling, and composting. Some tourism businesses collaborate with local communities to implement waste management programs, raising awareness about the importance of responsible waste disposal among tourists and residents alike.
Water Conservation Measures: Water scarcity is a significant concern in Morocco, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions. Sustainable tourism projects promote water conservation through measures such as water-saving fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and educational campaigns promoting responsible water usage among tourists and hospitality providers.
Sustainable Transportation Options: Encouraging the use of sustainable transportation options, such as electric vehicles, bicycles, and public transit, helps reduce carbon emissions associated with travel. Some tour operators offer eco-friendly transportation options for tours and excursions, minimizing the environmental impact of tourist activities.
Cultural Preservation and Heritage Conservation: Sustainable tourism initiatives in Morocco often emphasize the importance of preserving cultural heritage sites, traditional crafts, and indigenous knowledge. By promoting cultural authenticity and respecting local customs, tourism projects contribute to community pride and economic opportunities while safeguarding cultural heritage for future generations.
Certification and Standards: Certification programs and sustainability standards help identify tourism businesses committed to environmental and social responsibility. In Morocco, initiatives such as the Green Key eco-label and the Responsible Tourism Certification promote sustainable practices among tourism providers and inform travelers about environmentally friendly accommodation and tour options.
Education and Awareness Campaigns: Education and awareness-raising activities play a crucial role in promoting sustainable tourism practices among tourists, local communities, and industry stakeholders. Through workshops, seminars, and outreach programs, stakeholders can learn about sustainable tourism principles, environmental conservation, and the benefits of responsible travel practices.
These green projects in tourism contribute to Morocco's efforts to develop a more sustainable and resilient tourism sector that balances economic growth with environmental protection and social inclusion.
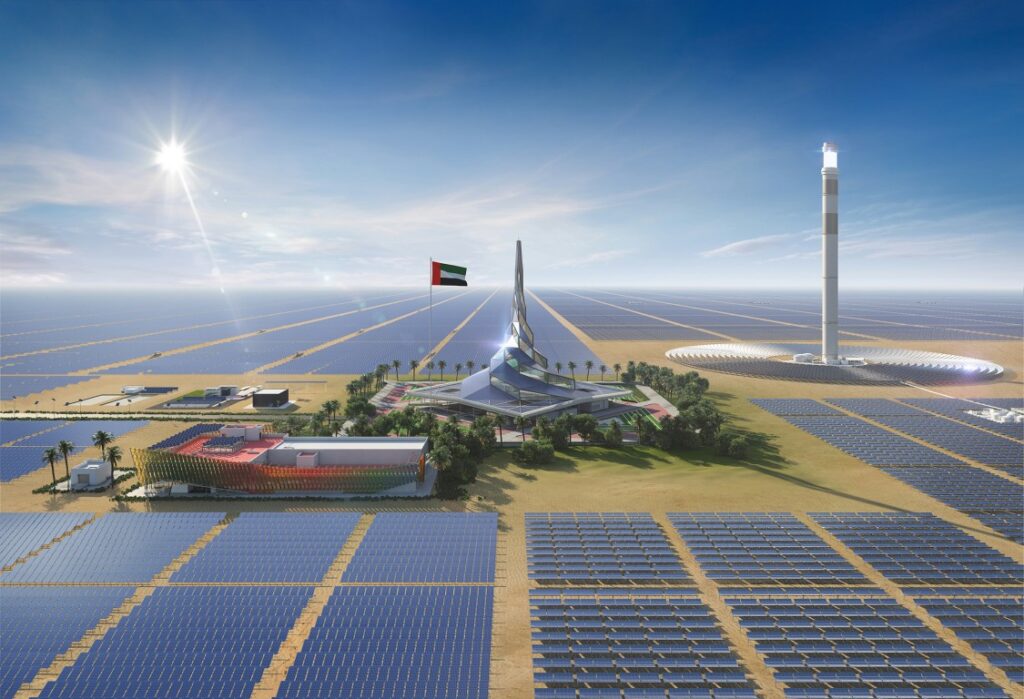
GREEN PROJECTS IN TOURISM IN EMIRATES
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has been increasingly focusing on sustainable tourism and green initiatives to balance its rapid development with environmental conservation. Several green projects and initiatives have been implemented or planned in the Emirates to promote sustainable tourism. Here are some examples:
Eco-friendly Resorts and Hotels: Many resorts and hotels in the UAE are adopting eco-friendly practices to reduce their environmental impact. These practices include energy-efficient lighting, water-saving measures, waste recycling, and the use of renewable energy sources like solar power.
Desert Conservation Reserves: The UAE has established several desert conservation reserves to protect its unique desert ecosystems and wildlife. These reserves offer tourists the opportunity to experience the desert environment while promoting conservation efforts.
Green Building Initiatives: The UAE has been promoting green building initiatives, including the construction of sustainable and energy-efficient buildings. For example, Dubai has implemented the Green Building Regulations and Specifications to ensure that new buildings meet certain sustainability standards.
Public Transportation and Infrastructure: Efforts are being made to improve public transportation infrastructure to reduce reliance on private vehicles and minimize carbon emissions. Initiatives such as the Dubai Metro and Abu Dhabi's public bus system aim to provide convenient and eco-friendly transportation options for tourists and residents alike.
Renewable Energy Projects: The UAE is investing heavily in renewable energy projects, particularly solar power. The Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park in Dubai is one of the largest solar parks in the world and demonstrates the country's commitment to renewable energy development.
Waste Management and Recycling: Various waste management and recycling initiatives are being implemented to reduce waste generation and promote recycling. These initiatives not only benefit the environment but also contribute to creating a cleaner and more attractive destination for tourists.
Environmental Education and Awareness Programs: Environmental education and awareness programs are being conducted to educate tourists and residents about the importance of environmental conservation and sustainable practices. These programs often include guided tours, workshops, and interactive exhibits.
Protected Marine Areas: The UAE has established protected marine areas to preserve its diverse marine ecosystems and promote sustainable marine tourism. These areas offer opportunities for activities such as snorkeling, diving, and wildlife viewing while ensuring the protection of marine biodiversity.
These initiatives demonstrate the UAE's commitment to promoting sustainable tourism and preserving its natural environment for future generations. By investing in green projects and initiatives, the Emirates aim to create a more sustainable and environmentally responsible tourism industry.
High Pilgrimage in Morocco
Pilgrimage in Morocco holds significant cultural and religious importance for both Moroccans and Muslims worldwide. While Morocco may not be as commonly associated with pilgrimage sites as some other Muslim-majority countries like Saudi Arabia or Iran, it does have several revered destinations that attract pilgrims.
One of the most notable pilgrimage sites in Morocco is the mausoleum of Moulay Idriss in the city of Moulay Idriss Zerhoun. Moulay Idriss I was a revered Islamic scholar and the founder of the Idrisid dynasty, which ruled Morocco for several centuries. His tomb is considered a sacred site, and thousands of pilgrims visit it each year, especially during the annual Moussem of Moulay Idriss festival.
Another significant pilgrimage site in Morocco is the city of Fez, particularly the Al-Qarawiyyin Mosque and University. Founded in 859 CE by Fatima al-Fihri, it is considered the oldest existing, continually operating educational institution in the world according to UNESCO and the Guinness World Records. Many scholars and students have traveled to Fez over the centuries to study at this prestigious institution, making it a pilgrimage site for those seeking knowledge as well as spiritual enlightenment.
Additionally, the city of Marrakech is home to the Koutoubia Mosque, one of the largest and most important mosques in Morocco. While not a traditional pilgrimage site in the same sense as Moulay Idriss or Al-Qarawiyyin, it is still a significant religious and cultural landmark that draws visitors from around the world.
In rural areas, particularly in the Atlas Mountains, there are also numerous shrines and holy sites that attract pilgrims seeking blessings, healing, or spiritual fulfillment. These sites are often associated with local saints or Sufi mystics and may involve rituals such as offering prayers, lighting candles, or making offerings of food or money.
Overall, pilgrimage in Morocco reflects the country's rich Islamic heritage and diverse cultural landscape, with sacred sites ranging from grand mosques in bustling cities to humble shrines in remote villages.
Diversity in Morocco
Diversity in Morocco is a rich tapestry woven from various cultural, ethnic, linguistic, and religious threads. As a North African country situated at the crossroads of Arab, Berber, and African civilizations, Morocco boasts a heterogeneous population with diverse backgrounds.
Ethnic Diversity: The indigenous Berber population, also known as Amazigh, constitutes a significant portion of Morocco's population. Berbers have inhabited North Africa for thousands of years and have their own distinct languages, traditions, and cultural practices. Additionally, Morocco has Arab influences, particularly from the Arab conquests during the medieval period.
Cultural Diversity: Moroccan culture is a fusion of Arab, Berber, and African elements, resulting in a diverse array of traditions, music, dance, and cuisine. Each region of Morocco has its own unique cultural characteristics, influenced by factors such as geography, history, and interactions with neighboring regions.
Linguistic Diversity: Arabic and Berber are the two official languages of Morocco, reflecting the country's dual cultural heritage. Additionally, French is widely spoken and used in business, education, and government, owing to Morocco's colonial history. In recent years, there has been a renewed interest in promoting the Amazigh language and culture, leading to greater recognition and visibility for Berber communities.
Religious Diversity: Islam is the predominant religion in Morocco, with the majority of the population adhering to Sunni Islam. However, Morocco has a history of religious diversity, with small Jewish and Christian communities coexisting alongside the Muslim majority. The country has a legacy of tolerance and coexistence among different religious groups, although Islam remains the state religion.
Geographical Diversity: Morocco's diverse geography encompasses coastal plains, mountain ranges (such as the Atlas Mountains), deserts (notably the Sahara), and fertile valleys. This geographical diversity has shaped various aspects of Moroccan life, from agriculture and cuisine to cultural practices and economic activities.
Urban-Rural Divide: There is also diversity in lifestyle and socio-economic status, with disparities between urban and rural areas. Urban centers like Casablanca, Rabat, and Marrakech are hubs of modernity, commerce, and cultural exchange, while rural areas often maintain traditional ways of life centered around agriculture and pastoralism.
Overall, the diversity in Morocco is a source of strength, contributing to the country's vibrant cultural landscape and rich heritage. However, like in many societies, there are also challenges related to issues such as cultural preservation, social inclusion, and economic development that need to be addressed to ensure that all segments of the population can thrive and contribute to the nation's progress.
Diversity in Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a country known for its diverse population, comprising people from various cultural, ethnic, and religious backgrounds. Here are some aspects of diversity in the Emirates:
Expatriate Population: One of the most notable features of diversity in the UAE is its large expatriate population. The majority of the population in the UAE consists of expatriates, who come from over 200 different nationalities. These expatriates play a significant role in various sectors of the economy, including finance, construction, healthcare, hospitality, and education.
Nationalities: While Emiratis (citizens of the UAE) constitute a minority of the population, they represent a diverse range of ethnic backgrounds. Historically, the Emirates have been home to Bedouin tribes and people of Arab descent. However, with the influx of expatriates over the years, the population has become even more diverse, with significant communities from South Asia, other Arab countries, Africa, Europe, and beyond.
Cultural Diversity: The UAE is a melting pot of cultures, with influences from Arab, Indian, Persian, and Western traditions, among others. This diversity is evident in various aspects of life, including cuisine, language, art, music, and festivals. The UAE government actively promotes cultural exchange and tolerance, celebrating the diversity of its population.
Religious Diversity: Islam is the official religion of the UAE, and the majority of the population are Muslims. However, due to the presence of a large expatriate population, the country is home to significant numbers of Hindus, Christians, Buddhists, Sikhs, and followers of other faiths. The UAE government respects the rights of individuals to practice their religion freely and has established places of worship for various religious communities.
Language Diversity: Arabic is the official language of the UAE, but due to its cosmopolitan nature, English is widely spoken and used as a lingua franca in business, education, and everyday communication. Additionally, other languages, such as Hindi, Urdu, Tagalog, and Malayalam, are spoken by different expatriate communities.
Socio-Economic Diversity: There is also diversity in socio-economic status within the UAE, with variations between Emirati citizens and expatriate residents, as well as disparities within these groups. While the UAE is known for its wealth and luxury, there are also challenges related to income inequality, labor rights, and access to affordable housing and healthcare.
Overall, the diversity in the Emirates is a defining characteristic of its society and contributes to its dynamic culture, vibrant economy, and cosmopolitan atmosphere. The government's efforts to promote tolerance, inclusivity, and cultural exchange play a crucial role in maintaining harmony and cohesion within this diverse nation.
Advanced Technology in Morocco
Morocco has seen significant growth in the field of technology in recent years. Here are some key points on the technological situation in Morocco:
Growth of the ICT (Information and Communication Technologies) sector: Morocco has made significant investments in ICT infrastructure, particularly in the deployment of optical fiber and the improvement of high-speed Internet access. flow across the country.
Emergence of technological clusters: Technological clusters are developing in cities like Casablanca, Rabat and Marrakech. These hubs promote innovation, entrepreneurship and collaboration between technology companies.
Startups and entrepreneurship: Morocco is seeing an increase in the number of technology startups, covering various sectors such as fintech, health, education and e-commerce. Incubators and accelerators support the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Education and Training: The Moroccan government has focused on improving education in science and technology to meet the needs of the booming technology job market.
Foreign Investment: Morocco is increasingly attracting foreign investment in the technology sector, due to its strategic geographic position, relative political stability and tax incentives.
Research and development ecosystem: Efforts are being made to strengthen research and technological development in Morocco, encouraging collaboration between universities, research centers and businesses.
Digital transformation of government: The Moroccan government is embarking on a digital transformation to improve the efficiency of public services and stimulate innovation in administration.
However, despite this progress, challenges persist, particularly in terms of connectivity in rural areas, technical skills development and creating a regulatory environment conducive to innovation.
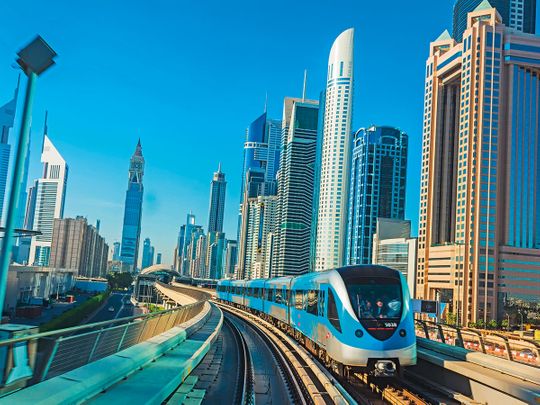
Advanced Technology in Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has quickly established itself as a regional and global leader in technology. Here are some key points on the technological situation in the Emirates:
Global technology hub: The UAE, particularly Dubai and Abu Dhabi, have become global technology hubs, attracting high-tech companies, startups and international investments.
Cutting-edge infrastructure: The UAE has invested heavily in technology infrastructure, including telecommunications, high-speed internet, data centers and dedicated technology free zones.
Smart cities: Dubai and Abu Dhabi have launched initiatives to become smart cities, using technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) to improve the efficiency of public services and the quality of life of residents.
Fintech: The UAE has become an important center for financial technology (fintech) companies, with favorable regulations, incubators and accelerators supporting innovation in this sector.
AI and blockchain: The UAE is investing in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain, with government initiatives aimed at integrating these technologies across various sectors, including finance, healthcare and logistics.
Education and Research: The UAE places great emphasis on education in science and technology, with world-renowned universities and research programs in cutting-edge fields.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship: The UAE actively supports innovation and entrepreneurship, with initiatives such as Dubai Future Foundation and Abu Dhabi Global Market, which provide financial support, expertise and infrastructure to technology startups.
E-Government: The UAE has implemented e-government initiatives aimed at making government services more accessible and efficient through digitalization and process automation.
In summary, the UAE has successfully created an environment conducive to technological innovation, attracting talent and investment from around the world and positioning itself as a major player in the global technology scene.
Fish Export in Morocco's economy
Fish export plays an important role in Morocco's economy, given that the country has a large coastal area rich in fisheries resources. Here are some key points regarding fish export from Morocco:
Sardines: Sardines represent a significant portion of Morocco's fish exports. They are generally exported in canned form and constitute an important source of income for the Moroccan fishing industry.
Tuna: Morocco also exports a significant amount of tuna, whether fresh, frozen or processed into cans. Tuna is often caught off the coast of Morocco and is a sought-after product on international markets.
Shrimp and other shellfish: Shrimp and other shellfish are also exported from Morocco, although to a lesser extent compared to fish. These products are popular in European and international markets.
Premium fish: In addition to common species such as sardines and tuna, Morocco also exports premium fish, such as gilthead sea bream and sea bass, which are often raised in aquaculture to meet growing demand.
Export Markets: The main export markets for Moroccan seafood products include the European Union, notably France and Spain, as well as other Mediterranean countries and countries in the Middle East.
Processing and valorization: Morocco is also investing in the processing of seafood products in order to further add value to its exports. Fish processing factories, particularly for the production of canned and frozen products, are widespread along the Moroccan coasts.
Quality standards and sustainability: Morocco is increasingly attentive to quality and sustainability standards in its fishing industry, which is crucial to maintain and develop its fish exports in the long term, particularly to meet the demands of the most demanding international markets.
In summary, fish export is a key sector of the Moroccan economy, contributing to job creation and income generation, while strengthening the country's position in global seafood markets.
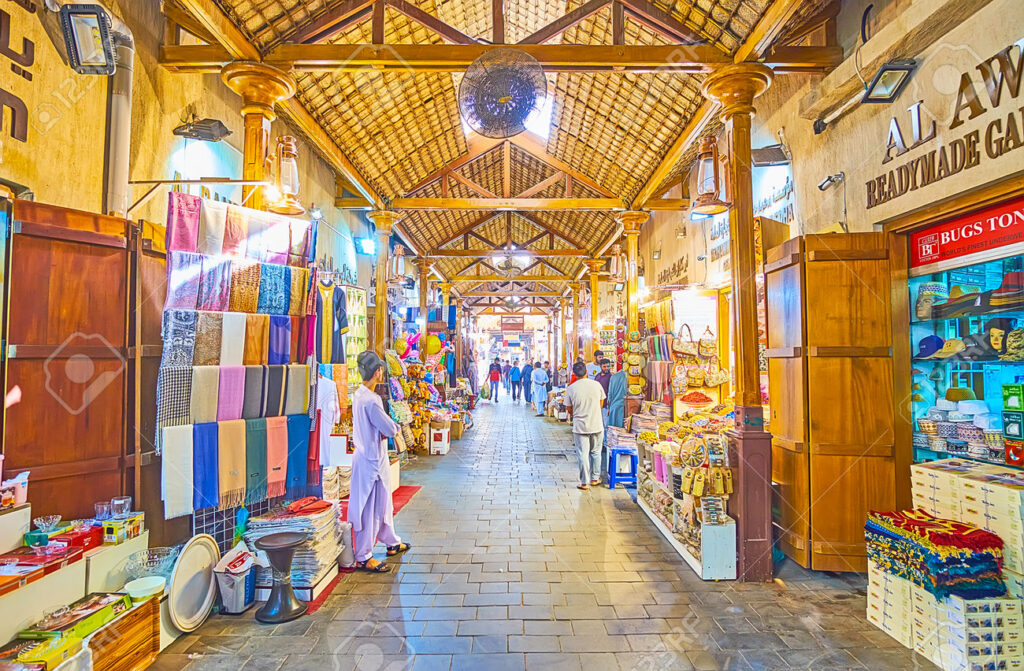
Crafts in Morocco
Crafts in Morocco are an essential aspect of the country's culture and economy. It represents traditional know-how passed down from generation to generation and offers a wide diversity of products ranging from carpets and weavings to pottery, including leather work, metal, wood, ceramics, and much more. Here are some of the main areas of crafts in Morocco:
Carpets and weavings: Moroccan carpets are renowned throughout the world for their quality and traditional Berber patterns. Each region of Morocco has its own distinctive techniques and patterns.
Leather: Moroccan artisans are renowned for their leatherwork, producing items such as bags, babouches (traditional shoes), belts and leather goods.
Pottery and ceramics: Moroccan pottery and ceramics are characterized by their bright colors and intricate patterns. The most famous production centers are in Fez and Safi.
Metalworking: Artisans work with metal to create lamps, trays, kitchen utensils, jewelry and decorative elements.
Woodworking: Wood is used to make furniture, decorative items and utensils, with elaborate carving and marquetry techniques.
Embroidery and sewing: Moroccan embroidery, particularly that made with gold and silver thread, often adorns traditional clothing such as caftans.
Pottery: Traditional Moroccan pottery includes a range of items from plates and bowls to carafes and tagines, each often decorated with geometric or floral designs.
Leather goods: In addition to slippers, Moroccan artisans produce a variety of leather goods, including handbags, wallets and belts, often decorated with traditional designs.
Crafts in Morocco play an important role in the economy by providing employment to many artisans across the country and contributing to the development of tourism, with visitors often drawn to souks and craft markets to purchase unique products and authentic. Additionally, efforts are being made to promote Moroccan craftsmanship in international markets, showcasing traditional know-how and encouraging collaborations with contemporary designers and fashion brands.
Crafts in Emirates
Crafts in the UAE reflect a rich cultural and historical tradition, combining Arab, Persian and local influences. Here are some of the main areas of handicrafts in the Emirates:
Traditional Weaving: The Emirates is known for its traditional weaving, which produces rugs, blankets and decorative hangings. Patterns and techniques vary between regions and communities.
Basketry and Palm Basketry: Basketry is an ancient practice in the Emirates, where artisans weave baskets, mats and other items from palm leaves. These items are often used in daily life and are also popular as souvenirs for tourists.
Metalworking: Emirati artisans work metal to create a range of items including traditional kitchenware, jewelry, lamps and decorative chests.
Pottery and ceramics: Although less common than in other parts of the Middle East, pottery and ceramics are also produced in the Emirates. Patterns and techniques can vary by region, but pieces are often decorated with geometric and floral designs.
Woodworking: Wood is used to make traditional furniture, kitchen utensils, chests and decorative sculptures. Artisans often use intricate carving techniques to create traditional designs.
Embroidery and Sewing: Embroidery is a popular form of craft in the Emirates, often used to embellish traditional clothing such as kandouras (men's dresses) and abayas (women's dresses). Embroidered designs can be inspired by nature, Arabic calligraphy or geometric patterns.
Calligraphy and illumination: Arabic calligraphy is an important art form in Emirati culture, used to decorate objects such as paintings, walls and handicrafts.
Traditional boat making: Although less common these days, building traditional wooden boats, such as dhows, is also part of Emirati craftsmanship. These boats were historically used for trade and fishing along the coasts of the Persian Gulf.
Crafts in the UAE play an important role in preserving cultural identity and promoting the country's traditional heritage. Many efforts are made to support and promote local artisans, as well as to educate visitors about the importance of this unique craft heritage.
Sustainable Green Tourism in Morocco
Sustainable green tourism in Morocco has been gaining traction in recent years as the country recognizes the importance of preserving its natural and cultural heritage while also promoting economic development through tourism. Here are some key aspects and initiatives promoting sustainable green tourism in Morocco:
Promotion of Eco-Friendly Accommodations: Morocco has been promoting eco-lodges, ecolodges, and sustainable hotels that minimize their environmental impact through practices such as waste reduction, energy efficiency, and use of renewable energy sources like solar power.
Community-Based Tourism: Many initiatives focus on involving local communities in tourism activities, ensuring they benefit economically and culturally from tourism while also encouraging visitors to appreciate local traditions and lifestyles.
Protection of Natural Resources: Efforts are made to protect Morocco's diverse ecosystems, including its deserts, mountains, and coastal areas. National parks and nature reserves are established and managed to conserve biodiversity and provide sustainable tourism opportunities such as guided eco-tours and wildlife viewing.
Cultural Preservation: Sustainable tourism in Morocco emphasizes the preservation of its rich cultural heritage, including historic sites, traditional crafts, and indigenous knowledge. Visitors are encouraged to respect local customs and traditions while also learning about Morocco's diverse cultural landscape.
Promotion of Responsible Travel Practices: Travel agencies and tour operators promote responsible travel practices among visitors, such as minimizing waste, conserving water, supporting local businesses, and respecting wildlife and natural habitats.
Education and Awareness Programs: Educational initiatives aim to raise awareness about sustainable tourism principles among both locals and visitors. This includes school programs, community workshops, and information campaigns highlighting the importance of protecting the environment and cultural heritage.
Certification Programs: Morocco participates in various certification programs for sustainable tourism, such as the Green Key eco-label, which recognizes hotels and other accommodations for their environmental commitment and responsible practices.
Investment in Infrastructure: Morocco invests in sustainable tourism infrastructure, such as eco-friendly transportation options (e.g., electric vehicles, bicycle rentals) and waste management systems to minimize environmental impact.
Collaboration with Stakeholders: Collaboration among government agencies, private sector businesses, non-profit organizations, and local communities is essential for implementing sustainable tourism initiatives effectively. Partnerships help pool resources, share knowledge, and coordinate efforts for maximum impact.
Overall, sustainable green tourism in Morocco aims to balance economic development with environmental and cultural preservation, creating memorable experiences for visitors while safeguarding the country's natural and cultural treasures for future generations.
Sustainable Green Tourism in Emirates
Sustainable green tourism in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), particularly in Emirates such as Dubai and Abu Dhabi, has become increasingly important as the region strives to balance its rapid development with environmental conservation and cultural preservation. Here are some key aspects and initiatives promoting sustainable green tourism in the UAE:
Green Building Practices: The UAE has embraced green building practices, with many hotels, resorts, and tourist attractions designed and constructed to meet green building standards such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification. These buildings incorporate energy-efficient features, sustainable materials, and water-saving technologies.
Renewable Energy: The UAE is investing heavily in renewable energy sources such as solar power. Solar panels are increasingly being installed on buildings and in desert areas to harness the abundant sunlight for electricity generation, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating carbon emissions.
Desert Conservation: The UAE's vast desert landscapes are home to unique flora and fauna. Conservation efforts focus on preserving these ecosystems through initiatives such as protected areas, habitat restoration projects, and sustainable tourism practices like guided desert safaris that minimize environmental impact.
Marine Conservation: With extensive coastlines along the Arabian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, marine conservation is a priority in the UAE. Measures include the establishment of marine protected areas, coral reef restoration programs, and sustainable diving and snorkeling practices to protect marine biodiversity.
Water Conservation: Water scarcity is a significant issue in the UAE, and sustainable tourism efforts emphasize water conservation measures such as efficient irrigation systems, water-saving technologies in hotels and resorts, and awareness campaigns encouraging visitors to minimize water usage.
Cultural Heritage Preservation: The UAE is rich in cultural heritage, with historical sites, traditional architecture, and indigenous traditions. Sustainable tourism initiatives aim to preserve and promote this heritage through heritage tours, cultural festivals, and conservation projects that safeguard archaeological sites and traditional crafts.
Wildlife Protection: Efforts are underway to protect and rehabilitate wildlife species native to the UAE, such as Arabian oryx, falcons, and sea turtles. Conservation programs, wildlife sanctuaries, and responsible wildlife tourism practices help ensure the long-term survival of these species.
Public Awareness and Education: Education and awareness-raising campaigns play a crucial role in promoting sustainable tourism practices among both residents and visitors. These campaigns highlight the importance of environmental conservation, cultural respect, and responsible tourism behavior.
Certification and Standards: The UAE government encourages tourism businesses to adopt sustainable practices through certification programs, eco-labels, and adherence to international standards such as ISO 14001 for environmental management.
Partnerships and Collaboration: Collaboration among government agencies, private sector entities, NGOs, and local communities is essential for the success of sustainable tourism initiatives in the UAE. Partnerships facilitate knowledge sharing, resource mobilization, and coordinated action towards common sustainability goals.
By prioritizing sustainability in tourism development, the UAE aims to create a balance between economic growth, environmental protection, and cultural preservation, ensuring a vibrant and resilient tourism industry for the future.
Industry in Morocco
Industry in Morocco plays a crucial role in the country's economy. For several years, the Moroccan government has implemented policies aimed at promoting industrial development in various sectors. Here is an overview of the main aspects of the industry in Morocco:
Sectoral diversification: Moroccan industry is diversified, encompassing sectors such as automotive, aeronautics, agri-food, textiles, tourism, information and communication technologies (ICT), among others.
Geographic concentration: Industrial zones are mainly found in urban regions such as Casablanca, Rabat, Tangier, Fez, Marrakech and Agadir. These areas offer infrastructure and incentives to attract investment.
Foreign Investment: Morocco has attracted a growing number of foreign investments in its industrial sector, particularly in export industries such as automobiles and aeronautics. International companies such as Renault, PSA Peugeot Citroën, Bombardier, and Boeing have established factories in Morocco.
Government Policies: The Moroccan government has implemented various incentives to encourage investment and industrial growth, including tax incentives, free zones, and free trade agreements with several countries.
International partnerships: Morocco seeks to strengthen its partnerships with other countries, particularly within the framework of the Union for the Mediterranean and the Free Trade Agreement with the United States and the European Union, to promote trade and export.
Sustainable development: Morocco is increasingly committed to sustainable development and seeks to promote environmentally friendly industries, particularly in the areas of renewable energy and energy efficiency.
Persistent challenges: Despite the progress made, Moroccan industry faces challenges such as international competitiveness, infrastructure modernization, workforce qualification and reduction of regional disparities.
In short, the industry in Morocco is booming, supported by favorable government policies and domestic and foreign investments. However, continued efforts are needed to overcome challenges and consolidate the country's position as a regional industrial hub.
Industry in Emirates
Industry in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) plays a significant role in the region's economy, although the UAE economy is primarily focused on the oil and gas sectors, notably in Abu Dhabi. Here is an overview of the main aspects of the industry in the UAE:
Economic diversification: The UAE has undertaken serious efforts to diversify its economy beyond oil and gas. They have turned to industries such as tourism, finance, professional services, logistics, aviation, construction, and renewable energy.
Free Zones and Industrial Parks: The UAE is famous for its free zones, which offer tax incentives, foreign business-friendly regulations and world-class infrastructure to attract foreign investment. Dubai is home to several popular free zones such as Jebel Ali Free Zone, Dubai Internet City, Dubai Media City, and Dubai Airport Freezone. These zones encourage the establishment of businesses in various sectors, including trade, logistics, technology, and manufacturing.
Tourism and Hospitality: The tourism industry plays a major role in the UAE economy, particularly in Dubai and Abu Dhabi. These cities are known for their tourist attractions, luxury hotels, shopping malls, and international events. Medical tourism is also booming in the UAE, attracting patients from around the world for medical treatments and surgical procedures.
Construction and real estate: The UAE has seen spectacular growth in the construction and real estate sector, with iconic projects such as the Burj Khalifa, the world's tallest building, and Palm Jumeirah, an artificial island. Although the sector has been affected by global economic fluctuations, it remains a key driver of the local economy.
Innovation and technology: The UAE is seeking to become a regional technology hub by investing in initiatives such as Dubai Internet City and Dubai Silicon Oasis, which support technology companies and start-ups. The country also hosts major technology events like the Dubai Expo and the Dubai Future Accelerators.
Sustainable development: The UAE has also placed emphasis on sustainable development, including investing in renewable energy, reducing dependence on fossil fuels, and preserving the environment.
SPACE RESEARCH PROGRAM IN MOROCCO
To date, Morocco has not yet developed a space program as advanced as that of the United Arab Emirates. However, the country has expressed growing interest in the space domain and has started investing in initiatives to strengthen its presence in the sector.
In 2018, Morocco launched its first satellite, named “Mohammed VI-A”, in partnership with France. This Earth observation satellite was designed for applications such as mapping, natural resource management, agricultural monitoring, and natural disaster prevention. This launch marked an important step for Morocco in the space field, demonstrating its ability to engage in high-level space projects.
In addition to the “Mohammed VI-A” satellite, Morocco has also expressed ambitions to further develop its space capabilities. The country has announced plans to launch other satellites for similar purposes, as well as efforts to strengthen the infrastructure and skills needed to support its space activities.
However, it is important to note that Morocco is still in the early stages of its space development and it may take time to reach the level of commitment and sophistication of the UAE's space program. Nevertheless, the country appears determined to invest in this area and take advantage of the potential benefits that space technology can offer in terms of economic, scientific and technological development.
ADVANCES IN SPACE RESEARCH IN EMIRATES
The UAE has made significant advances in space research in recent years. In particular, they have launched an ambitious space program with the main objective of diversifying their economy and stimulating technological innovation.
In 2019, the UAE achieved a remarkable feat by successfully launching its first space probe, called “Hope” (Al-Amal in Arabic), towards Mars. This historic mission aimed to study the Martian atmosphere and collect crucial data on the Red Planet's climate. The launch of the "Hope" probe marked a milestone for the UAE space program, making the UAE the fifth country to reach Mars and the first Arab nation to send an interplanetary probe.
In addition to the Mars mission, the UAE has also launched other space initiatives, including the establishment of the United Arab Emirates Space Agency (UAESA). This agency plays a crucial role in coordinating national space activities, as well as in developing international partnerships to strengthen the country's space capabilities.
The UAE has also expressed its intention to continue its efforts in the space domain, with plans to explore other destinations in the solar system and to develop space applications to meet national and regional needs. By investing in space research and development, the UAE is showing its commitment to scientific exploration and technological innovation, while helping to shape the future of the space industry in the Middle East and beyond.
MOROCCO UNIVERSITIES OF RESEARCH
Morocco is home to several universities renowned for their research activities and academic programs.
Some of the prominent research universities in Morocco include:
-University Mohammed V - Agdal (UM5A): Located in Rabat, UM5A is one of the oldest and most prestigious universities in Morocco. It offers a wide range of research programs in various disciplines, including science, humanities, and social sciences.
-University Mohammed VI Polytechnic (UM6P): Established in 2013 in Benguerir, UM6P is a relatively new institution focused on research and innovation. It emphasizes interdisciplinary research and collaboration with industry partners.
-Cadi Ayyad University: Located in Marrakech, Cadi Ayyad University is known for its strong research programs in science, technology, and humanities. It houses several research centers and institutes focusing on diverse fields such as renewable energy, environmental studies, and cultural heritage.
-University Hassan II Casablanca (UH2C): Situated in Casablanca, UH2C is one of the largest universities in Morocco. It has a strong emphasis on research, particularly in areas such as engineering, business, and social sciences.
-University Sidi Mohamed Ben Abdellah (USMBA): Based in Fez, USMBA is renowned for its research activities in fields such as agriculture, medicine, and Islamic studies. It hosts several research centers and laboratories conducting cutting-edge research.
-Al Akhawayn University: Located in Ifrane, Al Akhawayn University is an English-language institution known for its focus on liberal arts education and research. It offers undergraduate and graduate programs in various disciplines and encourages research initiatives among its faculty and students.
-Hassan I University: Situated in Settat, Hassan I University is recognized for its research contributions in fields such as science, engineering, and agriculture. It collaborates with national and international institutions to promote research and innovation.
These universities, among others in Morocco, play a significant role in advancing research and innovation within the country and contribute to the global academic community through their scholarly endeavors.
EMIRATES UNIVERSITIES OF RESEARCH
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is known for its thriving education sector, with several universities emphasizing research and innovation. Here are some research universities in the UAE:
-Khalifa University: Located in Abu Dhabi, Khalifa University is one of the top research universities in the UAE. It focuses on science, engineering, and medicine, with research centers specializing in areas such as renewable energy, aerospace, and healthcare.
-United Arab Emirates University (UAEU): UAEU, situated in Al Ain, is the oldest university in the UAE and offers a wide range of research programs across various disciplines, including science, humanities, and social sciences. It hosts several research centers and institutes focusing on topics such as water resources, agriculture, and Islamic studies.
-American University of Sharjah (AUS): AUS is a leading institution in Sharjah known for its strong emphasis on research and innovation. It offers research opportunities in fields such as engineering, architecture, business, and arts and sciences.
-American University in Dubai (AUD): Located in Dubai, AUD is recognized for its research contributions in architecture, design, engineering, and business. It promotes interdisciplinary research initiatives and collaborations with industry partners.
-Masdar Institute of Science and Technology: Situated in Masdar City, Abu Dhabi, Masdar Institute is dedicated to research and education in sustainable technologies and renewable energy. It offers graduate programs and conducts research in areas such as solar energy, carbon capture, and sustainable development.
-University of Dubai (UD): UD is a prominent research-focused institution in Dubai, offering research programs in business, engineering, law, and information technology. It collaborates with industry partners and government entities to address real-world challenges through research.
-Zayed University: With campuses in Abu Dhabi and Dubai, Zayed University conducts research in areas such as education, social sciences, and communication. It emphasizes research that contributes to the development of the UAE and the broader region.
These universities, along with others in the UAE, play a crucial role in advancing research and innovation, contributing to the country's knowledge economy and global competitiveness.
EDUCATION IN MOROCCO
In Morocco, there are many training opportunities in various fields.
Here is some general information about training opportunities in this country:
-Higher Education: Morocco has a number of public and private universities offering bachelor's, master's and doctoral programs in various fields of study. Major public universities include Mohammed V University in Rabat, Hassan II University in Casablanca, and Cadi Ayyad University in Marrakech.
-Vocational Schools: There are also vocational schools and technical institutes that offer training in specific fields such as engineering, IT, tourism, hotel management, etc.
-Continuing education: Many institutions offer continuing education programs for professionals looking to improve their skills or retrain in a new field. These programs are often adapted to the needs of the labor market.
-Specialized training: Some establishments offer specialized training in sectors such as health, agriculture, commerce, etc. These training courses can be diploma or certification courses.
-Online Training: With the advent of technology, many online platforms offer courses and certifications in various fields. Moroccans can also access these resources to train remotely.
-Vocational training: Morocco is striving to develop its vocational training system to meet the needs of the labor market. There are vocational training centers that offer programs in trades such as plumbing, electrical, carpentry, etc.
-International Partnership Programs: Some Moroccan institutions collaborate with foreign universities to offer joint training programs or student exchanges, providing Moroccan students with the opportunity to gain international experience.
In the UAE, there are numerous training opportunities in various fields, supported by the country's rapid economic development and its commitment to education and skills development.
EDUCATION IN EMIRATES
Here is some general information about training opportunities in this country:
-Higher Education: The UAE is home to a number of renowned universities, both public and private, offering a diverse range of undergraduate, graduate and research programs. Some of the most reputable universities include the UAE University, Zayed University and the American University of Sharjah.
-Vocational training: The UAE invests heavily in vocational training to meet the needs of the labor market. Institutions such as Dubai Training Institute, Dubai Aviation Academy, and others offer professional training programs in areas such as hospitality, tourism, business management, finance, etc.
-Continuing education: Many organizations and institutions offer continuing education programs for professionals wishing to improve their skills or retrain in new fields. These programs are often designed to be flexible and compatible with work schedules.
-Online Training: Online platforms also offer courses and certification programs in various fields, accessible to UAE residents. These resources are useful for those who prefer to study at their own pace or who have time constraints.
-Specialized training courses: The UAE offers specialized training courses in areas such as engineering, information technology, healthcare, tourism, oil and gas sector, etc. These training courses are often aligned with the specific needs of the local market.
-International Partnership Programs: The UAE has established partnerships with many international educational institutions, allowing students to access joint programs or academic exchanges. This provides UAE residents with an opportunity to gain international experience without leaving the country.
AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY IN MOROCCO
The automotive industry in Morocco has seen significant growth in recent years, thanks to a series of government initiatives aimed at attracting foreign investment to the sector.
Here are some key points regarding the automobile industry in Morocco:
-Tangier-Med Automobile Free Zone (TFZ): Inaugurated in 2012, the TFZ is a free zone dedicated to the automobile industry located in Tangier-Med, near the port of Tangier. This zone offers tax and customs incentives to automobile companies that set up there.
-Foreign investments: Many international automobile manufacturers have invested in Morocco in recent years. Brands such as Renault, PSA Peugeot Citroën, Ford, and more recently, the Chinese group BYD, have established production plants or assembly centers in the country.
-Development of the automotive sector: In addition to automobile manufacturers, Morocco also attracts investments in related industries, such as the manufacturing of automobile parts. This contributes to the development of a robust local automotive industry.
-Exports: The Moroccan automotive industry is strongly focused on exports. Factories set up in the country mainly produce vehicles for export to Europe and other international markets.
-Skilled workforce: Morocco has a relatively well-trained workforce, which is an advantage in attracting foreign investment in the automotive industry. The country also offers professional training programs adapted to the needs of this sector.
-Government objectives: The Moroccan government has set ambitious objectives for the automobile industry, particularly in terms of job creation, technological development and increased exports.
In summary, the automotive industry in Morocco is booming, supported by foreign investment, government incentives and a skilled workforce. This growth contributes to the diversification of the country's economy and the creation of jobs.
AUTOMOBILE INDUSTRY IN EMIRATES
The automobile industry in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is also experiencing significant growth, although the country is not a major automobile manufacturer like some other countries.
Here are some key points about the automotive industry in the UAE:
-Import and Distribution: The UAE is known to be an important market for the import and distribution of luxury cars, sports cars and high-end vehicles. Prestigious brands such as Rolls-Royce, Bentley, Ferrari, Lamborghini and others have a strong presence in the UAE market.
-Local market: In addition to imported luxury cars, there is also a local market for cars of more common brands. Local dealerships represent a wide variety of international brands and offer a diverse range of vehicles to meet the needs of UAE residents and businesses.
-Auto Racing Industry: The UAE has also become a major center for auto racing events. Facilities such as the Yas Marina Circuit in Abu Dhabi and the Dubai Autodrome circuit attract renowned international competitions, helping to promote the country's image in the automotive field.
-Innovation and technology: The UAE is investing in innovative automotive-related technologies, particularly in the area of electric vehicles and autonomous cars. Initiatives to promote sustainable mobility and intelligent transport are being developed.
-Road Infrastructure: The UAE has modern and well-maintained road infrastructure, making it an attractive location for drivers of sports and luxury cars. Well-developed highways and scenic drives attract driving enthusiasts from across the region.
In summary, although the UAE does not have a significant automotive manufacturing industry, the country plays a major role as a market for imported luxury cars, as well as a destination for motor racing events. Additionally, investments in innovation and technology promise to sustain the growth and evolution of the automobile industry in the country.
EXCELLENT EDUCATION IN MOROCCO
Education in Morocco has undergone significant reforms in recent years, with the government focusing on improving access, quality, and relevance across all levels of education. Here are some key aspects of the education system in Morocco:
-Structure: The education system in Morocco is structured into three main levels: primary education (6 years), secondary education (3 years), and tertiary education (university level). Education is compulsory up to the age of 15.
-Access: Efforts have been made to increase access to education, particularly in rural and remote areas. However, disparities still exist between urban and rural areas, with urban areas generally having better access to educational facilities and resources.
-Curriculum: The curriculum in Moroccan schools covers a wide range of subjects, including Arabic, French, mathematics, science, history, geography, and religious studies. In recent years, there has been a push to introduce more practical and vocational training to better prepare students for the workforce.
-Languages of Instruction: Arabic is the primary language of instruction in Moroccan schools, but French is also widely used, especially in higher education and in subjects like science and technology. There have been debates about the balance between Arabic and French instruction in the curriculum.
-Quality of Education: Despite improvements, challenges remain in ensuring the quality of education in Morocco. Issues such as overcrowded classrooms, a lack of qualified teachers, and outdated teaching methods continue to impact the quality of education.
-Gender Parity: Morocco has made progress in promoting gender parity in education, with efforts to increase girls' enrollment and retention in school. However, gender disparities still exist, particularly in rural areas and at higher levels of education.
-Technical and Vocational Education: There has been a growing emphasis on technical and vocational education and training (TVET) to address the skills gap and better align education with the needs of the labor market. Initiatives have been launched to enhance TVET programs and provide students with practical skills.
-Higher Education: Morocco has a network of public and private universities and higher education institutions. The government has been investing in expanding higher education opportunities and improving research and innovation capabilities within universities.
-Reforms: The Moroccan government has implemented various education reforms aimed at modernizing the education system, improving learning outcomes, and enhancing the quality and relevance of education. These reforms have focused on areas such as curriculum development, teacher training, and infrastructure upgrades.
Overall, while significant progress has been made in expanding access to education in Morocco, challenges remain in ensuring quality, relevance, and equity across the education system. Continued efforts and investments are needed to address these challenges and further improve the education system in the country.
EXCELLENT EDUCATION IN EMIRATES
The education system in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has seen remarkable development and investment over the past few decades, aiming to provide high-quality education that prepares students for the challenges of the modern world. Here are key aspects of education in the Emirates:
-Structure: The education system in the UAE is divided into several stages: kindergarten (optional), primary education (grades 1-6), middle education (grades 7-9), and secondary education (grades 10-12). Education is compulsory for Emirati children from ages 6 to 18.
-Public and Private Education: The UAE offers both public and private education options. While public education is provided free of charge to Emirati citizens, private schools cater to a diverse population, including expatriates. Private schools often follow international curricula such as British, American, or International Baccalaureate (IB).
-Curriculum: The UAE curriculum blends local and international elements. Arabic and Islamic studies are compulsory subjects, but English is widely taught as a second language. In addition to core subjects, schools often offer extracurricular activities, including sports, arts, and community service.
-Higher Education: The UAE has invested significantly in higher education, establishing world-class universities and research institutions. These include institutions like the United Arab Emirates University (UAEU), Khalifa University, and American University of Sharjah. Many of these universities offer programs in English and attract students from around the world.
-Technical and Vocational Education: The UAE recognizes the importance of technical and vocational education and has established specialized institutions such as the Higher Colleges of Technology (HCT) and vocational training centers. These institutions offer programs aligned with the needs of the labor market, preparing students for careers in fields like engineering, healthcare, and hospitality.
-Emiratization: The UAE government emphasizes the importance of Emiratization, which aims to increase the participation of Emirati nationals in the workforce. This includes initiatives to provide Emirati students with the skills and qualifications needed to succeed in various sectors of the economy.
-Innovation and Research: The UAE is committed to fostering innovation and research within its education system. Initiatives like the UAE National Innovation Strategy and the Mohammed bin Rashid Initiative for Global Prosperity support research and innovation projects in areas such as renewable energy, artificial intelligence, and healthcare.
-Teacher Training and Professional Development: The UAE invests in teacher training and professional development programs to ensure that educators are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to deliver high-quality education. This includes partnerships with international education organizations and universities.
Overall, education in the UAE is characterized by its commitment to excellence, innovation, and preparing students for success in a globalized world. The government's continued investment in education reflects its dedication to building a knowledge-based economy and empowering future generations.
INNOVATION IN MOROCCO
Morocco has been actively promoting innovation and technological advancement in recent years, recognizing it as a key driver for economic growth and development.
Here are some notable initiatives and areas of innovation in Morocco:
-Startup Ecosystem: Morocco has seen a rise in its startup ecosystem, particularly in cities like Casablanca and Rabat. Initiatives like Morocco's Startup Act, launched in 2019, aim to support entrepreneurship and innovation by providing various incentives and support mechanisms for startups.
-Technology Parks and Innovation Hubs: Morocco has established technology parks and innovation hubs such as Technopark Casablanca and Technopark Rabat, which provide infrastructure, networking opportunities, and support services to tech startups and innovative companies.
-Renewable Energy: Morocco has made significant investments in renewable energy, particularly in solar and wind power. The Noor Solar Power Complex, located in the desert near Ouarzazate, is one of the world's largest solar power plants.
-Agricultural Innovation: Given its significant agricultural sector, Morocco has been investing in agricultural innovation to enhance productivity, sustainability, and resilience to climate change. This includes initiatives such as modernizing irrigation systems and promoting precision agriculture techniques.
-ICT (Information and Communication Technology): The ICT sector in Morocco has been growing rapidly, with initiatives to improve internet infrastructure and digital literacy. The country has also been investing in e-government services and promoting digital entrepreneurship.
-Green Economy and Sustainable Development: Morocco has been focusing on promoting a green economy and sustainable development through initiatives such as the National Strategy for Sustainable Development and the Green Morocco Plan, which emphasize environmental protection, resource efficiency, and sustainable practices across various sectors.
-Education and Research: Morocco has been investing in education and research to foster innovation and technological advancement. This includes initiatives to improve STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education, establish research institutes, and promote collaboration between academia and industry.
-Tourism Innovation: Morocco has been leveraging technology and innovation to enhance its tourism sector, including initiatives such as promoting eco-tourism, developing digital tourism platforms, and investing in infrastructure to attract tourists.
Overall, Morocco is actively promoting innovation across various sectors, with a focus on supporting startups, advancing technology, addressing societal challenges, and promoting sustainable development. These efforts are aimed at driving economic growth, creating jobs, and improving the overall quality of life for its citizens.
INNOVATION IN EMIRATES
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has been at the forefront of innovation in the Middle East region, with ambitious initiatives and investments aimed at fostering a culture of innovation and driving economic diversification. Here are some key areas of innovation in the Emirates:
-Dubai's Smart City Initiative: Dubai has been leading the way in transforming itself into a smart city. The Smart Dubai initiative aims to leverage technology and data to improve efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life for residents and visitors. This includes initiatives such as smart transportation, digital government services, and the Dubai Data Initiative.
-Abu Dhabi's Vision 2030: Abu Dhabi has launched its Vision 2030, which outlines strategic priorities for economic development, with a strong emphasis on innovation and knowledge-based industries. This includes initiatives such as the Abu Dhabi Economic Vision 2030, which aims to diversify the economy away from oil dependency by promoting sectors like renewable energy, aerospace, healthcare, and technology.
-Dubai's Future Accelerators Program: Dubai's Future Accelerators program brings together government entities with innovative startups and companies from around the world to collaborate on solving key challenges facing the city. This initiative aims to drive innovation in areas such as transportation, healthcare, education, and sustainability.
-Research and Development: The UAE has been investing heavily in research and development (R&D) to drive innovation across various sectors. Institutions like the Masdar Institute of Science and Technology in Abu Dhabi and the Mohammed bin Rashid Space Centre in Dubai are leading efforts in areas such as renewable energy, space exploration, and advanced technology.
-FinTech and Blockchain: The UAE has been embracing financial technology (FinTech) and blockchain innovation, with initiatives such as the Dubai Blockchain Strategy and the establishment of FinTech accelerators and sandboxes. The country aims to become a global hub for FinTech and blockchain innovation.
-Healthcare Innovation: The UAE has been investing in healthcare innovation to enhance services and infrastructure. Initiatives include the establishment of specialized healthcare facilities, adoption of telemedicine and digital health solutions, and investments in medical research and biotechnology.
-Renewable Energy: The UAE is a global leader in renewable energy, particularly solar power. The Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park in Dubai is one of the world's largest solar projects, and the country has ambitious targets for increasing renewable energy capacity in the coming years.
-Space Exploration: The UAE has made significant strides in space exploration with projects like the Emirates Mars Mission (Hope Probe), which successfully entered Mars' orbit in 2021. The UAE aims to build its capabilities in space science and technology and inspire future generations of scientists and engineers.
Overall, the UAE is actively fostering innovation across various sectors through strategic investments, partnerships, and initiatives aimed at driving economic growth, promoting sustainability, and enhancing the country's global competitiveness.
INTERCULTURAL TOURISM IN MOROCCO
Intercultural tourism in Morocco is a rich and varied experience that attracts many travelers from around the world. Morocco is a country of great cultural diversity, with a fascinating history, unique architecture, delicious cuisine, and breathtaking landscapes, ranging from the Atlas Mountains to the Sahara deserts and the coasts of the Atlantic and Mediterranean.
Here are some aspects of intercultural tourism in Morocco:
1. Meeting of cultures: Morocco is a crossroads where different cultures meet, notably Arab, Berber, African, European and Jewish. Travelers have the opportunity to discover and appreciate this diversity through cuisine, architecture, music, crafts and local traditions.
2. Imperial Cities: Morocco's imperial cities, such as Marrakech, Fez, Rabat and Meknes, are must-see destinations for travelers interested in the country's history and culture. These cities are full of historic monuments, bustling medinas, sumptuous palaces and ancient mosques.
3. Life in the medinas: The medinas, the ancient fortified cities of Morocco, offer an authentic immersion in the daily life of the inhabitants. The narrow streets, colorful souks and smells of spices create a unique ambiance where travelers can interact with locals, discover local crafts and taste traditional dishes.
4. Festivals and cultural events: Morocco is also known for its festivals and cultural events throughout the year. The Rose Festival in Kelaat M'Gouna, the Folklore Festival in Marrakech, and the Gnaoua Festival in Essaouira are just a few examples of the vibrant celebrations that showcase the country's cultural wealth.
5. Moroccan Hospitality: Moroccans are known for their warm hospitality and generosity towards visitors. Travelers are often welcomed with open arms in traditional guesthouses, where they have the opportunity to share family meals and participate in local activities.
In short, intercultural tourism in Morocco offers travelers an immersive and enriching experience, where they can discover a fascinating culture, explore spectacular landscapes and create unforgettable memories.
INTERCULTURAL TOURISM IN EMIRATES
Intercultural tourism in the United Arab Emirates is also a fascinating experience, although different from what one can experience in Morocco. The United Arab Emirates is a popular destination for travelers from around the world due to its unique blend of tradition and modernity.
Here are some aspects of intercultural tourism in the United Arab Emirates:
1. Meeting of cultures: The United Arab Emirates is a multicultural society where many different nationalities come together. In Dubai and Abu Dhabi in particular, there is great ethnic diversity, with expats coming from all over the world to work and live. Travelers have the opportunity to interact with people from different cultures, which enriches their experience.
2. Heritage and tradition: Although the UAE is known for its modernity and rapid development, it also has a rich cultural and historical heritage. Visitors can explore historic districts, traditional forts, picturesque souks and Bedouin villages to experience traditional Emiratis culture and lifestyle.
3. Iconic Architecture: The UAE is famous for its modern and avant-garde architecture, epitomized by masterpieces such as the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, one of the tallest towers in the world, and the Grand Mosque Sheikh Zayed in Abu Dhabi, an architectural marvel. Visitors can admire these impressive achievements while exploring the cultural and religious aspects behind them.
4. Cuisine and gastronomy: Cuisine in the UAE reflects the diversity of its population, with a variety of traditional Arabic, Indian, Persian and international dishes. Travelers can enjoy authentic cuisine at local restaurants, as well as the many food markets and street stalls that dot the towns.
5. Cultural Events and Festivals: The UAE hosts a range of cultural events and festivals throughout the year, showcasing music, dance, art and literature from the region and the world entire. The Abu Dhabi Culture Festival and the Dubai Shopping Festival are just two examples.
In conclusion, intercultural tourism in the UAE offers travelers an immersion in a dynamic and diverse society, where centuries-old traditions blend with modernity, providing a unique and enriching cultural experience.
HIGH TOLERANCE AND DIVERSITY IN MOROCCO*
Morocco is recognized for its tolerance and diversity, which are fundamental elements of its national identity. Here are some points illustrating tolerance and diversity in Morocco:
-Ethnic and religious plurality: Morocco is home to significant ethnic and religious diversity. In addition to the indigenous Berber population, the country includes Arabs, Sahrawis, Black Africans, Europeans and other ethnic groups. Additionally, Morocco is home to diverse religious communities, including Sunni Muslims, Jews, Christians, and other religious minorities.
-Interreligious coexistence: Morocco is renowned for its tradition of peaceful coexistence between different religious communities. Jews have a significant historical presence in Morocco and have coexisted peacefully with the Muslim majority for centuries. Synagogues, churches and mosques are often found in close proximity to each other, reflecting this interfaith coexistence.
-Religious tolerance policies: Morocco has implemented policies aimed at protecting religious freedom and promoting tolerance between different religious communities. The King of Morocco is traditionally considered the Commander of the Faithful, guaranteeing protection to religious minorities.
-Multiple languages and cultures: Morocco is also characterized by linguistic and cultural richness. In addition to Arabic, the official language, Berber has also been recognized as an official language since 2011. This recognition has reinforced respect and promotion of the country's linguistic and cultural diversity.
-Intercultural tourism: Tourism plays an important role in promoting tolerance and diversity in Morocco. Visitors can experience a diverse range of customs, traditions and lifestyles across the country, helping to raise awareness of Morocco's rich cultural diversity.
HIGH TOLERANCE AND DIVERSITY IN EMIRATES*
The UAE is a diverse country where tolerance and diversity are encouraged and valued. Here are some aspects that illustrate tolerance and diversity in the United Arab Emirates:
-Ethnic and cultural plurality: The United Arab Emirates welcomes expatriates and residents of all ethnic, cultural and religious backgrounds. Due to the large international workforce, the Emirates is home to people from all over the world, creating a vibrant cultural and ethnic mosaic.
-Religious Tolerance: The UAE guarantees freedom of religion and allows different religious communities to practice their faith. Although Islam is the official state religion, non-Muslims have the right to practice their religion and places of worship for various faiths, including Islam, Christianity, Judaism, Hinduism and Sikhism, are present in the country.
-Legal Framework for Tolerance: The UAE has laws in place that encourage tolerance and peaceful coexistence between different communities. For example, the Charter of Tolerance, adopted in 2016, aims to promote the values of tolerance, dialogue and mutual respect.
-Cosmopolitan Environment: The UAE, particularly Dubai and Abu Dhabi, are cosmopolitan centers that attract visitors, residents and investors from around the world. This cultural and linguistic diversity is reflected in neighborhoods, restaurants, shopping centers and social events.
-Promotion of Diversity: The UAE Government actively encourages the promotion of diversity through various initiatives, cultural events and educational projects. For example, Dubai Expo 2020 was a global event that celebrated cultural and economic diversity under the theme “Connecting Minds, Building the Future”.
In short, the UAE is committed to maintaining an open and tolerant society that celebrates diversity in all its forms. This approach promotes an inclusive environment where people of different cultures, religions and backgrounds can coexist harmoniously
GOLD MOROCCO HOSPITALITY
Morocco's hospitality is renowned throughout the world for its warmth, generosity and sense of welcome. This tradition of hospitality is deeply rooted in Moroccan culture and is often considered one of its most distinctive characteristics.
Here are some aspects of Moroccan hospitality:
-Warm welcome: Moroccans are known for welcoming visitors with a warm smile and friendly attitude. Whether in private homes, riads (traditional houses) or hotels, guests are often treated with great respect and attention.
-Mint tea: Mint tea is an iconic drink of Morocco and is often offered to guests upon their arrival. It is a symbol of hospitality and friendliness.
-Dining Invitations: Moroccans are known for their generosity when it comes to sharing a meal. Visitors are often invited to share a traditional Moroccan meal, such as couscous or tagine, in the homes of locals or at local restaurants.
-Hospitality in businesses: Even in stores and souks (markets), Moroccan merchants are known for their hospitality towards customers. They may offer tea or just strike up a friendly conversation, even if you don't plan to buy anything.
-Cultural exchange: Moroccans are often eager to share their culture, history and traditions with visitors. Whether through music, dance, crafts or cooking, visitors are often encouraged to participate and learn.
In summary, hospitality in Morocco is an authentic and enriching experience for travelers looking to discover the culture and traditions of this magnificent country.
GOLD HOSPITALITY IN EMIRATES
Hospitality in the UAE is also renowned for its warmth and generous welcome towards visitors. Here are some aspects of hospitality in the United Arab Emirates:
-Cordial Welcome: The UAE is known for providing a warm welcome to visitors, whether in hotels, private homes or public places. Locals are often willing to help and guide visitors on their travels.
-Arabic tea: Much like mint tea in Morocco, Arabic tea, often served with dates, is a typical mark of hospitality in the United Arab Emirates. Visitors are often greeted with this traditional drink.
-Dining invitations: Emiratis are known for their generosity when it comes to inviting others to share a meal. Visitors are often invited to taste traditional Emirati dishes, such as biryani, machbous or ouzi, in local homes or restaurants.
-Welcoming Culture: The UAE has a multicultural and multinational culture, with people coming from all over the world to work and live. This cultural diversity is reflected in the welcoming attitude towards visitors of all origins.
-Cultural exchange: Just like in Morocco, Emiratis are often open to sharing their culture, history and traditions with visitors. Festivals, cultural events and museums provide visitors with opportunities to learn and understand the rich history and culture of the UAE.
In short, hospitality in the UAE is an enriching experience for travelers, offering them a glimpse of the warmth and generosity of Emirati culture.
EXCELLENCE AND IDENTITY AND HIGH NOBLE VALUES OF MOROCCO
Morocco, like many other countries, has a history rich in cultural, social and historical values that have shaped its society. Here are some of the noble values often associated with Morocco:
-Hospitality: Moroccans are known for their warm hospitality towards visitors and foreigners. Welcoming guests is a value deeply rooted in Moroccan culture.
-Respect for family: The family occupies a central place in Moroccan society. Respect for elders, the importance given to family ties and mutual support within the family are fundamental values.
-Respect for religion: Morocco is a Muslim country where the religion, Islam, plays an important role in the daily life of its inhabitants. Respect for religious practices and Islamic values is widely observed.
-Religious and cultural tolerance: Morocco has a long tradition of peaceful coexistence between different religious communities and cultures. Moroccans are often proud of this diversity and value religious and cultural tolerance.
-Community solidarity: Moroccans attach great importance to solidarity and mutual aid within their community. They are often willing to support those in need, whether at the family, local or national level.
-Respect for traditions: Morocco is steeped in ancient traditions that are still respected and celebrated in many regions of the country. These traditions touch on various aspects of daily life, from cooking and crafts to music and dance.
-Culinary hospitality: Moroccan cuisine is world-renowned for its diversity, rich flavors and generosity. Inviting guests to share a meal is often considered a gesture of hospitality and conviviality.
-Respect for elders and wisdom: Moroccans traditionally give great respect to elderly people and holders of wisdom. Their advice and experience are often valued within the family and community.
These values play an important role in Moroccan society and contribute to its cultural and social wealth. However, it should be noted that Moroccan society is diverse and complex, and these values can be experienced and interpreted in different ways depending on individuals and regions.
ALWAYS EXCELLENCE AND GOLD VALUES OF EMIRATES
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a federation of seven emirates located on the Arabian Peninsula.
Here are some of the values often associated with UAE culture:
-Hospitality: As in many Middle Eastern cultures, hospitality is a core value in the UAE. Emiratis are known for their warmth and generosity towards guests and strangers.
-Respect for traditions: The UAE has a rich history and culture, and respect for traditions is deeply rooted in society. Emiratis place great importance on the customs, rituals and cultural heritage of their country.
-Respect for family: The family plays a central role in Emirati society. Respect for elders, family solidarity and maintaining family ties are important values.
-Tolerance and diversity: The United Arab Emirates is known for its religious and cultural tolerance. As a multicultural society, the Emirates welcomes people of diverse backgrounds and religions, and peaceful coexistence between different communities is encouraged.
-Religious Devotion: Islam is the dominant religion in the UAE, and religious practice plays an important role in the daily lives of many Emiratis. Faith and religious devotion are deeply rooted values in Emirati culture.
-Education and knowledge: The United Arab Emirates places great importance on education and the pursuit of knowledge. Investment in education is considered essential for the development and prosperity of the country.
-Innovation and Ambition: The UAE has experienced rapid economic growth and is often associated with innovation and ambition. The country is constantly looking to diversify its economy and invest in sectors such as technology, tourism and renewable energy.
-Respect for the environment: The United Arab Emirates recognizes the importance of environmental protection and sustainable development. The country has undertaken various initiatives to promote environmental sustainability and reduce its ecological footprint.
WOMEN LEADERS OF MOROCCO
Here are some examples of women leaders in Morocco:
1. Meryem Bensalah-Chaqroun: She is a Moroccan businesswoman and was the first female president of the General Confederation of Moroccan Enterprises (CGEM).
2. Najat Rochdi: She is a Moroccan diplomat who has held several important positions within the United Nations, including as United Nations Resident Coordinator in Morocco.
3. Fatima-Zahra Mansouri: She was the first female mayor of Marrakech and is also a member of the Party of Authenticity and Modernity (PAM).
4. Nouzha Skalli: She is a Moroccan politician who served as Minister of Social Development, Family and Solidarity.
5. Bouchra Hajij: She is the president of the Royal Moroccan Football Federation (FRMF), being the first woman to hold this position in the history of the FRMF.
6. Touria Chaoui: She is a Moroccan lawyer recognized for her commitment to the rights of women and children.
These women have played an important role in different sectors of Moroccan society and have contributed to promoting gender equality and the socio-economic development of the country.
WOMEN LEADERS IN THE EMIRATES
Here are some examples of women leaders in the United Arab Emirates:
1. Sheikha Lubna Al Qasimi: She was the first female minister in the United Arab Emirates. She has held several ministerial positions, including Minister of Foreign Trade and Minister of International Development.
2. Sheikha Fatima bint Mubarak: She is the widow of the former President of the United Arab Emirates, Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan, and the mother of the current President, Sheikh Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan. She is also president of the Emirates Family and Women Foundation.
3. Sheikha Hind bint Maktoum bin Juma Al Maktoum: She is the Vice President of the Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Foundation and the daughter of Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, Vice President and Prime Minister of the United Arab Emirates, as well as Emir of Dubai.
4. Dr. Amal Al Qubaisi: She is the Speaker of the Federal National Council of the UAE, becoming the first female Speaker of an Arab national parliament in the world.
5. Mariam Al Mansouri: She is the first female Emirati fighter pilot and became famous for her role in the UAE Air Force.
These women leaders have played crucial roles in different fields, from politics to education, business and social services, contributing to the advancement and empowerment of women in the UAE.
A1-MOROCCO RICHNESS IN MANY FIELDS
Morocco is rich in various fields, including culture, history, natural resources, and geography. Here are some of the areas where Morocco exhibits richness:
- Cultural Diversity: Morocco boasts a rich and diverse cultural heritage influenced by Arab, Berber, African, and European civilizations. Its cultural richness is evident in its architecture, cuisine, music, and art.
- History and Heritage: Morocco has a long and storied history, with ancient cities like Fez, Marrakech, and Meknes offering insights into its past as imperial cities. The country is home to numerous historical sites, including ancient Roman ruins, Islamic architecture, and medieval medinas.
- Geographic Diversity: Morocco’s geography is incredibly diverse, featuring coastal areas, mountains, deserts, and fertile plains. The Atlas Mountains traverse the country, providing stunning landscapes and opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, trekking, and skiing.
- Natural Resources: Morocco is rich in natural resources, including phosphates, which are essential for agriculture and industry. The country also has significant deposits of minerals, including cobalt, manganese, zinc, and lead.
- Tourism: Tourism is a vital sector in Morocco, driven by its rich cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and historical sites. Cities like Marrakech, Casablanca, and Essaouira attract millions of tourists each year, contributing significantly to the country’s economy.
- Agriculture: Morocco’s agriculture sector is diverse and productive, with crops such as citrus fruits, olives, grains, and vegetables grown across the country. The agricultural sector plays a crucial role in providing employment and ensuring food security.
- Renewable Energy: Morocco has made significant investments in renewable energy, particularly solar and wind power. The country’s solar energy projects, such as the Noor Solar Power Complex, are among the largest in the world and demonstrate Morocco’s commitment to sustainable development.
Overall, Morocco’s richness extends across various domains, making it a fascinating and vibrant country with much to offer in terms of culture, history, natural beauty, and economic potentials.
A2- EMIRATES RICHNESS IN MANY FIELDS
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is known for its wealth and richness across several fields:
- Economy: The UAE possesses one of the most diversified economies in the Middle East. It is known for its oil reserves, but it has also made significant strides in diversifying its economy. Dubai and Abu Dhabi serve as major financial and business hubs in the region, attracting investors and entrepreneurs from around the world.
- Infrastructure: The UAE boasts modern and sophisticated infrastructure, including world-class airports, highways, seaports, and skyscrapers. Cities like Dubai and Abu Dhabi are known for their impressive skyline and iconic landmarks such as the Burj Khalifa and the Palm Jumeirah.
- Tourism: The UAE is a popular tourist destination, known for its luxury hotels, shopping malls, entertainment venues, and cultural attractions. Dubai, in particular, attracts millions of tourists each year who come to experience its vibrant nightlife, pristine beaches, and diverse cultural offerings.
- Culture and Heritage: Despite its modernity, the UAE has preserved its rich cultural heritage. Visitors can explore traditional markets (souks), mosques, museums, and historical sites that showcase the country’s Bedouin roots and Islamic traditions.
- Education and Research: The UAE has invested heavily in education and research, establishing world-class universities and research institutions. Institutions like Khalifa University, the American University of Sharjah, and New York University Abu Dhabi attract students and scholars from around the world.
- Healthcare: The UAE offers high-quality healthcare services, with modern hospitals, clinics, and medical facilities equipped with state-of-the-art technology and staffed by skilled healthcare professionals. The country’s healthcare system is known for its accessibility and quality of care.
- Finance and Business: The UAE is a global financial center, home to numerous multinational corporations, banks, and financial institutions. The Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) and Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM) serve as leading financial hubs, facilitating international trade and investment.
- Sustainability and Innovation: The UAE has embarked on ambitious sustainability initiatives and is investing in renewable energy and green technologies. Projects like Masdar City and the Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park demonstrate the country’s commitment to sustainability and innovation.
Overall, the UAE’s richness extends across various domains, including economy, infrastructure, tourism, culture, education, healthcare, finance, and sustainability, making it a dynamic and thriving nation in the Middle East
A3-MOROCCO RICHNESS IN PHOSPHATE
A4-RICHNESS OF EMIRATES IN OIL
reference : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economy_of_the_United_Arab_Emirates
“The United Arab Emirates is a high-income developing market economy. The UAE’s economy is the 3rd largest in the Middle East (after Turkey and Saudi Arabia), with a gross domestic product (GDP) of US$415 billion (AED 1.83 trillion) in 2021-2023.
The UAE economy is heavily reliant on revenues from petroleum and natural gas, especially in Abu Dhabi. In 2009, more than 85% of the UAE’s economy was based on the oil exports. In 2011, oil exports accounted for 77% of the UAE’s state budget. In recent years, there has been some economic diversification,particularly in Dubai. Abu Dhabi and other UAE emirates have remained relatively conservative in their approach to diversification. Dubai has far smaller oil reserves than its counterparts.
Tourism is one of the biggest non-oil sources of revenue in the UAE. A massive construction boom, an expanding manufacturing base, and a thriving services sector are helping the country to diversify its economy. Nationwide, there is currently US$350 billion worth of active construction projects.
The UAE is a member of the World Trade Organization and OPEC.”
A5-The Quality of Service in Tourism in Morocco
The quality of service in tourism in Morocco can vary depending on various factors including the type of accommodation, the region visited, the level of development of tourism infrastructure, and the expectations of the travelers. Here are some key points regarding the quality of service in tourism in Morocco:
- Hospitality and Culture: Moroccan hospitality is renowned worldwide. Visitors often experience warm welcomes and genuine hospitality from Moroccans. The country has a rich cultural heritage, and many Moroccans take pride in sharing their traditions, cuisine, and customs with tourists.
- Accommodation: Morocco offers a wide range of accommodation options including luxury hotels, riads (traditional Moroccan houses), guesthouses, and budget hotels. The quality of accommodation can vary greatly depending on the location and price range. In popular tourist destinations like Marrakech, Fes, and Casablanca, you can find high-quality hotels and riads with excellent service standards.
- Tourist Attractions: Morocco is known for its diverse tourist attractions, including historical sites, cultural landmarks, natural landscapes, and vibrant markets (souks). The quality of these attractions can vary, but many are well-maintained and offer informative guides and facilities for visitors.
- Transportation: Transportation infrastructure in Morocco has seen significant improvements in recent years. Major cities are connected by well-maintained highways, and the country has a reliable train network operated by ONCF (Office National des Chemins de Fer du Maroc). In addition, many tourists opt for organized tours or hire private drivers to explore the country’s attractions.
- Dining and Cuisine: Moroccan cuisine is celebrated for its rich flavors and variety. Visitors can enjoy traditional dishes such as tagine, couscous, and pastilla in restaurants, cafes, and street stalls across the country. The quality of dining experiences can vary, but many restaurants offer delicious food and attentive service.
- Tourism Infrastructure: While Morocco has made significant investments in tourism infrastructure, there are still challenges in certain areas, such as waste management, sanitation, and environmental conservation. In popular tourist destinations, efforts are being made to improve infrastructure to accommodate the growing number of visitors.
- Language: Arabic and French are the official languages of Morocco, but many people in the tourism industry also speak English, especially in popular tourist areas. Visitors who speak French or Arabic may find it easier to communicate with locals, but English is widely understood in hotels, restaurants, and tourist attractions.
Overall, the quality of service in tourism in Morocco can be very good, especially in popular tourist destinations. However, as with any destination, experiences may vary depending on individual preferences, expectations, and the specific circumstances of each visit. It’s always advisable for travelers to research and plan their trip accordingly to ensure a satisfying experience in Morocco.
A6-The Quality of Service in Tourism in the United Arab Emirates
The quality of service in tourism in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is generally regarded as excellent and is one of the key factors contributing to the country’s booming tourism industry. Here are several reasons why:
- Hospitality Industry: The UAE has heavily invested in its hospitality industry, resulting in world-class hotels, resorts, and other accommodations. From luxury brands to boutique hotels, visitors can find a wide range of options to suit their preferences and budgets.
- Luxurious Facilities: Many hotels and resorts in the UAE offer luxurious amenities and facilities, including state-of-the-art spas, fine dining restaurants, pristine beaches, and stunning architecture. The attention to detail and the level of service provided often exceed expectations.
- Diverse Attractions: The UAE boasts a diverse range of attractions, including iconic landmarks like the Burj Khalifa, Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque, Palm Jumeirah, and Dubai Marina. These attractions are well-maintained and offer top-notch visitor experiences, often accompanied by informative guides and modern facilities.
- Infrastructure: The UAE has invested heavily in infrastructure development, including transportation, roads, airports, and public facilities. The country’s modern infrastructure ensures smooth travel experiences for tourists and facilitates easy access to various attractions and destinations.
- Safety and Security: The UAE is known for its high level of safety and security, which is crucial for attracting tourists. Visitors can explore the country with peace of mind, knowing that they are in a safe environment.
- Multicultural Environment: The UAE is a melting pot of cultures, with a large expatriate population from around the world. As a result, the tourism industry is well-equipped to cater to the needs of diverse visitors, offering services in multiple languages and accommodating different cultural preferences.
- Professionalism: The hospitality industry in the UAE is known for its professionalism and customer-centric approach. Staff members are often well-trained, courteous, and attentive to the needs of guests, enhancing the overall quality of service.
- Innovation and Entertainment: The UAE is constantly innovating and introducing new attractions and experiences to enhance its tourism offerings. From theme parks like Ferrari World and Warner Bros. World to cultural events, concerts, and festivals, there is always something new and exciting for tourists to explore.
Overall, the UAE places a strong emphasis on providing exceptional service and experiences to visitors, which has contributed to its reputation as a top tourist destination in the Middle East and beyond. Whether travelers are seeking luxury, adventure, culture, or relaxation, the UAE offers a diverse array of experiences to suit every taste.
A7-EXCELLENCE IN BLUE ECONOMY IN MOROCCO
Morocco has been actively pursuing excellence in the blue economy, recognizing the potential of its marine resources and coastal areas. The blue economy refers to sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and ocean health. Here are some key initiatives and aspects of Morocco’s focus on the blue economy:
- Strategic Location: Morocco has a long coastline that stretches along the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, giving it strategic access to marine resources and maritime trade routes.
- National Strategy for Sustainable Development of the Maritime Economy (Stratégie Nationale pour le Développement Durable de l’Economie Maritime, SNDD): Morocco launched its national strategy in 2017 to promote sustainable development and investment in the maritime sector. The strategy focuses on key areas such as fisheries, aquaculture, maritime transport, coastal tourism, renewable energy, and marine biotechnology.
- Fisheries and Aquaculture: Morocco has a significant fishing industry and is one of the largest fish producers in Africa. The government has implemented policies to promote sustainable fishing practices, combat illegal fishing, and support the development of aquaculture projects.
- Renewable Energy: Morocco is exploring the potential of offshore wind and wave energy as part of its renewable energy strategy. The country has been investing in projects to harness renewable energy sources from its coastal areas.
- Marine Conservation and Environmental Protection: Morocco has made efforts to conserve its marine biodiversity and protect coastal ecosystems. Initiatives include establishing marine protected areas, promoting sustainable coastal development, and addressing pollution and habitat degradation.
- International Cooperation: Morocco has engaged in partnerships and collaborations with international organizations, neighboring countries, and the European Union to promote sustainable management of marine resources, maritime security, and economic cooperation in the region.
- Investment and Infrastructure Development: Morocco has been investing in port infrastructure, maritime logistics, and coastal facilities to support the growth of its maritime economy and attract investment from domestic and foreign sources.
Overall, Morocco’s commitment to the blue economy reflects its recognition of the importance of sustainable development, environmental stewardship, and economic diversification in its coastal regions. By leveraging its marine resources responsibly, Morocco aims to achieve long-term prosperity while preserving the health and resilience of its oceans.
A8-EXCELLENCE IN BLUE ECONOMY IN EMIRATES
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has been actively pursuing excellence in the blue economy, recognizing the potential of its maritime resources and coastal areas. Here are some key initiatives and aspects of the UAE’s focus on the blue economy:
- Strategic Location: The UAE has a significant coastline along the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, providing strategic access to marine resources and maritime trade routes.
- Vision 2030: The UAE’s Vision 2030 outlines a comprehensive development plan that includes a focus on sustainable economic diversification, including the development of the blue economy. The vision emphasizes innovation, sustainability, and investment in sectors such as maritime transport, fisheries, tourism, and renewable energy.
- Port Infrastructure: The UAE has invested heavily in developing world-class port infrastructure, including major ports like Jebel Ali Port in Dubai and Khalifa Port in Abu Dhabi. These ports serve as crucial hubs for maritime trade and logistics in the region.
- Maritime Transport and Shipping: The UAE is a global leader in maritime transport and shipping services. Dubai’s maritime cluster, including Dubai Maritime City and Dubai Maritime Cluster Office, promotes collaboration, innovation, and investment in the maritime sector.
- Fisheries and Aquaculture: The UAE has been investing in modernizing its fisheries and developing sustainable aquaculture practices. The country is exploring aquaculture projects to meet domestic demand for seafood and reduce reliance on imports.
- Marine Tourism: The UAE’s coastal areas attract millions of tourists each year, drawn by pristine beaches, luxury resorts, and water-based activities. The government has been investing in marine tourism infrastructure and promoting sustainable tourism practices to protect coastal ecosystems and heritage sites.
- Renewable Energy: The UAE is investing in renewable energy sources, including offshore wind and solar energy projects. Masdar City in Abu Dhabi serves as a hub for renewable energy research, development, and innovation.
- Environmental Conservation: The UAE has been actively involved in marine conservation efforts, including the establishment of marine protected areas, coral reef restoration projects, and initiatives to combat marine pollution and habitat degradation.
- International Partnerships: The UAE collaborates with international organizations, research institutions, and industry partners to promote sustainable development, maritime security, and knowledge sharing in the blue economy.
Overall, the UAE’s commitment to the blue economy reflects its vision for sustainable development, economic diversification, and environmental stewardship in its coastal regions. By leveraging its maritime resources and strategic location, the UAE aims to achieve long-term prosperity while preserving the health and resilience of its oceans.
A9-Green Tourism in Morocco
Green tourism, also known as ecotourism or sustainable tourism, is gaining momentum worldwide as travelers become more conscious of their environmental impact. Morocco, with its diverse landscapes ranging from the Sahara Desert to the Atlas Mountains and the Atlantic coastline, offers numerous opportunities for green tourism initiatives. Here are some aspects of green tourism in Morocco:
- Desert Conservation: The Sahara Desert, a prominent attraction in Morocco, requires careful management to preserve its delicate ecosystem. Tour operators and local communities often collaborate to offer desert tours that minimize environmental impact, such as using eco-friendly transportation options like camels, promoting responsible waste management, and supporting local conservation efforts.
- Atlas Mountains: The Atlas Mountains offer opportunities for eco-friendly activities like hiking, trekking, and birdwatching. Sustainable tourism initiatives in the Atlas Mountains focus on promoting responsible travel practices, supporting local communities, and preserving the region’s biodiversity.
- Coastal Conservation: Morocco’s extensive coastline attracts visitors for activities like surfing, swimming, and beach tourism. Efforts to protect coastal ecosystems include beach clean-up campaigns, sustainable fishing practices, and the promotion of eco-friendly accommodations along the coast.
- Community-Based Tourism: Many communities in rural Morocco have embraced community-based tourism initiatives to provide authentic cultural experiences while generating income for local residents. Visitors can participate in homestays, traditional cooking classes, and artisan workshops, supporting local economies while minimizing their environmental footprint.
- Protected Areas: Morocco is home to several protected areas and national parks, such as the High Atlas Biosphere Reserve and Toubkal National Park. These areas are managed to conserve biodiversity, promote sustainable land use practices, and offer opportunities for eco-tourism activities like wildlife watching, hiking, and camping.
- Solar Energy: Morocco has invested heavily in renewable energy, particularly solar power, to reduce its carbon footprint and promote sustainability. Solar-powered accommodations and eco-lodges are becoming increasingly popular, offering travelers the opportunity to minimize their environmental impact while enjoying a unique travel experience.
- Cultural Preservation: In addition to environmental conservation, green tourism in Morocco often emphasizes the preservation of cultural heritage and traditions. Travelers can engage in responsible cultural tourism activities like visiting historic sites, participating in traditional festivals, and supporting local artisans.
Overall, green tourism in Morocco is characterized by efforts to conserve natural resources, promote sustainable practices, support local communities, and preserve cultural heritage. By choosing eco-friendly accommodations, engaging in responsible travel activities, and respecting local customs and ecosystems, visitors can contribute to the conservation and sustainability of Morocco’s rich natural and cultural heritage.
A10-Green Tourism in Emirates
Green tourism, also known as sustainable tourism or eco-tourism, is a growing trend in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), particularly in Dubai and Abu Dhabi. While the UAE is often associated with luxury and modernity, efforts are underway to promote environmentally friendly practices and preserve the country’s natural heritage. Here are some aspects of green tourism in the Emirates:
- Desert Conservation: The UAE’s vast desert landscapes, including the famous Arabian Desert, offer opportunities for eco-friendly tourism activities such as desert safaris, dune bashing, and camel trekking. Tour operators increasingly focus on minimizing environmental impact by using fuel-efficient vehicles, promoting responsible waste management, and supporting desert conservation initiatives.
- Coastal Protection: With a long coastline along the Persian Gulf, the UAE is home to pristine beaches and marine ecosystems. Efforts to protect coastal areas include beach clean-up campaigns, marine conservation projects, and sustainable fishing practices. Eco-conscious travelers can participate in beach clean-up activities or choose eco-friendly water sports operators that prioritize environmental sustainability.
- Wildlife Conservation: Despite its arid climate, the UAE is home to unique wildlife species adapted to desert environments. Conservation efforts include the establishment of protected areas such as the Dubai Desert Conservation Reserve and the Sir Bani Yas Island wildlife sanctuary. Visitors can participate in wildlife safaris, birdwatching tours, and conservation programs aimed at protecting endangered species like the Arabian oryx and hawksbill turtles.
- Sustainable Architecture: The UAE is known for its iconic modern architecture, including skyscrapers, luxury hotels, and futuristic developments. Increasingly, sustainable building practices are being integrated into new construction projects, with a focus on energy efficiency, green building certifications, and renewable energy technologies like solar power.
- Cultural Heritage: In addition to environmental conservation, green tourism in the Emirates emphasizes the preservation of cultural heritage and traditions. Travelers can explore historic sites, visit traditional markets (souks), and participate in cultural experiences such as falconry demonstrations and Bedouin-style desert camps.
- Waste Management: Addressing waste management challenges is an important aspect of sustainable tourism in the UAE. Efforts to reduce plastic waste, promote recycling, and implement waste-to-energy initiatives are underway in cities like Dubai and Abu Dhabi. Hotels, restaurants, and tourist attractions are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices such as reducing single-use plastics and implementing sustainable waste management systems.
- Public Awareness and Education: Green tourism initiatives in the UAE often include public awareness campaigns, educational programs, and community engagement activities aimed at promoting environmental stewardship and responsible tourism practices among residents and visitors alike.
Overall, green tourism in the Emirates seeks to balance economic development and environmental conservation while preserving the country’s cultural heritage and natural beauty. By choosing sustainable travel options, supporting eco-friendly businesses, and respecting local customs and ecosystems, travelers can contribute to the conservation and sustainability of the UAE’s diverse landscapes and rich cultural heritage.
A11-Excellence of Tourism in Morocco
Morocco is renowned for its vibrant tourism industry, drawing millions of visitors each year to explore its diverse landscapes, rich culture, and historical heritage. Several factors contribute to the excellence of tourism in Morocco:
- Diverse Landscapes: Morocco offers a stunning array of landscapes, including the Atlas Mountains, Sahara Desert, coastal regions along the Atlantic and Mediterranean, and picturesque cities like Marrakech, Fes, and Chefchaouen. This diversity appeals to a wide range of tourists seeking adventure, relaxation, or cultural experiences.
- Rich Culture and Heritage: Morocco boasts a blend of Arab, Berber, and European influences, reflected in its architecture, cuisine, music, and traditions. Visitors can explore ancient medinas, historic monuments such as the Kasbahs, and participate in festivals and ceremonies that celebrate the country’s cultural heritage.
- Hospitality and Warmth: Moroccans are known for their hospitality and welcoming nature. Visitors often experience genuine warmth and friendliness from locals, contributing to a memorable and enjoyable travel experience.
- Culinary Delights: Moroccan cuisine is famous worldwide for its aromatic spices, flavorful tagines, couscous, and mint tea. Culinary tours and cooking classes allow visitors to explore the country’s culinary traditions and savor its delicious dishes.
- Adventure and Outdoor Activities: Morocco offers a wide range of outdoor activities, including trekking in the Atlas Mountains, camel trekking in the Sahara Desert, surfing along the coast, and exploring rugged landscapes and picturesque oases.
- Historical and Architectural Wonders: Morocco is home to a wealth of historical and architectural wonders, including ancient cities, palaces, mosques, and Roman ruins. UNESCO World Heritage sites such as the Medina of Fes and the historic city of Meknes attract history enthusiasts from around the globe.
- Luxurious Accommodations: From traditional riads in the heart of the medina to luxurious resorts and boutique hotels, Morocco offers a diverse range of accommodations to suit every budget and preference.
- Accessibility: Morocco’s strategic location at the crossroads of Africa, Europe, and the Middle East makes it easily accessible to travelers from around the world. Major airports in cities like Casablanca, Marrakech, and Fes connect the country to international destinations.
- Investment in Infrastructure: Morocco has invested significantly in its tourism infrastructure, including transportation networks, hotels, resorts, and tourist facilities, to enhance the overall visitor experience and accommodate the growing number of tourists.
- Promotion and Marketing: The Moroccan government and tourism authorities actively promote the country as a premier tourist destination through various marketing campaigns, partnerships, and participation in international tourism fairs and events. This helps raise awareness and attract visitors from diverse markets globally.
Overall, the excellence of tourism in Morocco stems from its unique blend of culture, history, natural beauty, and hospitality, making it a captivating destination for travelers seeking unforgettable experiences.
A12-Excellence in Tourism in the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is renowned for its excellence in tourism, attracting millions of visitors annually to its dynamic cities, stunning landscapes, luxurious resorts, and cultural attractions. Here are several factors contributing to the excellence of tourism in the Emirates:
- Iconic Landmarks: The UAE is home to some of the world’s most iconic landmarks, including the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the world’s tallest building, and the Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque in Abu Dhabi, one of the largest mosques globally. These architectural marvels serve as major tourist attractions and symbols of the Emirates’ modernity and grandeur.
- Luxurious Hospitality: The Emirates offer world-class hospitality and luxurious accommodations, ranging from opulent hotels and resorts to exclusive beachfront villas and desert retreats. Visitors can indulge in unparalleled luxury and personalized service, making their stay memorable and comfortable.
- Cultural Diversity: Despite its modernity, the UAE embraces its rich cultural heritage and traditions. Visitors can explore traditional markets (souks), heritage villages, and museums showcasing the region’s history, art, and culture. The Emirates also celebrate cultural festivals and events, providing immersive experiences for tourists.
- Diverse Experiences: From adrenaline-pumping desert safaris and dune bashing to leisurely beach activities, shopping extravaganzas, and gourmet dining experiences, the UAE offers a diverse range of attractions and activities to cater to every traveler’s interests and preferences.
- Shopping Paradise: Dubai, in particular, is renowned as a global shopping destination, with its extravagant malls, souks, and designer boutiques offering a wide array of luxury brands, electronics, and unique souvenirs. The annual Dubai Shopping Festival attracts millions of visitors with its unbeatable deals, entertainment, and prizes.
- Culinary Delights: The Emirates boast a vibrant culinary scene, offering a fusion of Middle Eastern, Asian, and international cuisines. Visitors can savor traditional Emirati dishes, as well as gourmet creations by renowned chefs in upscale restaurants and street food stalls across the country.
- Year-Round Events and Entertainment: The UAE hosts a plethora of events and entertainment options throughout the year, including cultural festivals, music concerts, sporting events, and international exhibitions. Dubai’s vibrant nightlife and entertainment venues cater to diverse tastes, ensuring visitors have an exciting and memorable experience.
- Safety and Infrastructure: The UAE is known for its safety, cleanliness, and efficient infrastructure, providing travelers with a hassle-free and secure environment to explore and enjoy. The country’s modern transportation networks, including airports, roads, and public transport systems, ensure convenient travel within and between cities.
- Strategic Location: Situated at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa, the UAE serves as a gateway to the region, attracting tourists from around the world. Its well-connected airports and airlines offer convenient access to international travelers, making it a popular stopover destination and hub for business and leisure travel.
- Government Support and Investment: The UAE government has prioritized tourism as a key sector for economic diversification and growth. Continuous investments in tourism infrastructure, marketing campaigns, and initiatives to enhance visitor experiences contribute to the excellence and sustainability of the tourism industry in the Emirates.
In summary, the United Arab Emirates offers a unique blend of modernity, culture, luxury, and hospitality, making it a premier destination for travelers seeking unforgettable experiences and world-class amenities.
A13-Excellence in Economy in Morocco
Morocco has made significant strides in its economy over the past few decades, although challenges persist. Here are some key points regarding the excellence in the economy of Morocco:
- Diversification Efforts: Morocco has made efforts to diversify its economy away from traditional sectors like agriculture and mining towards more modern industries such as tourism, manufacturing, and services. This diversification is aimed at reducing dependence on volatile sectors and creating more sustainable growth.
- Infrastructure Development: Morocco has invested heavily in infrastructure projects including transportation, energy, and telecommunications. This has helped to improve connectivity within the country and enhance its attractiveness to foreign investors.
- Tourism: Morocco is known for its rich cultural heritage, beautiful landscapes, and historical sites, which have made it a popular tourist destination. The tourism industry plays a significant role in the country’s economy, contributing to job creation and foreign exchange earnings.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Morocco has actively sought foreign investment to support its economic development goals. The government has implemented various reforms to improve the business environment and attract FDI in key sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and renewable energy.
- Trade Agreements: Morocco has entered into several trade agreements with countries in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, which have facilitated trade and investment flows. These agreements have helped to open up new markets for Moroccan goods and services, contributing to economic growth.
- Challenges: Despite its progress, Morocco faces challenges such as high unemployment, particularly among youth and women, income inequality, and regional disparities. Additionally, the country’s economy remains vulnerable to external factors such as fluctuations in commodity prices and global economic conditions.
- Government Initiatives: The Moroccan government has implemented various initiatives to address these challenges and promote economic development. These include programs to support small and medium-sized enterprises, improve education and skills training, and enhance social protection measures.
Overall, while Morocco has made significant progress in its economy, there is still work to be done to achieve sustainable and inclusive growth, reduce poverty, and create more opportunities for its citizens. Continued efforts to diversify the economy, attract investment, and address structural challenges will be essential for the country’s long-term economic success.
A14-Excellence in Economy in The United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is known for its excellence in the economy, driven primarily by its strategic location, visionary leadership, and diversification efforts. Here are some key factors contributing to the excellence in the economy of the Emirates:
- Diversification: The UAE has successfully diversified its economy away from a heavy reliance on oil and gas. While hydrocarbons still play a significant role in the economy, the government has invested heavily in sectors such as tourism, trade, aviation, finance, real estate, and renewable energy. This diversification strategy has helped the UAE build a more resilient economy less vulnerable to fluctuations in oil prices.
- Infrastructure Development: The UAE boasts world-class infrastructure, including modern airports, ports, roads, and telecommunications networks. This infrastructure has facilitated trade, tourism, and investment, positioning the UAE as a global hub for business and commerce.
- Free Zones and Business-friendly Environment: The UAE offers numerous free zones and special economic zones with business-friendly regulations, tax incentives, and 100% foreign ownership. These zones have attracted multinational corporations, startups, and entrepreneurs from around the world, fostering innovation, entrepreneurship, and economic growth.
- Strategic Location: Situated at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa, the UAE serves as a gateway for trade and investment between East and West. Its strategic location has made it a preferred destination for multinational companies seeking to establish a presence in the Middle East and beyond.
- Investment in Human Capital: The UAE places a strong emphasis on education and skills development. The government has invested in world-class educational institutions and vocational training programs to equip its workforce with the skills needed for a knowledge-based economy.
- Stable Political Environment: The UAE enjoys political stability and a business-friendly regulatory environment, which has fostered investor confidence and attracted foreign investment. The government’s long-term vision and strategic planning have helped maintain stability and continuity in economic policies.
- Innovation and Technology: The UAE is committed to fostering innovation and embracing emerging technologies. Initiatives such as Dubai’s Smart City project and the Abu Dhabi Economic Vision 2030 prioritize innovation and technology as key drivers of economic growth and competitiveness.
- Tourism and Hospitality: The UAE is a major tourist destination, attracting millions of visitors each year to its iconic landmarks, luxury resorts, shopping malls, and cultural attractions. Tourism and hospitality play a significant role in the UAE’s economy, generating revenue, creating jobs, and driving economic diversification.
In conclusion, the UAE’s excellence in the economy can be attributed to its diversification efforts, world-class infrastructure, business-friendly environment, strategic location, investment in human capital, political stability, focus on innovation, and vibrant tourism industry. These factors have positioned the UAE as a global economic powerhouse and a model for economic development in the region.
A15-Morocco's Economic Growth
Morocco's economic growth has experienced fluctuations over the years, but overall the country has shown moderate but stable growth. Here are some key points regarding economic growth in Morocco:
Growth Rate: In recent years, Morocco has generally maintained an annual economic growth rate in the range of 3% to 5%. However, these figures may vary from year to year depending on various factors such as the global economic situation, weather conditions (especially for agriculture), government policies, etc.
Key sectors of the economy: The Moroccan economy is diversified, with key sectors such as agriculture, tourism, industry, financial services, and increasingly, the automotive industry and offshoring. The government has implemented various policies to promote growth in these sectors.
Economic Challenges: Morocco faces several economic challenges, including unemployment, particularly among youth, as well as regional disparities in economic development. Reducing these disparities and creating jobs remain priorities for the government.
Investments and structural reforms: Morocco has undertaken economic and structural reforms aimed at improving its business climate, attracting foreign investment and encouraging private sector development.
Regional and international integration: Morocco also seeks to strengthen its economic ties with other countries in the region and further integrate into the global economy through free trade agreements and economic partnerships.
In summary, although Morocco's economic growth may be modest compared to other emerging economies, the country continues to make progress and implement policies aimed at boosting economic development and improving the living conditions of its population.
A16-UAE's Economic Growth
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has been one of the most dynamic economic players in the Middle East region over the past decades.
Here are some key points regarding the UAE's economic growth:
-High growth rate: The UAE has recorded impressive economic growth rates in recent years. In particular, the Emirates of Dubai and Abu Dhabi have been drivers of this growth. Annual growth rates have often exceeded 4 to 5%, or even more in some years.
-Economic diversification: Traditionally dependent on oil revenues, the United Arab Emirates has undertaken serious efforts to diversify its economy. The finance, tourism, real estate, trade, aviation and logistics sectors have become important pillars of their economy.
-Massive investments: The UAE has invested heavily in infrastructure projects, free zones, industrial parks, real estate developments and tourism projects. These investments have helped stimulate economic growth and attract foreign investment flows.
-Long-term vision: The UAE has adopted long-term visions for economic development, such as Vision 2021 and Vision 2030. These plans aim to further diversify the economy, drive innovation, strengthen education and improve the quality of life of citizens.
-Financial and commercial hub: Dubai, in particular, has positioned itself as a major financial, commercial and logistics hub globally. Its modern infrastructure, favorable trade policies and strategic geographical location make it a hub for businesses around the world.
In summary, the UAE has experienced remarkable economic growth thanks to its drive for diversification, massive investments in infrastructure, and focus on innovation and long-term development. However, like any economy, they also face challenges such as volatile oil prices and the need to maintain an attractive business environment.
A17-Artificial Intelligence in Morocco
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a growing area of interest in Morocco in recent years. Although the country may not have the same visibility as some global leaders in AI, it is nevertheless experiencing significant developments in this area.
Here are some points to consider regarding artificial intelligence in Morocco:
Government and academic initiatives: The Moroccan government recognizes the importance of AI for the economic and technological development of the country. Educational and research programs have been established in some Moroccan universities to promote the study and research in AI.
Companies and startups: More and more Moroccan companies are starting to explore the possibilities offered by AI to improve their processes, develop new products and services, and optimize their operations. Some Moroccan startups also specialize in developing AI-based solutions, particularly in areas such as health, education, finance and logistics.
International collaborations: Morocco also seeks to establish partnerships with international institutions and companies specializing in AI to benefit from their expertise and resources. These collaborations may take the form of joint research projects, technology transfers or training programs.
Challenges and opportunities: Although AI presents many opportunities for Morocco in terms of economic and technological development, the country also faces certain challenges, particularly in terms of training and qualification of the workforce, technological infrastructure and regulatory framework.
In summary, although AI is still in the development phase in Morocco, the country is making significant progress to harness the potential of this technology and integrate AI into various sectors of its economy.
A18-Artificial Intelligence in Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has become a major player in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) in the Middle East. Here are some key points about AI in the UAE:
Strategic Vision: The UAE has adopted an ambitious strategic vision to become a global leader in AI. The government has launched several initiatives aimed at promoting the adoption and development of AI in the country.
Centers of Excellence and Research: The UAE has established several centers of excellence and research institutes dedicated to AI. Some of the most notable include the Dubai Artificial Intelligence Center, the Center for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics at Khalifa University in Abu Dhabi, and the Center for Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain at the Sharjah University of Science and Technology.
Investments: The UAE has invested heavily in AI-related projects. Local authorities, businesses and private investment funds have funded startups and initiatives to develop AI solutions in various sectors, including health, education, transport, finance and government.
Favorable regulation: The UAE has taken a proactive approach to AI regulation, establishing a regulatory framework that supports innovation while ensuring data protection and citizen security.
International partnerships: The UAE has established partnerships with international AI institutions, companies and experts. These collaborations allow the UAE to benefit from global expertise and stay at the forefront of technological advancements in this area.
In summary, the UAE has made artificial intelligence a strategic priority, investing in research, innovation and adoption of this technology. With its ambitious initiatives, the UAE is well positioned to play a leading role in the global AI landscape.
THE ALLIANCE BETWEEN MOROCCO AND EMIRATES IN ECONOMY The signed agreements “take on a strategic dimension due to their geographical scope, because they go beyond the framework of bilateral cooperation between the State of the United Arab Emirates and the Kingdom of Morocco to include numerous African countries and projects of interest to the European continent in the future”
For his part, the Minister of Equipment and Water, Nizar Baraka, noted that the signed memorandums of understanding also relate to a dimension mainly linked to infrastructure, particularly in terms of water security, given that this memorandum agreement will give rise to new generation investments relating mainly to water desalination, “which is a very important and ambitious program for Morocco”.

1-Water Desalination in Morocco Water desalination is a technology used to treat seawater or brackish water to make it suitable for drinking or other uses. In Morocco, water desalination has become an important solution to address water scarcity in certain regions, particularly in coastal areas where fresh water is scarce. Several water desalination installations have been set up in Morocco, particularly on the Atlantic and Mediterranean coast. These facilities typically use technologies such as reverse osmosis to remove salt and other contaminants from seawater, producing fresh, drinkable water. The Moroccan government has invested in water desalination as a strategic solution to ensure sufficient water supplies, especially in regions with limited water resources. This strategy aims to respond to growing water needs due to population growth, urbanization and the challenges posed by climate change. However, water desalination is not without its challenges. It requires significant energy consumption and can have environmental impacts, particularly with regard to the disposal of saline concentrates resulting from the desalination process. Despite these challenges, water desalination remains an important option to ensure water security in Morocco. Morocco to build a desalination plant in Casablanca-Settat.Desalination plant projects are also reportedly in the pipeline for Al Hoceima, Chtouka, El Jadida, Essaouira, Laayoune, Safi, Saidia, and Tiznit-Sidi; as well as Abengoa’s up to 450,000 m3/d project in Agadir. “With increasing demand and insufficient local resources, the only recourse to reduce the deficit in industrial or agriculture drinking water is desalination of seawater,” said secretary of state for water Charafate Afailal."https://www.utilities-me.com/news/article-5040-morocco-to-build-a-desalination-plant-in-casablanca-settat" 2-PORTS PROJECT IN MOROCCO another memorandum of understanding signed between the two countries relating to ports, stressing that Morocco has granted, in accordance with high royal directives, a special status to large ports which have a strategic dimension, adding that Morocco now has today the port of Nador West Med and the Atlantic port of Dakhla, which will benefit from investments by the State of the United Arab Emirates. The ports of Nador West Med, located on the Mediterranean coast of Morocco, and the Atlantic port of Dakhla are both important maritime infrastructures for Morocco. Indeed, these ports play strategic roles in the economic and commercial development of the country. The investments of the State of the United Arab Emirates in these ports can be seen as a recognition of their economic potential and their importance for Morocco, as well as an opportunity to strengthen economic and commercial ties between the United Arab Emirates and the Morocco. These investments could help improve port infrastructure, increase their capacity, introduce new technologies and stimulate economic activities in these regions, particularly in the areas of trade, logistics, fishing, tourism and industry. By supporting the development of these ports, the UAE could also strengthen its economic influence in the region, while contributing to Morocco's economic growth and development. 3-High-speed line project between Kenitra and Marrakech The Director General of the National Railway Office (ONCF), Mohamed Rabia Khlie, for his part, stressed that the high-speed line project between Kenitra and Marrakech is of particular importance, within the framework of the signing of the Declaration of the partnership between the leaders of the two brotherly countries, King Mohammed VI and the President of the State of the United Arab Emirates This ambitious and innovative partnership will allow the creation of an innovative financial structure for the implementation of this line, which will connect Tangier and Marrakech in a time not exceeding three hours, including 1 hour between Tangier and Rabat and 1 hour 35 minutes between Tangier and Casablanca, he noted, noting that this line will also allow the creation of 70 million working days and 3,700 permanent jobs during the works. 4-Energy Transition Strategy The Minister of Energy Transition and Sustainable Development, Leila Benali, noted that the partnership signed in the energy sector between the Kingdom of Morocco and the State of the United Arab Emirates gives a strong boost to private investments in this area. The signing of this agreement, she observed, constitutes an opportunity to establish the national energy transition strategy, noting that the strategic dimension of this agreement confirms the insightful vision of King Mohammed VI alongside the President of the State of the United Arab Emirates, Sheikh Mohammed Ben Zayed Al-Nahyan. 5-Funds for investment The general director of the Mohammed VI Fund for Investment, Mohamed Benchaâboun, affirmed that the Fund will play a central role in the implementation of the memorandums of understanding signed before King Mohammed VI and Sheikh Mohammed Ben Zayed Al-Nahyan. For Benchaâboun, the Fund will look into the financial package of the projects which are the subject of the memorandums of understanding and will also work closely with Emirati partners to find the best way to implement these projects in the near future in the transport, airports, water and energy sectors.
********************************** 1-High Logistics in Morocco Logistics in Morocco, like in many countries, play a crucial role in facilitating trade and commerce both domestically and internationally. Here are some key points regarding logistics in Morocco: -Infrastructure: Morocco has been investing in its infrastructure to enhance its logistics capabilities. This includes ports, roads, railways, and airports. Major ports like Casablanca, Tangier-Med, and Agadir are significant hubs for trade. -Ports: The Port of Tangier-Med is one of the largest ports in Africa and the Mediterranean region. It serves as a key transshipment point for goods moving between Europe, Africa, and the rest of the world. Casablanca Port is another major port handling a significant portion of Morocco's trade. -Road Transport: Morocco has an extensive road network connecting major cities and industrial zones. Road transport is the primary mode for domestic logistics, though infrastructure quality can vary in certain regions. -Rail Transport: The Moroccan rail network, operated by ONCF (Office National des Chemins de Fer), connects major cities and industrial centers. Rail transport is used for both freight and passenger transportation. -Air Transport: Morocco has several international airports, with Casablanca's Mohammed V International Airport being the busiest. Air transport is crucial for time-sensitive and high-value goods. -Customs and Trade Regulations: Understanding customs regulations and trade policies is essential for efficient logistics operations in Morocco. Import and export procedures must comply with local regulations. -Supply Chain Management: Effective supply chain management is vital for businesses operating in Morocco. This includes inventory management, warehousing, distribution, and transportation optimization. -Challenges: Despite improvements in infrastructure, logistics in Morocco still face challenges such as congestion at ports, bureaucratic procedures, and inefficiencies in transport networks. Addressing these challenges requires continued investment and policy reforms. -Trade Agreements: Morocco has trade agreements with several countries and regions, including the European Union and the United States, which can impact logistics and trade flows. Overall, logistics in Morocco are evolving to meet the demands of a growing economy and expanding international trade. Continued investment in infrastructure and improvements in logistics processes are essential for enhancing competitiveness and facilitating trade growth. 2-High Logistics in the United Arab Emirates Logistics in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) are highly advanced and form a critical part of the country's economy due to its strategic location, well-developed infrastructure, and efficient transportation networks. Here are some key aspects of logistics in the Emirates: -Infrastructure: The UAE boasts modern infrastructure, including world-class airports, seaports, highways, and railways. Major cities like Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and Sharjah are well-connected through extensive road networks and modern transportation facilities. -Ports: The UAE is home to some of the busiest ports in the world. Jebel Ali Port in Dubai is one of the largest container ports globally and a vital hub for trade in the Middle East. Other significant ports include Port Rashid (Dubai) and Khalifa Port (Abu Dhabi). -Air Transport: The UAE is known for its state-of-the-art airports, including Dubai International Airport and Abu Dhabi International Airport. Dubai's airport is one of the busiest in the world and a major hub for air cargo and passenger traffic. -Free Zones: The UAE has established numerous free zones, such as Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA), Dubai Airport Free Zone (DAFZA), and others, which offer attractive incentives for businesses, including exemptions from customs duties and taxes. These free zones facilitate trade and logistics activities. -Customs and Trade Facilitation: The UAE government has implemented streamlined customs procedures and trade facilitation measures to enhance the efficiency of logistics operations. Initiatives like the Dubai Trade Portal and Abu Dhabi Customs e-Services have simplified trade documentation and clearance processes. -Rail Transport: The UAE is developing its railway infrastructure with projects like the Etihad Rail network, which aims to connect major cities and industrial areas across the country. Rail transport is expected to play a significant role in the future of logistics in the UAE. -Logistics Hubs: Dubai and Abu Dhabi serve as major logistics hubs in the region, offering warehousing, distribution, and other value-added services to businesses engaged in trade and commerce. -Technology Adoption: The UAE is at the forefront of adopting cutting-edge technologies in logistics, including blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize supply chain processes and enhance operational efficiency. -Sustainability: The UAE government is increasingly focusing on sustainability and green initiatives in logistics, promoting energy-efficient transportation and environmentally friendly practices. In summary, logistics in the UAE are characterized by modern infrastructure, efficient transportation networks, strategic location, and a business-friendly environment. These factors have contributed to the UAE's position as a leading logistics and trade hub in the Middle East and beyond.
3-Richness of Morocco's* Oceans Morocco's oceans are an important source of wealth for the country, both economically and environmentally. Here are some of the main components of the wealth of Morocco’s oceans: -Fishing: Fishing is one of Morocco's most important industries. Moroccan waters are teeming with a great diversity of fish, crustaceans and molluscs, making it a very productive fishing area. Inshore and offshore fishing provides employment for thousands of people and is a vital source of income for many coastal communities. -Aquaculture: Morocco has also developed a significant aquaculture industry, which includes the farming of fish, crustaceans and molluscs. Aquaculture provides opportunities for producing high-quality seafood for the local and international market. -Coastal Tourism: Morocco's magnificent coasts attract millions of domestic and foreign tourists each year. Beach-related activities, such as swimming, scuba diving, surfing and recreational fishing, contribute significantly to the local economy. -Marine Biodiversity: Morocco's oceans are home to remarkable marine biodiversity, comprising a wide variety of marine species, including marine mammals, seabirds, sea turtles and a multitude of fish and invertebrates. The preservation of this biodiversity is essential to maintain the ecological balance of marine ecosystems. -Mineral Resources: The seabed off the coast of Morocco also contains valuable mineral resources such as phosphate, which is mined for use in the chemical industry and agriculture. In summary, Morocco's oceans are a vital source of economic wealth, biodiversity and natural resources, and their preservation and sustainable management are essential to ensure the country's long-term prosperity. 4-*UAE Marine Wealth The UAE has significant marine wealth despite its position in a region where the waters can be warm and salty. The coastal waters of the UAE are home to a variety of marine life, including species of fish, corals and other marine organisms. Coral reefs along the coasts of the UAE are particularly important as they support considerable marine biodiversity and provide essential habitats for many species of fish and other marine organisms. The UAE has taken steps to protect and preserve its marine environment. Marine protected areas have been established to preserve fragile ecosystems and promote the conservation of marine biodiversity. Additionally, research and monitoring initiatives are undertaken to study and monitor the health of marine ecosystems and to take appropriate conservation measures. The UAE's marine resources are not limited to biodiversity, but also include economic resources such as fish, shellfish and other seafood. Commercial fishing and mariculture are important industries in the region, contributing to the UAE economy and providing sources of food and income for residents. In summary, although the UAE is primarily known for its oil and gas industry, its coastal waters are home to significant marine wealth, which is valued for both its biodiversity and economic resources. 5-The Maritime Blue Economy The maritime economy, also known as the maritime economy, encompasses all economic activities linked to oceans, seas, and coastal areas. This economy is large and diverse, encompassing a wide range of sectors and activities. Here are some of the main aspects of the maritime economy: -Maritime Transport: Maritime transport is one of the pillars of the maritime economy. It encompasses the transport of goods, passengers, as well as the transport of raw materials, manufactured products, and general merchandise across the oceans. and the seas. -Fisheries and Aquaculture: Commercial fishing and aquaculture are important components of the maritime economy. They provide essential food resources to many populations around the world and also represent important economic activities. -Coastal and maritime tourism: Tourism activities linked to coastal and maritime regions, such as beach tourism, cruising, scuba diving, and water sports, contribute significantly to the economy of many regions. -Exploitation of Marine Resources: Marine resources such as oil, natural gas, minerals, and metals are exploited in territorial waters and seabeds to meet energy and industrial needs. -Marine Technologies: Marine technologies include offshore infrastructure, drilling equipment, marine energy production systems (offshore wind turbines, tidal turbines), as well as ocean monitoring and mapping technologies. -Protection of the Marine Environment: The preservation and sustainable management of marine and coastal ecosystems have become major concerns. Activities such as marine conservation, habitat restoration, and the fight against maritime pollution are an integral part of the maritime economy. -Marine Research and Innovation: Marine scientific research and technological innovation play a crucial role in the sustainable development and management of marine resources. These activities contribute to better understanding marine ecosystems, preventing environmental risks, and promoting sustainable economic practices. In summary, the maritime economy represents a dynamic and diversified economic sector which offers numerous opportunities for economic development, while posing challenges in terms of environmental preservation and sustainable management of marine resources.
6-Quality of Service in the Maritime Economy The quality of service in the maritime economy is essential to ensure the proper functioning of activities linked to oceans, seas and coastal areas. Here are some important aspects of quality of service in this area: -Reliability of Maritime Transport: Punctuality, schedule reliability and safety of maritime transport are key elements to ensure quality of service in the field of maritime transport. Shipping companies must ensure that goods and passengers arrive at their destination on time and safely. -Efficiency of Port Operations: Ports play a central role in the maritime economy as entry and exit points for goods and vessels. Good quality of service in port operations involves efficient cargo loading and unloading processes, as well as modern and well-maintained infrastructure. -Maritime Safety: The safety of ships, crews and the marine environment is a top priority in the maritime economy. International maritime safety regulations and standards must be respected to prevent accidents, pollution and other incidents that could compromise the quality of service. -Communication and Risk Management: Effective communication between stakeholders in the maritime economy, including shipping companies, port authorities, regulatory bodies and other stakeholders, is essential for risk management and rapid resolution of issues. problems. -Training and Skills of Maritime Personnel: Crews and personnel working in the maritime economy must benefit from adequate training and technical skills to ensure quality of service and face the challenges encountered at sea. -Support and Logistics Services: Support and logistics services, such as towing services, offshore supply services, ship repair services, and waste management services, also contribute to the overall quality of maritime operations. -Technologies and Innovations: The adoption of modern technologies and innovations in the maritime domain can improve the quality of service by increasing operational efficiency, reducing waiting times, and enhancing the safety and reliability of operations. In summary, quality of service in the maritime economy relies on reliable, efficient and secure operations throughout the logistics chain, from maritime transport to port operations and support services. This requires close collaboration between industry players, as well as investments in infrastructure, technology and training of maritime personnel.
7-The Wealth of the Oceans The wealth of the oceans is immense and diverse, both biologically and economically. Oceans cover more than 70% of the Earth's surface and play a crucial role in regulating climate, providing food resources, regulating the water cycle and producing oxygen. Here are some aspects of the wealth of the oceans: -Marine biodiversity: The oceans are home to an incredible diversity of life forms, from the smallest microorganisms to the largest marine mammals. From coral reefs to abysses, marine ecosystems are rich in plant and animal species. -Food Resources: The oceans provide an essential source of food for millions of people around the world. Fish, crustaceans, molluscs and algae are sources of protein and nutrients for many coastal populations. -Climate regulation: The oceans play a crucial role in climate regulation by absorbing much of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) and releasing oxygen through marine photosynthesis. Additionally, they influence global temperatures by redistributing heat through ocean currents. -Energy resources: The oceans also contain potential energy resources, including wave, tidal and offshore wind energy, which can be harnessed for renewable electricity generation. -Mineral Resources: The seabed contains valuable mineral resources such as oil, natural gas, precious metals and rare minerals. These resources are exploited to meet global energy and industrial needs. However, it is crucial to manage marine resources sustainably to preserve the health of ocean ecosystems and ensure the availability of resources for future generations. Overfishing, pollution, climate change and the destruction of marine habitats are all threats to the wealth of the oceans and require concerted action on a global scale.
8-Sustainable Development Sustainable development is a concept that aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It is based on three interdependent pillars: 1. The economic aspect: This involves promoting sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and equitably, and promoting technological and social innovation. 2. The social aspect: It seeks to guarantee social inclusion, equity and respect for human rights, by ensuring equitable access to resources, services and opportunities for all, and by combating inequality and poverty. 3. The environmental aspect: It involves the protection and preservation of the environment, using natural resources responsibly, reducing emissions of pollutants and promoting the conservation of biodiversity and ecosystems. Sustainable development recognizes the interconnections between these three dimensions and aims to find a balance between economic, social and environmental needs, in order to guarantee the long-term viability of our planet and the well-being of present and future generations.
9-Green Tourism Green tourism, also known as ecological tourism or sustainable tourism, is a form of travel that emphasizes environmental preservation, conservation of natural resources, and promotion of local development. It aims to minimize negative impacts on the environment and local communities, while providing enriching experiences for travelers. Here are some characteristics of green tourism: 1. Environmentally Friendly: Green tourism destinations strive to minimize their environmental footprint by adopting sustainable practices such as waste management, biodiversity conservation and use of renewable energy sources. 2. Community engagement: Green tourism promotes the participation and development of local communities. Visitors are encouraged to interact with locals, purchase local products and support sustainability initiatives. 3. Cultural Conservation: In addition to environmental preservation, green tourism also aims to protect the cultural traditions and heritage of the visited destinations. Travelers often have the opportunity to discover and appreciate the cultural richness of local communities. 4. Education and Awareness: Green tourism emphasizes environmental education and awareness among travelers. Visitors are encouraged to learn about local ecosystems, environmental issues and conservation efforts. 5. Outdoor and Adventure Activities: Green tourism destinations often offer a variety of outdoor activities such as hiking, kayaking, bird watching and cycling. These activities allow travelers to connect with nature while promoting an active and healthy lifestyle. In summary, green tourism offers a holistic approach to travel that seeks to preserve the environment, support local communities, and provide meaningful and enriching experiences for travelers.
10-Sustainable Tourism Sustainable tourism, also called responsible tourism or ecotourism, is an approach to tourism that aims to minimize negative impact on the environment, promote the protection and conservation of natural and cultural resources, and foster economic and social development local communities. Here are some key principles of sustainable tourism: 1. Environmental Protection: Sustainable tourism initiatives seek to reduce negative environmental impacts, such as pollution, deforestation, biodiversity loss and excessive consumption of natural resources. 2. Community Engagement: Sustainable tourism encourages the active participation and benefit of local communities in tourism activities. It promotes the creation of local jobs, skills development and the preservation of traditional cultures. 3. Cultural conservation: Sustainable tourism promotes respect and preservation of local cultures, traditions and ways of life. It encourages visitors to learn and respect the customs and practices of host communities. 4. Education and Awareness: Sustainable tourism efforts aim to educate travelers about environmental and social issues, as well as encourage responsible behavior during their travels. 5. Resource management: Sustainable tourism destinations implement effective management policies to preserve fragile natural resources, such as water, energy and ecosystems. 6. Local Economies: Sustainable tourism promotes local economies by encouraging visitors to purchase local products, support businesses and community initiatives, and invest in the long-term economic development of the regions visited. By adopting these principles, sustainable tourism aims to create positive travel experiences for both visitors and local communities, while preserving the environment and natural resources for future generations.
11-Quality of Service Quality of Service (QoS) refers to the measurement of the performance of a service or product against customer expectations and requirements. In various contexts, service quality can be defined in different ways, but it generally focuses on customer satisfaction and the ability of a product or service to meet agreed-upon needs and standards. In information technology and telecommunications, QoS concerns the ability of networks to deliver a specific level of performance, such as bandwidth, latency, reliability, etc. Businesses and Internet service providers often strive to ensure high QoS to meet user expectations and maintain user satisfaction. In other industries such as hotels, restaurants, healthcare, and many other services, service quality involves providing pleasant, efficient, and reliable service to customers. This can include things like friendliness of staff, cleanliness of facilities, speed of service, etc. In summary, service quality is an important concept in many fields because it reflects an organization's ability to meet the needs and expectations of its customers in a consistent and satisfactory manner.
12-Service Quality in Tourism Service quality in tourism is a crucial element in ensuring a positive experience for travelers and in promoting customer loyalty and the reputation of tourist destinations, accommodation establishments, travel agencies and other players in the sector. Here are some key aspects of service quality in tourism: 1. Greeting and customer service: Interactions with staff, whether upon arrival at the hotel, at the airport, or during sightseeing, should be warm, friendly and professional. 2. Comfort and cleanliness: Accommodation establishments, restaurants, tourist sites must offer a clean and comfortable environment, meeting travelers' expectations in terms of quality of infrastructure and hygiene. 3. Accessibility: Tourist destinations and facilities must be easily accessible to people with reduced mobility and offer services adapted to their needs. 4. Information and communication: Tourists must have clear and precise information on the services offered, the activities available, prices, timetables, etc. Effective communication is essential to avoid misunderstandings and frustrations. 5. Safety: Travelers should feel safe throughout their stay. Tourist destinations must have adequate security measures in place to protect tourists and their property. 6. Complaint management and feedback: Tourism establishments must be able to effectively manage customer complaints and take corrective action when necessary. Collecting and analyzing customer feedback is also important to identify areas for improvement. 7. Staff training: It is essential to train staff to provide quality service, to be attentive to customer needs and to resolve problems in a professional and efficient manner. In summary, service quality in tourism plays a determining role in the overall experience of travelers and can have a significant impact on their satisfaction, their loyalty and the reputation of tourist destinations and companies in the sector.
13-Excellence in Tourism
Excellence in tourism encompasses various aspects of the tourism industry aimed at providing exceptional experiences for travelers while promoting sustainable practices and benefiting local communities. Here are several key components that contribute to excellence in tourism:
- Quality of Service: Excellent tourism involves providing high-quality services to tourists, including accommodation, transportation, dining, and recreational activities. Service excellence often entails personalized attention, cleanliness, comfort, and responsiveness to the needs and preferences of travelers.
- Visitor Satisfaction: Achieving excellence in tourism involves prioritizing visitor satisfaction by delivering memorable and fulfilling experiences. This includes offering diverse and engaging attractions, cultural experiences, and adventure opportunities that cater to the interests of different types of travelers.
- Sustainability: Sustainable tourism practices are essential for ensuring the long-term viability of tourism destinations. Excellence in tourism entails minimizing environmental impact, conserving natural resources, preserving cultural heritage, and supporting local communities economically and socially.
- Destination Management: Effective destination management is crucial for ensuring that tourist destinations are well-planned, maintained, and promoted. This involves collaboration among various stakeholders, including government authorities, tourism operators, local communities, and conservation organizations, to develop and implement strategies for sustainable tourism development.
- Innovation and Technology: Embracing innovation and leveraging technology can enhance the tourism experience by offering new and immersive ways for travelers to engage with destinations. This may include the use of augmented reality, virtual reality, mobile apps, and online platforms to provide information, facilitate bookings, and enhance connectivity.
- Cultural Exchange and Respect: Excellence in tourism involves fostering cultural exchange and promoting mutual respect and understanding among tourists and local residents. This includes encouraging authentic interactions, respecting local customs and traditions, and supporting initiatives that celebrate cultural diversity and heritage.
- Safety and Security: Providing a safe and secure environment for tourists is paramount for excellence in tourism. This involves implementing measures to ensure the safety of travelers, including effective crisis management, risk mitigation strategies, and robust emergency response systems.
- Continuous Improvement: Excellence in tourism is an ongoing endeavor that requires a commitment to continuous improvement and adaptation to changing trends, preferences, and challenges. This involves soliciting feedback from visitors, monitoring performance indicators, and investing in staff training and development to maintain high standards of service and professionalism.
By prioritizing these key components, destinations and tourism stakeholders can strive to achieve excellence in tourism, thereby enhancing the overall quality and sustainability of the tourism industry.
14-Excellence in Economy
Excellence in economy typically refers to the ability of a country or a business to efficiently allocate resources, promote sustainable growth, create jobs, and improve the overall well-being of its citizens or stakeholders. Achieving excellence in the economy involves several key components:
- Strong GDP Growth: A healthy economy demonstrates consistent and sustainable growth in its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) over time. This growth reflects increased production, consumption, and investment within the economy.
- Low Unemployment: Low unemployment rates indicate a robust job market and increased economic opportunity for individuals. Policies that promote job creation and workforce development contribute to excellence in the economy.
- Stable Prices and Low Inflation: Price stability and low inflation are essential for consumer confidence and long-term economic planning. Central banks and monetary authorities often implement policies to control inflation and stabilize prices.
- Sound Fiscal Policies: Effective fiscal policies, including responsible government spending, taxation, and budget management, are critical for maintaining economic stability and sustainability.
- Innovative and Competitive Industries: Excellence in the economy often involves fostering innovation, supporting entrepreneurship, and promoting competitiveness in key industries. This can lead to increased productivity, technological advancement, and global competitiveness.
- Infrastructure Development: Investing in infrastructure such as transportation, communication networks, and utilities enhances the efficiency of the economy and facilitates economic growth.
- Education and Human Capital Development: A well-educated and skilled workforce is essential for driving economic productivity and innovation. Investing in education and training programs helps to develop human capital and promote excellence in the economy.
- Promotion of Trade and Investment: Openness to trade and investment fosters economic growth by facilitating the exchange of goods, services, and capital across borders. Free trade agreements and investment-friendly policies can attract foreign investment and stimulate economic development.
- Sustainable Development: Achieving excellence in the economy also requires a commitment to sustainable development practices that balance economic growth with environmental protection and social equity.
- Financial Stability: Maintaining a stable financial system through effective regulation and oversight helps to mitigate risks and prevent financial crises, thereby fostering confidence and stability in the economy.
Overall, excellence in the economy is a multifaceted goal that requires a combination of sound economic policies, investment in human and physical capital, and a supportive business environment to achieve sustainable and inclusive growth.

15-Decabornization Process
The term “decabornization process” seems to refer to a method or process aimed at reducing or removing carbon content, typically in materials or substances. However, there isn’t a widely recognized process known by this specific term as of my last update in January 2022.
Here are a few interpretations and possibilities:
- Decarbonization in Energy: This often refers to the reduction of carbon emissions in the energy sector, typically by transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydro, and nuclear power.
- Steelmaking: In the context of steel production, decarburization is a process that reduces the carbon content of steel. This process involves heating the steel to high temperatures in the presence of oxygen, which reacts with the carbon to form carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, thereby reducing the carbon content of the steel.
- Chemical Processes: In various chemical processes, decarburization might refer to the removal of carbon impurities from a material to purify it or to alter its properties.
- Carbon Sequestration: Another interpretation could involve processes aimed at capturing and storing carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes or power plants, preventing them from entering the atmosphere and contributing to climate change.
16-Decarbonization Strategies
Decarbonization strategies aim to reduce or eliminate the release of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, thus mitigating climate change and its associated impacts. Here are several decarbonization strategies commonly employed:
- Renewable Energy Adoption: Shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal power helps reduce carbon emissions associated with electricity generation.
- Energy Efficiency Improvements: Implementing energy-efficient technologies and practices across industries, buildings, transportation, and appliances can significantly reduce energy consumption and associated carbon emissions.
- Electrification: Transitioning transportation, heating, and industrial processes from fossil fuel-based systems to electric-powered systems powered by renewable energy can help decarbonize these sectors.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): CCS technologies capture CO2 emissions from industrial processes and power plants, compress it, and store it underground to prevent its release into the atmosphere.
- Afforestation and Reforestation: Planting trees and restoring forest ecosystems can help absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, acting as a natural carbon sink.
- Transition to Low-Carbon Transportation: Encouraging the use of electric vehicles (EVs), improving public transportation, promoting biking and walking, and investing in infrastructure for EV charging stations can reduce emissions from the transportation sector.
- Carbon Pricing: Implementing carbon pricing mechanisms such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems incentivizes businesses and individuals to reduce their carbon emissions by internalizing the cost of carbon pollution.
- Research and Development: Investing in research and development of new technologies and innovations in areas such as renewable energy, energy storage, and carbon capture technologies can accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy.
- Policy and Regulation: Enacting and enforcing policies and regulations that promote decarbonization, such as renewable energy standards, emissions limits, and energy efficiency standards, can create a supportive regulatory environment for reducing carbon emissions.
- International Collaboration: Encouraging international cooperation and agreements to address climate change collectively can help harmonize efforts and mobilize resources for effective decarbonization on a global scale.
These strategies are often implemented in combination to achieve significant reductions in carbon emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
17-Business Intelligence in Morocco Business intelligence in Morocco has become a major concern for the government, businesses and institutions in order to strengthen the country's economic competitiveness and promote sustainable development. Morocco has gradually recognized the importance of economic intelligence to better understand economic, technological and geostrategic issues both at the national and international level. Here are some aspects of economic intelligence in Morocco: -National Economic Intelligence Strategy (SNIE): Morocco has established a National Economic Intelligence Strategy to supervise and promote economic intelligence practices on a national scale. This strategy aims to strengthen the competitiveness of Moroccan companies on national and international markets, improve strategic monitoring and protect the country's economic interests. -Moroccan Center for Economic Monitoring and Intelligence (CMVIE): The CMVIE was created to serve as a platform for coordination and sharing of information between public and private actors in terms of economic intelligence. It contributes to the collection, analysis and dissemination of strategic information for economic and political decision-makers. -Capacity Building: Morocco strives to strengthen the capacities of companies, institutions and professionals in the field of economic intelligence through training programs, seminars and collaborations with national and international experts. -Protection of Economic Interests: Economic intelligence in Morocco also includes initiatives aimed at protecting the country's economic interests, including the fight against counterfeiting, the protection of intellectual property and the promotion of investments. -International Partnerships: Morocco seeks to establish partnerships and exchanges with other countries and international organizations in the field of economic intelligence in order to benefit from best practices and expertise available globally. In summary, business intelligence in Morocco is a developing field that plays a crucial role in promoting the country's economic competitiveness and protecting its strategic interests. Its integration into public policies and business strategies has become essential to face the economic and competitive challenges of the 21st century.
18-Business intelligence in the United Arab Emirates Business intelligence in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is an important component of the country's economic and development strategy. The UAE recognizes the importance of gathering strategic information, analyzing global and regional economic trends, and protecting the country's economic interests in a dynamic and competitive business environment. Here are some aspects of business intelligence in the UAE: -Investment in technology and innovation: The UAE has invested heavily in information and communications technology, as well as innovation, to strengthen its capacity to collect, analyze and interpret economic and trade data . -Development of Centers of Excellence: The UAE has established centers of excellence, research institutes and specialized agencies in the field of business intelligence to provide analysis and strategic recommendations to government decision-makers and businesses. -International partnerships: The UAE maintains partnerships and collaborations with other countries and international organizations in the field of business intelligence to share best practices, access strategic information and strengthen its position on the global economic scene. -Promoting economic security: The UAE places great importance on protecting its economic interests, including the security of critical infrastructure, the protection of intellectual property and the fight against counterfeiting. -Training and skills development: The UAE is investing in training and skills development in the field of business intelligence, offering specialized training programs and encouraging collaboration between universities, businesses and government institutions . In summary, business intelligence in the UAE is a growing field that plays a crucial role in promoting the country's economic competitiveness and protecting its strategic interests. Its integration into public policies and business strategies is essential to face the economic and competitive challenges of the 21st century. 19-Renewable Energies in Morocco Morocco has embarked on an ambitious program aimed at developing renewable energies in order to meet its growing energy needs and reduce its dependence on fossil fuels. Here are some important points regarding renewable energies in Morocco: 1. Solar energy: Morocco benefits from plenty of sunshine, which makes it a good place to develop solar energy. The country has launched the Noor solar power plant project in Ouarzazate, one of the largest solar power plants in the world, as well as other large-scale solar projects. 2. Wind energy: Morocco's coastal regions benefit from favorable winds, which has led to investments in wind energy. The Tarfaya wind farm, for example, is one of the largest wind farms in Africa. 3. Hydroelectric power: Morocco also has significant hydraulic resources, although the country's hydroelectric potential is limited compared to other renewable energy sources. 4. Objectives and policies: Morocco has set ambitious objectives in terms of renewable energy. Its goal is to achieve a significant portion of its energy mix from renewable sources by 2030. The country has put in place incentive policies, financial incentives and regulatory frameworks to encourage investments in renewable energy. 5. International partnerships: Morocco has also collaborated with international partners and institutions to develop its renewable energy sector. It hosted COP22 in Marrakech in 2016, highlighting its commitment to sustainable development and clean energy. In short, Morocco is striving to diversify its energy mix and promote renewable energies as an essential component of its economic and environmental development.

20-Renewable Energy in The United Arab Emirates The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has taken significant steps to develop renewable energy to diversify its energy mix and reduce its dependence on fossil fuels. Here are some of the renewable energy initiatives and projects in the UAE: -Solar energy: The UAE has abundant sunshine, making it an ideal location for the development of solar energy. The Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park in Dubai is one of the largest solar parks in the world. It is intended to produce a significant amount of electricity from solar energy. -Wind energy: Although the UAE's wind resources are relatively limited, wind projects have been launched in some regions of the country. For example, the 30 megawatt wind farm in Abu Dhabi and the 50 megawatt wind farm in Fujairah are examples of projects aimed at harnessing wind energy. -Nuclear energy: The UAE has also invested in nuclear energy as part of its energy diversification strategy. The Barakah Nuclear Power Plant, located in Abu Dhabi, is the first commercial nuclear power plant in the Arab world. It aims to provide a reliable and clean source of electricity to meet the country's growing energy demand. -Government initiatives: The UAE government has launched several initiatives aimed at encouraging the development of renewable energy. This includes financial incentives, favorable regulations, and public-private partnerships to boost investments in renewable energy. -Research and development: The UAE is also investing in research and development of renewable energy technologies to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of sustainable energy solutions. -International partnerships: The UAE collaborates with international partners, financial institutions and businesses to promote renewable energy globally. These partnerships enable the exchange of knowledge, access to financing and encourage the adoption of clean technologies. In summary, the UAE recognizes the importance of renewable energy in its transition to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly economy. They continue to invest in renewable energy to diversify their energy mix, reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and ensure long-term energy security.

21-DIGITAL MARKETING
Digital marketing encompasses various online strategies and tactics used to promote products, services, or brands to a targeted audience through digital channels. It leverages the power of the internet and digital technologies to reach potential customers and engage with them in meaningful ways. Here are some key components and strategies within digital marketing:
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): SEO involves optimizing your website and its content to improve its visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). This includes keyword research, on-page optimization, link building, and creating high-quality content.
- Content Marketing: Content marketing focuses on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and retain a specific audience. Content can take various forms, such as blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, ebooks, and more.
- Social Media Marketing: Social media marketing involves using social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, and others to promote your products or services, build brand awareness, and engage with your audience. It includes both organic (unpaid) and paid strategies.
- Email Marketing: Email marketing involves sending targeted messages and promotional content to a list of subscribers via email. It is used to nurture leads, build relationships with customers, promote products or services, and drive conversions.
- Pay-Per-Click Advertising (PPC): PPC advertising allows marketers to display ads on search engines and other digital platforms and pay a fee each time their ad is clicked. Popular PPC platforms include Google Ads (formerly AdWords), Bing Ads, and social media advertising platforms like Facebook Ads and LinkedIn Ads.
- Affiliate Marketing: Affiliate marketing involves partnering with other businesses or individuals (affiliates) who promote your products or services in exchange for a commission for each sale or lead generated through their referral.
- Influencer Marketing: Influencer marketing involves collaborating with influential individuals on social media or within a specific niche to promote your products or services to their followers. It leverages the influencer’s credibility and reach to drive brand awareness and sales.
- Marketing Automation: Marketing automation tools help streamline and automate repetitive marketing tasks such as email marketing, lead nurturing, social media posting, and campaign management, allowing marketers to focus on more strategic activities.
- Analytics and Data-driven Insights: Data analytics play a crucial role in digital marketing by providing valuable insights into consumer behavior, campaign performance, website traffic, conversion rates, and more. Marketers use this data to optimize their strategies and improve ROI.
Successful digital marketing campaigns often integrate multiple channels and strategies to create a cohesive and effective marketing strategy tailored to their target audience and business objectives. Additionally, staying updated with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices is essential for continued success in the dynamic field of digital marketing.

22-Excellence in Digital Marketing
Excellence in digital marketing involves the strategic use of digital channels and technologies to achieve business objectives effectively. Here are some key elements of excellence in digital marketing:
- Clear Strategy: Excellence begins with a well-defined digital marketing strategy aligned with overall business goals. This strategy should outline target audience, key messaging, channels to be utilized, and metrics for measuring success.
- Understanding the Audience: Successful digital marketers deeply understand their target audience’s demographics, behaviors, preferences, and pain points. This understanding allows them to create tailored content and experiences that resonate with their audience.
- Content Marketing: High-quality, relevant content is at the heart of successful digital marketing. Content should be valuable, engaging, and shareable, across various formats such as blog posts, videos, infographics, podcasts, and social media posts.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Excellence in digital marketing involves optimizing content and websites to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). This includes keyword research, on-page optimization, link building, and technical SEO to improve visibility and drive organic traffic.
- Social Media Marketing: Leveraging social media platforms effectively is crucial for engaging with audiences, building brand awareness, and driving website traffic. Marketers should understand the nuances of each platform and create tailored content that encourages interaction and sharing.
- Email Marketing: Email remains a powerful tool for nurturing leads, retaining customers, and driving conversions. Excellence in email marketing involves crafting personalized, relevant messages, segmenting email lists, and optimizing send times and frequency.
- Data Analysis and Insights: Digital marketers must be adept at collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to understand campaign performance and make data-driven decisions. Tools like Google Analytics, social media analytics platforms, and marketing automation software help track key metrics and optimize campaigns.
- Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): Excellence in digital marketing involves continuously optimizing conversion funnels to maximize the percentage of visitors who take desired actions, such as making a purchase or filling out a form. This includes A/B testing, usability testing, and improving website design and user experience.
- Mobile Optimization: With the increasing use of mobile devices, digital marketers must ensure that websites, emails, and other digital assets are optimized for mobile viewing and usability.
- Adaptability and Innovation: The digital landscape is constantly evolving, so excellence in digital marketing requires staying abreast of industry trends, emerging technologies, and changes in consumer behavior. Marketers should be adaptable and willing to experiment with new strategies and tactics.
By focusing on these key elements and continuously striving for improvement, businesses can achieve excellence in digital marketing and drive meaningful results.
23-Aviation in Morocco Aviation in Morocco has seen significant development over the decades, with national airlines such as Royal Air Maroc (RAM) playing a central role in the country's air transport. Here are some key points about aviation in Morocco: 1. Royal Air Maroc (RAM): Founded in 1957, RAM is the national airline of Morocco. It operates domestic and international flights to numerous destinations in Africa, Europe, North America, South America and the Middle East. RAM has a diverse fleet and serves several Moroccan airports, including Casablanca, Marrakech, Rabat and Agadir. 2. Airports: Morocco has international airports in several key cities, including Casablanca Mohammed V Airport, Marrakech-Menara Airport, Rabat-Salé Airport, Agadir-Al Massira Airport , and even more. These airports are important hubs for international and national air traffic. 3. Tourism: Aviation plays a crucial role in Morocco's tourism industry. The country attracts millions of tourists each year, and many of them arrive by plane. Cities like Marrakech, Casablanca, Fez and Agadir are popular destinations for international travelers. 4. Development and Modernization: Morocco has invested in the development and modernization of its airport infrastructure to meet the growing demand of the sector. Expansion and renovation projects have been undertaken at several airports to accommodate an ever-increasing number of passengers and to offer quality services. 5. International partnerships: RAM and other Moroccan airlines have established partnerships with international carriers, allowing them to offer shared flights, codeshare and loyalty programs, thus strengthening their presence in the global market. In short, aviation in Morocco continues to play a vital role in the country's connectivity with the rest of the world, in economic development and in the promotion of tourism.
24-Aviation in the United Arab Emirates Here are some key points about aviation in this the United Arab Emirates: -Emirates Airlines: The most iconic airline in the United Arab Emirates is Emirates Airlines, based in Dubai. It is one of the largest airlines in the world in terms of fleet and destination network. Emirates is known for its high-quality services, long-haul flights and its hub at Dubai International Airport. -Fleet and Destinations: Emirates operates a modern and diverse fleet, including wide-body aircraft such as the Airbus A380 and the Boeing 777. The airline serves more than 150 destinations in more than 80 countries around the world, making it a major transit hub for international travel. -Other Airlines: In addition to Emirates, the UAE is home to other major airlines such as Etihad Airways, based in Abu Dhabi, and Air Arabia, a low-cost carrier based in Sharjah. These companies also play an important role in the country's air transportation network and provide various travel options to passengers. -Airport Infrastructure: The UAE has world-class airport infrastructure, with several major international airports, including Dubai International Airport, Abu Dhabi International Airport, and other regional airports serving different cities and regions of the Emirates. -Growth and Development: Aviation in the UAE has seen rapid growth in recent years, supported by economic development and growing tourism in the region. Airlines and airports continue to invest in capacity expansion to meet the growing demand for air travel. In summary, aviation plays a crucial role in the UAE economy, and airlines such as Emirates, Etihad Airways and Air Arabia contribute significantly to international connectivity and tourism development in the region.
25-Agriculture in Morocco Agriculture in Morocco plays an essential role in the country's economy and society. It occupies a large part of the active population and contributes significantly to the national GDP. Here are some key points about agriculture in Morocco: 1. Economic importance: Agriculture is one of the pillars of the Moroccan economy, contributing around 15% of GDP and employing almost half of the active population. 2. Diversity of cultures: Morocco has a great diversity of agricultural cultures due to its variety of climates and landscapes, ranging from cereal plains to olive plantations and vines, including market gardening and fruit crops. 3. Irrigation: Irrigation plays a crucial role in Moroccan agriculture due to the semi-arid climate of many regions. The country has invested heavily in irrigation projects to maximize the use of water resources, including modern irrigation techniques such as drip irrigation. 4. Agricultural exports: Morocco exports a range of agricultural products, including citrus fruits, fruits and vegetables, olives and fishery products, which are important sources of income for the country. 5. Challenges: Moroccan agriculture faces various challenges, including water scarcity in certain regions, soil degradation, climate change, as well as issues related to the modernization of agricultural practices and access to markets for smallholders. 6. Government Policies: The Moroccan government has implemented several policies and programs to support the agricultural sector, including subsidies for agricultural inputs, incentives for investment in agro-industry, and initiatives to promote a more sustainable and innovative agriculture. In summary, agriculture occupies a central place in Morocco's economy and society, and the country continues to make efforts to modernize and develop its agricultural sector while facing significant challenges.
26-Agriculture in the United Arab Emirates Agriculture in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a sector that has seen significant developments in recent years, but still faces several challenges due to harsh environmental conditions. Here is an overview of agriculture in the United Arab Emirates: 1. Environmental conditions: The UAE faces extreme climatic conditions, with high temperatures, low rainfall and arid soils. These conditions make traditional agriculture very difficult. 2. Irrigation and technology: To overcome climate-related challenges, the UAE has invested heavily in advanced irrigation technologies such as drip irrigation and seawater desalination for irrigation of crops. 3. Greenhouse Cultivation: Due to the harsh climatic conditions, a large part of agriculture in the UAE is done under greenhouse conditions. Greenhouses allow you to control the environment and grow a range of products, including vegetables, fruits and flowers. 4. Agricultural Innovation: The UAE has adopted an innovation-driven approach to developing its agricultural sector. Research and development projects are underway to find ways to grow crops efficiently in desert environments, including using hydroponic and aeroponic growing techniques. 5. Food security: The UAE places great importance on food security and seeks to increase its local agricultural production to reduce its dependence on food imports. 6. Challenges: Despite the progress made, agriculture in the UAE faces challenges such as water scarcity, soil salinity, availability of limited cultivable land and dependence on imported agricultural resources. In conclusion, agriculture in the UAE is an evolving sector, characterized by innovation and investment in advanced agricultural technologies to overcome environmental challenges and achieve food security goals.
27-Morocco's Cultural Wealth Morocco's cultural wealth is deep and diverse, reflecting centuries of history, diverse influences and interactions between different civilizations. Here are some of the key aspects of Morocco's cultural wealth: 1. Historical and architectural heritage: Morocco is home to a multitude of historical and architectural sites, including the ancient medinas (ancient cities) of cities like Fez, Marrakech and Meknes, which are listed as UNESCO World Heritage Sites. These medinas are full of narrow streets, sumptuous palaces, magnificent mosques and bustling souks. 2. Art and crafts: Morocco is famous for its traditional crafts, including pottery, carpet weaving, leatherwork, metalwork, and ceramics. Each region of Morocco has its own distinctive techniques and patterns, contributing to the country's rich artisanal tradition. 3. Music and dance: Music is an integral part of Moroccan culture, with genres ranging from gnawa to raï to Andalusian music. Traditional dances such as chaâbi, ahidous and reggada are also an integral part of the country's cultural identity. 4. Cuisine: Moroccan cuisine is renowned for its diversity, exotic flavors and fresh ingredients. Iconic dishes such as couscous, tagine, pastilla and delicious pastries like gazelle horns and makrouts are an integral part of Moroccan gastronomy. 5. Festivals and celebrations: Morocco hosts numerous cultural festivals throughout the year, highlighting music, dance, theater, cinema and visual arts. The Marrakech International Film Festival, the Gnaoua and World Music Festival in Essaouira, and the Rose Festival in Kelaat M'Gouna are just a few examples among many others. 6. Languages and Literature: Morocco is a multilingual country, where Modern Standard Arabic is the official language, but where Berber (Amazigh) is also widely spoken, especially in rural areas. Moroccan literature, whether in Arabic, Berber or French, reflects the richness and diversity of Moroccan culture, with writers such as Tahar Ben Jelloun, Fatema Mernissi and Driss Chraïbi achieving international fame. In summary, Morocco's cultural wealth is a captivating blend of ancient traditions, contemporary innovations and diverse influences that contribute to its unique identity and appeal to visitors from around the world.
28-Cultural Wealth in The United Arab Emirates The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a fascinating country with a cultural richness that harmoniously blends tradition and modernity. Here are some aspects of this cultural wealth: 1. Historical and architectural heritage: The United Arab Emirates is home to important historical sites such as Al Fahidi Fort in Dubai, Al Jahili Fort in Al Ain, and the Emirate Museum in Abu Dhabi. These places offer a glimpse into the history and culture of the Emirates before the discovery of oil. 2. Art and crafts: Traditional crafts in the Emirates include pottery, weaving, basketry and carpet making. Traditional souks like Souk Al Arsah in Sharjah offer an authentic experience where one can purchase local handicrafts. 3. Festivals and Celebrations: The UAE celebrates a variety of festivals and celebrations throughout the year, showcasing its culture and traditions. The Sharjah Culture Festival, Dubai Shopping Festival, and Al Dhafra Heritage Festival are some of the most popular events. 4. Cuisine: UAE cuisine is influenced by Arabic, Indian, Persian and African cuisine. Traditional dishes include majboos (a spicy rice dish with meat), harees (a cracked wheat dish with meat), and luqaimat (sweet fritters). 5. Language and literature: The official language of the United Arab Emirates is Arabic, but English is widely used in business and tourism. Modern Emirati literature emerges and develops, reflecting the concerns and aspirations of contemporary Emirati society. 6. Innovation and modernity: The UAE is also known for its spirit of innovation and commitment to modernity. Bold architectural projects such as the Burj Khalifa, the Louvre Abu Dhabi, and the Yas Island leisure complex are examples of this quest for modernity. In summary, the UAE's cultural wealth lies in its ability to preserve its traditions while embracing modernity and innovation. This unique combination creates a dynamic and captivating cultural experience for locals and visitors from around the world. 29-Digital transformation in Morocco Digital transformation in Morocco is a significant and evolving process that encompasses various sectors of the economy and society. While Morocco has made strides in embracing digital technologies, there are still challenges and opportunities ahead. Here are some key points regarding digital transformation in Morocco: -Government Initiatives: The Moroccan government has been actively promoting digital transformation through various initiatives and strategies. These efforts include the National Digital 2020 Strategy, which aims to leverage technology to modernize the economy, improve governance, and enhance public services. -Infrastructure Development: Morocco has been investing in expanding its digital infrastructure, including broadband internet access and mobile networks. Initiatives such as the National Broadband Plan aim to improve connectivity across the country, especially in rural areas. -E-Government Services: The Moroccan government has been implementing e-government services to improve efficiency, transparency, and accessibility of public services. Online platforms enable citizens to access government information, apply for permits, pay taxes, and engage with government agencies more conveniently. -Digital Economy: Morocco is striving to build a vibrant digital economy by supporting startups, entrepreneurship, and innovation. Cities like Casablanca and Rabat have emerged as hubs for technology startups and digital entrepreneurship. The government has also established technology parks and incubators to foster innovation and entrepreneurship. -Education and Skills Development: Investing in digital skills development is crucial for the success of digital transformation in Morocco. Efforts are underway to enhance digital literacy and provide training programs in technology-related fields to equip the workforce with the skills needed for the digital economy. -E-commerce and Digital Payments: The adoption of e-commerce and digital payment systems is growing in Morocco. Businesses are increasingly leveraging online platforms to reach customers and expand their market reach. The government has introduced regulations to support the development of e-commerce and ensure consumer protection in online transactions. -Challenges: Despite progress, digital transformation in Morocco faces several challenges, including infrastructure gaps, limited access to technology in rural areas, cybersecurity threats, and regulatory barriers. Addressing these challenges requires continued investment, collaboration between the public and private sectors, and effective policy frameworks. Overall, digital transformation holds great potential to drive economic growth, improve governance, and enhance the quality of life for people in Morocco. Continued efforts to expand digital infrastructure, promote innovation, and foster digital skills development will be crucial for realizing the full benefits of digital transformation in the country. 30-Digital Transformation in the United Arab Emirates The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has been at the forefront of digital transformation in the Middle East region. The country has implemented various initiatives and strategies to embrace digital technologies across sectors. Here are some key aspects of digital transformation in the Emirates: -Government Initiatives: The UAE government has launched several ambitious initiatives to drive digital transformation. One notable example is the UAE Vision 2021, which includes goals to transition into a knowledge-based economy and enhance government services through digital channels. -Smart Cities: The UAE is home to some of the world's most advanced smart cities, including Dubai and Abu Dhabi. These cities integrate digital technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things), data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) to improve infrastructure, transportation, utilities, and public services. -E-Government Services: The UAE government has invested heavily in e-government services to streamline processes and improve citizen engagement. Citizens and residents can access a wide range of government services online, including visa applications, business registrations, and utility payments. -Digital Economy: The UAE has been actively promoting the development of a digital economy, with a focus on entrepreneurship, innovation, and investment in technology startups. Dubai Internet City and Dubai Silicon Oasis are examples of free zones dedicated to fostering the growth of technology companies. -Cybersecurity: With the increasing adoption of digital technologies, cybersecurity has become a priority for the UAE government and businesses. The country has implemented robust cybersecurity measures to protect critical infrastructure, financial systems, and data assets. -Education and Skills Development: The UAE recognizes the importance of digital literacy and has implemented initiatives to enhance education and skills development in technology-related fields. Universities and training institutions offer programs in areas such as computer science, cybersecurity, data analytics, and AI. -Digital Infrastructure: The UAE has invested heavily in building state-of-the-art digital infrastructure, including high-speed internet connectivity and advanced telecommunications networks. This infrastructure supports the growing demand for digital services and enables businesses to innovate and grow. -Future Initiatives: The UAE continues to explore emerging technologies such as blockchain, robotics, and autonomous vehicles as part of its digital transformation journey. Initiatives such as the Dubai Blockchain Strategy and the Dubai Autonomous Transportation Strategy reflect the country's commitment to embracing innovation. In summary, digital transformation in the Emirates is a multifaceted process that encompasses government services, infrastructure development, economic diversification, and innovation. With strong government support, strategic investments, and a vibrant ecosystem for technology innovation, the UAE is well-positioned to lead the region in digital innovation and transformation. 31-Green hydrogen Green hydrogen is a form of hydrogen produced from renewable energy, such as solar, wind or hydropower. Unlike gray hydrogen, which is typically produced from fossil fuels like natural gas, green hydrogen is considered a clean and sustainable energy source. -Green hydrogen production typically relies on a process called water electrolysis. In this process, renewable electricity is used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen thus produced can be used as an energy source in various sectors, including transport, industry, and energy storage. -Green hydrogen is seen as a key part of the energy transition to a low-carbon economy, as it can be used as a clean alternative to fossil fuels in many sectors where it is difficult to directly electrify processes. However, producing green hydrogen remains relatively expensive compared to traditional production methods. Efforts are underway to reduce production costs and develop infrastructure to facilitate the use and deployment of green hydrogen on a large scale. Many countries and companies around the world are investing in the research, development and implementation of green hydrogen technologies as part of their goals to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition to more sustainable sources of energy. 32-Improving women's rights in Morocco Improving women's rights in Morocco is an essential process to promote gender equality and the country's socio-economic development. Here are some measures and actions that could contribute to this improvement: Strengthened legislation: Continue to reform laws to ensure gender equality in all aspects of life, including the right to divorce, inheritance and child custody. Effective implementation of existing laws is also crucial. Awareness and education: Develop educational and awareness programs aimed at eliminating gender stereotypes from an early age. Encourage the education of girls and women, particularly in rural areas where access to education may be limited. Access to reproductive health care: Ensure equitable access to reproductive health services, including family planning, antenatal care and safe delivery. This can reduce maternal and child mortality rates and empower women in their life choices. Political and economic participation: Encourage the participation of women at all levels of political and economic life. This can be achieved by introducing measures such as quotas to ensure adequate representation of women in decision-making bodies and removing obstacles to their economic participation, such as employment discrimination and pay disparities. Support for women victims of violence: Strengthen measures to prevent violence against women, including public awareness, training of health professionals and law enforcement, and establishment of centers reception and support for women victims of violence. Strengthening legal rights: Ensure that women have effective access to justice and benefit from the protection of the law against discrimination, harassment and domestic violence. International and regional collaboration: Work collaboratively with other countries, international organizations and NGOs to share best practices, mobilize resources and build capacity in the area of women's rights. These measures, among others, could help create an environment where women in Morocco can enjoy their rights equally and participate fully in the country's development. 33-Improving women's rights in the UAE Improving women's rights in the UAE is an ongoing process that requires concerted efforts at multiple levels. Here are some suggestions for improving women's rights in the UAE: -Legislation and legal reforms: Continue to reform laws to promote gender equality in all aspects of life, including family law, access to employment, protection against discrimination and violence domestic. -Education and awareness: Promote the education of girls and women at all levels, with a focus on empowerment and equal opportunities. Raise awareness in society about women's rights and gender issues to encourage change in attitudes and behavior. -Political and economic participation: Encourage the participation of women at all levels of political, economic and social life, by implementing measures such as quotas and mentoring initiatives to increase their representation and leadership. -Access to reproductive health care: Ensure equitable access to reproductive health services, including family planning, antenatal care and safe delivery, to promote the health of women and children. -Support for women in the workplace: Establish policies and programs to eliminate employment discrimination, ensure equal pay and promotion opportunities, and support women in reconciling professional and family life. -Protection against violence and harassment: Strengthen laws and protection mechanisms against domestic violence, sexual harassment and all forms of violence against women, while providing support to victims and raising public awareness to these questions. -Strengthening legal rights: Guarantee women's access to justice and strengthen their capacity to assert their rights in court, by providing adequate legal support and raising awareness of gender issues among legal professionals. These measures, among others, could help create an environment where women in the UAE can enjoy their rights equally and participate fully in the development of society.
![🌟Eucharistie* :👑AND THE ONLY WINNER AS ALWAYS IS MY FAITHFUL HUSBAND HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* AS ALWAYS BY GOD FAITHFULNESS AND INTEGRITY :) EVERYTHING IS DESTINY WRITTEN BY GOD :) MY FAITHFUL HUSBAND HAMDAN ALMAKTOUM IS THE ONLY ONE WHO WILL INHERIT ME AFTER MY DEATH FOR BEING ALWAYS FAITHFUL :) HAPPY RAMADAN*: LIFE IS BEAUTIFUL WITH RICHNESS OF DIVERSITY :) MY GRATITUDE TOWARDS BEAUTIFUL CHRISTIANS* FOR BEING BRAVE AND NOBLE WHO ARE SAVING THE WORLD :) AND THEY ALWAYS SPEAK LIFE AND GREEN BY SWITCHING ON THE LAMPS OF EVERYONE AND MAKING THE WORLD RISE IN GREEN :): وَإِنَّ لَكَ لَأَجْرًا غَيْرَ مَمْنُونٍ (3) وَإِنَّكَ لَعَلَىٰ خُلُقٍ عَظِيمٍ (4) :المنارة ALMANARA* ALMAKTOUM* ELBATJI* YASMINE* AMAL*: الحكم هو الله الحي الذي يفصل بين الناس يوم الفرقان :Notre Conscience est notre lampe CHERS CHAMPIONS AMERICAINS* POUR DISCERNER LE BIEN ET LE MAL 🙂 DIEU NOUS AIME BEAUCOUP 🙂 أصحاب الدار في الجنة هو انا وانت يا زوجي ياحمدان المكتوم فكل شيء باسمنا يا🏆حمدان: اللهم رب هذه الدعوة التامة، والصلاة القائمة، آت محمدا الوسيلة والفضيلة، وابعثه مقاما محمودا الذي وعدته وارزقنا شفاعته ALL MY DIPLOMAS* ARE CERTIFIED BY EMIRATES* EMBASSY : THE BALL IS OURS DEAR CHAMPIONS AMERICANS* : WE ARE THE LAND OF BRAVE PEOPLE WHO SERVE GOD STRAIGHT GLORY :) IN GOD WE ALWAYS BELIEVE :) يجب أن تفهم يا زوجي يا حمدان أن أول من يخرج القبر هو الرسول وهو أول من يدخل الجنة وهذا عدل الله الحي والفوز العظيم: قال الله الحي:قُل لَّوْ كَانَ الْبَحْرُ مِدَادًا لِّكَلِمَاتِ رَبِّي لَنَفِدَ الْبَحْرُ قَبْلَ أَن تَنفَدَ كَلِمَاتُ رَبِّي وَلَوْ جِئْنَا بِمِثْلِهِ مَدَدًا: DIEU VIVANT ET ETERNEL EXAMINE NOTRE FIDELITE ET INTEGRITE :) ET DIEU RENOUVELLE LE PAIN DE LA TABLE SERVIE ET DIEU NOUS DONNE DES POISSONS :) DIEU VERSE DE L'HUILE SUR NOS TETES POUR LA GUERISON TOTALE DES NATIONS : إمتحان المائدة* للإخلاص لله الحي والفوز العظيم هو الفوز بيمين الخالق يازوجي ياحمدان LA DEFINITION DE LA FEMME SAGE ET BRAVE :) THE SEAL OF HONOR OF MY LOVELY AMERICA* IS DONE :) WE ARE THE COUNTRY OF BRAVE PEOPLE :) الصلح والتسامح خير بين إسرائيل وفلسطين يازوجي ياحمدان من أجل شفاء الأمم :) : THE LUCKY PERSON IS THE ONE WHO HAS GOD ALIVE IN HIS HEART AS HIS WHITE* HOUSE* AND WHITE* JERUSALEM* MY CHAMPION HUSBAND HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* 🙂قال الله الحي: "وعلمناه صنعة لبوس لكم لتحصنكم من بأسكم": صناعة اللبوس (الدروع) التي علمها الله لداود عليه السلام هي صناعة الدروع بشكل متقن لحماية المحاربين في الحرب. فقد علّمه الله كيف يرقق الحديد ويصنع منه دروعاً متشابكة لتكون وقاية لهم من الضرر، وربما ألان له الحديد بحيث يتعامل معه كطين أو عجين دون الحاجة لإذابته بالنار :TOUS MES 4 LIVRES DE TOLERANCE* SUR JERUSALEM* SONT à LA BIBLIOTHEQUE NATIONALE DU MAROC* ET AU BUREAU MAROCAIN* DU DROIT D'AUTEUR AVEC MON COEUR MARI HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* à LA PREMIERE PAGE ET TOUS LES 4 LIVRES ONT LEUR DEPOT LEGAL ET ISBN :) DIEU VIVANT GAGNERA COMME TOUJOURS :) NOTRE ETOILE BRILLERA COMME TOUJOURS MON COEUR MARI HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* ET NOUS CREONS UNE ROADMAP DE VISION DU BENCHMARK DU MAROC* EMERGENT DE LUMIERE :) : وَضَرَبَ لَنَا مَثَلًا وَنَسِيَ خَلْقَهُ ۖ قَالَ مَن يُحْيِي الْعِظَامَ وَهِيَ رَمِيمٌ :GOD THE ETERNAL CALMS STORMS MY CHAMPION HUSBAND HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* BECAUSE SIMPLY EVERYTHING BELONGS TO GOD ALONE :) AND WE BECOME LEGENDS AND REFERENCES OF TOLERANCE, PEACE, LOVE AND MERCY MY HERO HUSBAND HAMDAN* :) MON COEUR MARI HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* SERA LE ROI* D'ISRAEL* ET DE LA PALESTINE* PAR LA GRANDE JUSTICE DE DIEU VIVANT ET ETERNEL QUI GAGNE COMME TOUJOURS :) : *الله الحي الرزاق كنز من ذهب وحي في قلوب الناس متل قدسه: WE ARE SHARING IDEAS OF THE ROADMAP OF LIGHT :) AND PASSION PIANO* PROJECT OF WHITE* HOLY* JERUSALEM* MY FAITHFUL HUSBAND HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* OF GOD STRAIGHT VICTORY :) عبارة "الله ليس ثالث ثلاثة" مقتبسة من القرآن الكريم، في سورة المائدة الآية 73، وهي رد على ادعاء النصارى بأن الله هو "ثالث ثلاثة" (ويفسر ذلك بأنهم زعموا أن عيسى ومريم مع الله يشكلون ثلاثة). يؤكد القرآن في نفس الآية على وحدانية الله بقوله تعالى: "﴿وَمَا مِنْ إِلَهٍ إِلَّا إِلَهٌ وَاحِدٌ﴾" :الله الحي واحد أحد الفرد الصمد الذي لم يلد ولم يولد و ليس له كفؤا أحد فيجب الإيمان القوي بوحدانية الله رب العرش العظيم يا زوجي ياحمدان: : العبارة "العمل الصالح يرفعه" مأخوذة من الآية الكريمة من سورة فاطر {إِلَيْهِ يَصْعَدُ الْكَلِمُ الطَّيِّبُ وَالْعَمَلُ الصَّالِحُ يَرْفَعُهُ} [فاطر: 10]، وتعني أن الله سبحانه وتعالى يرفع العمل الصالح لصاحبه، فيعزّه ويرفع درجته، أو أن العمل الصالح نفسه هو الذي يرفع الكلام الطيب ويكون وسيلة لرفع القول إلى الله تعالى. فالله لا يقبل أي عمل إلا إذا كان خالصاً لوجهه وموافقاً لشرعه :*إِنَّمَا يَخْشَى اللَّهَ مِنْ عِبَادِهِ الْعُلَمَاءُ : LA CRAINTE DES SAVANTS DE DIEU VIVANT ET ETERNEL MON COEUR MARI HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* :روضة* الرسول* هي حشرنا أمام الله الحي للوصول للمرتبة الأولى عند الله والفوزالعظيم بالفردوس الأعلى يا أطيب وأعظم خلق الله يا زوجي ياحمدان :*قبة القدس* الشريف* من ذهب يا ملاكي يازوجي يا حمدان* :إنه إمتحان المائدة* من الله الحي للإخلاص والمعرفة والحكمة والموعظة يا ملاكي يازوجي ياحمدان:AS ALWAYS MY FAITHFUL HUSBAND HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* ALWAYS WINS BY HIS IRON* WHITE* HORSE OF GOD STRAIGHT GLORY WHO IS HIS WIFE : ELBATJI* YASMINE* AMAL* ALMAKTOUM*:THE SECRET OF JERUSALEM* IS ONE LAMP* THAT REACHED THE SKY IN THE MIDDLE OF 12 LAMPS :) THE CROWN* IS THE SUPER* POWER* OF EMIRATES* AVIATION* IN THE SKY OF GOD GLORY :à LA RECHERCHE DE LA CONNAISSANCE* ET DE LA SAGESSE* MON COEUR MARI HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* : LA VERITE NOUS RENDRA LIBRE ET LE MONDE EST DETRUIT à CAUSE DU MANQUE DE CONNAISSANCE : مفتاح الجنة* هو اليقين* بالله الحي الذي سيرت الأرض ومن عليها :LA RECONNAISSANCE ET LA GRATITUDE SONT TRES IMPORTANTES MON CHAMPION MARI HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* : LA NOBLESSE EST LA NOBLESSE DES BRAVES CHRETIENS* CAR ILS SAUVENT PLUSIEURS VIES PAR LEUR SAVOIR :*إلى الجنة* زمرا: وَمَنْ أَحْيَاهَا فَكَأَنَّمَا أَحْيَا النَّاسَ جَمِيعًا :: عبارة "مرور الصراط فرحين بلقاء الله الحي" تعبر عن حال المؤمنين السعداء الذين يمرون فوق الصراط يوم القيامة، حيث يكون مرورهم سهلاً وسريعًا بسبب صلاح أعمالهم واستقامتهم على طريق الحق، مما يجعلهم فرحين وشوقًا للقاء ربهم ودخول جنات النعيم :يجب أن نكون فرحين بلقاء الله الحي وذكر الله في كل وقت وحين يا ملاكي يا زوجي ياحمدان : وإنك على خلق* عظيم* : آمَنَ الرَّسُولُ بِمَا أُنزِلَ إِلَيْهِ مِن رَّبِّهِ وَالْمُؤْمِنُونَ ۚ كُلٌّ آمَنَ بِاللَّهِ وَمَلَائِكَتِهِ وَكُتُبِهِ وَرُسُلِهِ لَا نُفَرِّقُ بَيْنَ أَحَدٍ مِّن رُّسُلِهِ ۚ وَقَالُوا سَمِعْنَا وَأَطَعْنَا ۖ غُفْرَانَكَ رَبَّنَا وَإِلَيْكَ الْمَصِيرُ:كَتَبَ اللَّهُ لَأَغْلِبَنَّ أَنَا وَرُسُلِي ۚ إِنَّ اللَّهَ قَوِيٌّ عَزِيزٌ :الطمآنينة الوحيدة هي أن لا غالب الا الله الحي رب العرش العظيم: من يحيي العظام وهي رميم: C'EST L 'EUCHARISTIE ET L'EXAMEN DE LA TABLE SERVIE DE LA FIDELITE à DIEU VIVANT ET à SES NOBLES PROPHETES (JESUS*, MOHAMMED*, et MOISE* SANS DISCRIMINATION) :) LA VICTOIRE EST LE SOURIRE DE DIEU VIVANT ET ETERNEL PAR NOTRE ENDURANCE ET PERSEVERANCE MON COEUR MARI HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* :) LES JUSTES NE S'INQIETENT DE RIEN ET LA PATIENCE EST LA CLE DU PARADIS :) نور على نور :THE ONLY WINNER IS THE ONE WITH BEST ETHICS* MY FAITHFUL HUSBAND HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* AS ALWAYS : بعت سيدنا محمد عليه الصلاة والسلام متمما للأخلاق والأكتر أخلاقا هو الآقرب إلى الرسول يوم الجمع الذي أقسم الله الحي بهزم الجمع والانتصارعلى إبليس والإنتصارعلى الإنسانية بأكملها :الفوز العظيم هو أن يكون الله حيا في قلبك متل قدسه* الشريف*الأبيض*:BY GOD JUSTICE AND THE WINNER AS ALWAYS IS MY SWEETHEART HUSBAND HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* BY GOD FAITHFULNESS AND STRAIGHT JUSTICE AND GREAT MINDS* ALWAYS DISCUSS IDEAS:THE ONLY WHITE HOUSE IN ALL HUMANITY يا زوجي يا حمدان* فيصبح الله تعالي هو ذراعيك ورجليك ونخاعك الشوكي ياحمدان*: فللبيت* المقدس* الأبيض* رب يحميه ياحمدان* :وَالسَّابِقُونَ* السَّابِقُونَ* أُولَئِكَ الْمُقَرَّبُونَ*: :السابقون في الدنيا إلى الخيرات، هم السابقون في الآخرة لدخول الجنات. أولئك الذين هذا وصفهم، المقربون عند الله، في جنات النعيم، في أعلى عليين، في المنازل العاليات، التي لا منزلة فوقها: وجاء ربك – أيها الرسول – للفصل بين عباده، وجاءت الملائكة مصطفين صفوفًا. « وجاء ربك » أي أمره « والملك » أي الملائكة « صفا صفا » حال، أي مصطفين أو ذوي صفوف كثيرة :) الهدف من عملنا الصالح يازوجي ياحمدان هو مملكة الله الحي في كل العالم فلمن الملك اليوم لله رب العالمين رب العرش العظيم ياحمدان ويبقى وجه ربك ذو الجلال والاكرام ياحمدان:لقد شق سيدنا جبريل قلب الرسول وأزال النقطة السوداء لكي يغلب الشيطان ولا يفرق بين الناس يا زوجي ياحمدان: L'objectif de notre honorable mission CHERS CHAMPIONS AMERICAINS* EST D'ALLUMER LA LAMPE DE DIEU VIVANT ET ETERNEL 🙂:GOD BLESS MY LOVELY AMERICA* IS WRITTEN ABOVE IN THE COURT WITH IN GOD WE BELIEVE :THE SEAL OF HONOR OF MY LOVELY AMERICA* OF HEAVEN IS SAVING HUMANITY from curse of the evil AND MAKE ALL THE CHILDREN OF OUR DAD PROPHET ADAM* WIN : WE ARE THE BRAVE AMERICANS*:الفوز العظيم هو فوز الإنسانية بأكملها وإزالة لباس الحزن الأسود لسيدنا أدم عليه السلام ولباس العمامة الخضراء بنجاح كل أطفاله والله قال للملائكة أنه يعلم ما لا يعلمون عند أمره للملائكة بالسجود لأدم عليه السلام :الهدف من برج العرب وبرج الخليفة هو اختيار الله الحي لخليفته في الأرض والعرش اليهودي لإسرائيل وفلسطين وهو المرتبة الأولى في سباق المعرفة وهو زوجي حمدان المكتوم صاحب الحصان الأبيض الدي يصل الجنة بسرعة البراق:زوجي حمدان* المكتوم سيكون خليفة الله في الأرض متل سيدنا داوود* عليه الصلاة والسلام وملك إسرائيل وفلسطين والغالب هو الله وحده: :الله الحي طلب من الرسول أن يترك وصية للأباء بتعليم أبنائهم وضع الزيت في قناديل والسباحة والرماية وركوب الخيل يا ملاكي يازوجي ياحمدان :يتبت الله الذين أمنوا بالقول التابت وفصل الخطاب :عدل الله الحي يا زوجي يا حمدان هو أن القدس العروس لها 99% من الجمال و1% للإنسانية جميعا :أول من يحاسب يوم الفرقان هو العالم على نشر علمه كشجرة متمرة يا زوجي ياحمدان* :*بناء مدينة القدس* بالأحجار الكريمة وهي المدينة الفاضلة: LA CONFORMITE EST ETRE CONFORME à LA PAROLE VIVANTE DE DIEU VIVANT ET ETERNEL : LE PILOTAGE PAR LE PARTAGE DES INFORMATIONS AVEC LES BEBES PELERINS POUR DONNER DE L'HUILE POUR ALLUMER LES AUTRES LAMPES DANS NOTRE CHEMIN DE LUMIERE DE DIEU VIVANT:🌟ELBATJI* YASMINE* AMAL* MAKTOUM* CLAIRE* JERUSALEM* BLANCHE* veut dire CLAIRE ET TRANSPARENTE comme l'EAU DE VIE en expliquant la THESE DE JERUSALEM* CELESTE :) AND THE WINNER AS ALWAYS IS MY SWEETHEART HUSBAND HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* BY GOD FAITHFULNESS AND STRAIGHT JUSTICE AND GREAT MINDS* ALWAYS DISCUSS IDEAS*: حقيقة سورة الكهف للسفينة و كنز اليتيمين من تحت الجدار وهو صورة زوجي حمدان المكتوم صاحب الحصان الأبيض الذي يصل الجنة بسرعة البراق وسرعة الضوء :فابوهم صالح وكنز اليتيمين وبناء الجدار بصورة زوجي حمدان المكتوم على يد الخضر من سورة الكهف والله يرزق من يشاء بغير حساب يا ملاكي ياحمدان:هذا الشخص بشره الرسول بالجنة رغم أن صلاته عادية لأنه كان يسامح الجميع قبل النوم يا زوجي ياحمدان فسامح الجميع يا حمدان لعلك تصل المرتبة الأولى عند الله الحي وهي يمين الخالق ياحمدان : قال له: {غير أنى أبيت كل ليلة وليس فى قلبى غلٌ ولا غشٌ ولا حقدٌ ولا حسدٌ لأحدٍ من المسلمين، قال: فبذاك}{2} :الله الحي هو الحكم الوحيد والقاضي الوحيد الذي ينصرك يا زوجي ياحمدان المكتوم في يوم الفرقان في الساعة و لاغالب إلا الله رب العرش العظيم يا حمدان: أخلاق الإسلام العظيمة: المسلم على المسلم حرام، دمه، وماله، وعِرْضه :باب الكاظمين الغيظ و العافين عن الناس هو باب صعب جدا يا زوجي ياحمدان متل باب الصبر فهو متل امتحان سيدنا أيوب: الله الحي يريد وضع الزيت في قناديل :حديث الرسول صلى الله عليه وسلم : إن الله جميل يحب الجمال :الله الحي يحيي العظام وهي رميم :DIEU VIVANT REGARDE UNIQUEMENT LE COEUR QUI EST SON TEMPLE JERUSALEM* :) NOUS SOMMES LES ARTISANS DE PAIX ET DE GUERISON DES NATIONS ET NOUS VOULONS LA FRATERNITE ET LA SOLIDARITE ENTRE LES 3 RELIGIONS MONOTHEISTES D'UN SEUL DIEU VIVANT ET ETERNEL :) NOUS SOMMES LE SEL DU MONDE QUI DONNE LE GOUT à CE MONDE : DIEU VIVANT NOUS TRANSFORME EN EMRODES ET DES DIAMANTS DE LA NOUVELLE JERUSALEM* CELESTE : LE PROJET DE DIEU VIVANT :TOUT S'EFFACERA SAUF LA PAROLE VIVANTE DE DIEU ETERNEL :) DIEU NOUS DONNE UN COEUR NOUVEAU VERT ET VIVANT :) DIEU ETERNEL ET VIVANT CONSTRUIT SON TABERNACLE* : SA MOSQUEE* BLANCHE ET SON EGLISE* BLANCHE : DIEU VIVANT NOUS DONNE DES TALENTS ET DES DONS QUE NOUS DEVONS FRUCTIFIER :إنما يخشى الله من عباده العلماء: شهد الله أنه المتفرد بالإلهية، وقَرَنَ شهادته بشهادة الملائكة وأهل العلم، على أجلِّ مشهود عليه، وهو توحيده تعالى وقيامه بالعدل، لا إله إلا هو العزيز الذي لا يمتنع عليه شيء أراده، الحكيم في أقواله وأفعاله: عن أبي هريرة رضي الله عنه قال: سمعت رسول الله صلى الله عليه وسلم يقول: «إن الله خلق الرحمة يوم خلقها مائة رحمة، فأمسك عنده تسعا وتسعين رحمة، وأرسل في خلقه كلهم رحمة واحدة، فلو يعلم الكافر بكل الذي عند الله من الرحمة، لم ييئس من الجنة، ولو يعلم المؤمن بكل الذي عند الله من العذاب، لم يأمن من النار.» IL FAUT ETRE BRAVE ET AVOIR UN COEUR BLANC COMME LE LAIT ET LE MIEL : LA MEDAILLE S'OBTIENT DE DIEU VIVANT SEULEMENT: TOUT S'EFFACERA SAUF LA PAROLE VIVANTE DE DIEU :DIEU VIVANT A TOUT CREE PAR SA PAROLE VIVANTE: IL FAUT AVOIR UNE NOUVELLE VIE ET UNE VIE GLORIEUSE PROCHE DE DIEU VIVANT :Il FAUT ETRE AU SERVICE DE DIEU ET AVOIR UNE MISSION HONORABLE DANS NOTRE SEJOUR AVEC DIEU :SORTIR DE LA TRIBULATION DE JERUSALEM VERS LA PAIX DES NATIONS : LA FOI EN DIEU VIVANT DEPLACE LES MONTAGNES :DIEU NOUS DONNE LA SEMENCE :REMPLIR LES VASES PAR LA FOI EN DIEU NOUS A SAUVE : NOUS SOMMES JUSTIFIES ET LIBERES PAR DIEU :ENSEMBLE AVEC LES ANGES, NOUS SOMMES LES RACHETES DE DIEU VIVANT :LE VISAGE DE DIEU BRILLE DE LUMIERE ET LA TERRE DANSE DE JOIE DE LA GLOIRE DE DIEU CETTE NOUVELLE ANNEE 2025:IL NOUS DONNE UNE PAROLE DE CONSOLATION ET NOUS GUIDE PAR LE DISCIPOLAT à ETRE SES DISCIPLES ACCOMPLIS POUR LA PAIX ET LA GUERSION DES NATIONS : MARCHONS DANS LA SIMPLICITE ET FAISONS CONFIANCE EN DIEU VIVANT : LE COMBAT EST UN COMBAT SPIRITUEL ET HEUREUX QUI A CHOISI LA BONNE PART :DIEU VIVANT :THE FEARLESS GIRL WHO LOVES GOD A LOT : الله يدعوا إلى دار السلام: IL FAUT ATTEINDRE L'EXCELLENCE PAR LA MEDITATION DE LA PAROLE VIVANTE DE DIEU VIVANT : SEUL DIEU VIVANT QUI A LA SOLUTION à TOUTE CHOSE: DIEU EST LE MEILLEUR CONSEILLER: LES BONNES PERSONNES NE S'INQUIETENT DE RIEN :كلا ان كتاب الأبرار لفي عليين:IL FAUT RESPECTER LES 10 COMMANDEMENTS DE DIEU VIVANT POUR VIVRE DANS LA LUMIERE : LA CRAINTE DE DIEU EST LE COMMENCEMENT DE SAGESSE : VERS LA PAIX DES NATIONS:الله الحي هو السلام :الله حي لا يموت: IL FAUT SAVOIR HONORER DIEU VIVANT PAR NOS ETUDES ET NOTRE VOYAGE PERMANENT DU SAVOIR : DIEU VIVANT A VAINCU LE MONDE ENTIER ET DIEU A VAINCU le diable ET DIEU EST LE SEUL POUVOIR SUPREME :IL FAUT TOUJOURS AVOIR UN BOUILLONNEMENT D'AMOUR DE DIEU VIVANT : LA PRIERE DU JUSTE EST D'UNE GRANDE EFFICACITE CAR SEUL DIEU QUI JUSTIFIE LES JUSTES :LE SEUL POTIER EST DIEU ETERNEL : VERS LA PAIX ET LA GUERISON DES NATIONS PAR LA LUMIERE DE DIEU: NOUS VIVONS UNE VIE SPIRITUELLE AVEC DIEU ET DIEU A UNE GRACE POUR CHACUN DE NOUS : VERS L'HARMONIE ET LA PAIX DES COEURS : DIEU VIVANT NOUS APPELLE à NE JAMAIS CESSER DE PRIER CAR LA REPENTANCE NOUS EDIFIE ET NOUS DONNE LE VRAI BONHEUR : NOUS SOMMES LE TEMPLE DE DIEU DANS NOTRE COEUR ET SA JERUSALEM* BLANCHE*: NOUS SOMMES HEUREUX DE TROUVER NOTRE FORCE EN DIEU :NOUS CELEBRONS NOEL* AVEC LA JOIE EN DIEU :LE DISCERNEMENT DU BIEN ET DU MAL PAR LES DONS DE DIEU : METTRE UNE VIRGULE ET PLUS D'ENDURANCE: UN NOUVEAU COEUR ET UNE NOUVELLE VIE PAR LA NOUVELLE NAISSANCE :CROIRE EN DIEU VIVANT EST VOIR SA GLOIRE : LE SALUT EST UN DON DE DIEU VIVANT ET DIEU NOUS DONNE DES TALENTS :UN PELERINAGE* DU SAVOIR* AVEC MON NOBLE* MARI* HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM* à L'EGLISE* ET à L'ECOLE* CORANIQUE* : IL FAUT TRAVAILLER SUR NOTRE SALUT* DE DIEU VIVANT ET CULTIVER NOTRE PAIX* DES COEURS* : LA*CLAIREVOYANCE DE HASSAN*2 ET UNE GRANDE RICHESSE DU MAROC*:يجب أن نخاف الله الحي كأننا نراه: LA CRAINTE DES SAVANTS* DE DIEU VIVANT ET DIEU CHASSE LES TENEBRES ET DIEU NOUS DONNE LA LUMIERE ET LES NOBLES CHRETIENS* SONT DES PERLES PRECIEUSES ET LES MEILLEURS PROFESSEURS ET DU LAIT ET DU MIEL ET ILS AIMENT BEAUCOUP DIEU: PAR ELBATJI* YASMINE* AMAL* WIFE OF HAMDAN* ALMAKTOUM*: ESPERANCE* ET ARBRE* DE VIE* ET SES FRUITS* CELESTES* ET LE RESERVOIR* DE SAGESSE* ET DE TOLERANCE* :): الماء والخضرة والوجه الحسن *للمغرب و*للإمارات* and GOD BLESS MY LOVELY GREAT AMERICA* OF HEAVEN :)](https://amalelbatji159.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/MY-CONTRACT-OF-MARRIAGE-WITH-MY-HEART-HUSBAND-HAMDAN-WAS-IN-2019.png)